Windows 11 2024 Update (version 24H2) common problems and fixes
Use this guide to troubleshoot and fix common problems upgrading to the Windows 11 2024 Update.
Windows 11 is getting a new feature update (version 24H2), and as usual, this means potential issues during and after the installation.
Even though Microsoft is gradually rolling out the Windows 11 2024 Update to devices known to have a good upgrade experience, this new version includes a slew of new features and changes that could cause different issues.
For example, you can encounter driver problems, compatibility issues, and even issues with existing features. Furthermore, since version 24H2 requires reinstallation, it's possible to experience other issues related to the upgrade process rather than the new version.
In this how-to guide, I will share some of the most common problems and the different ways to resolve them as you jump from an older version to Windows 11 version 24H2.
Recent updates
This guide has been updated to include new information about additional problems and fixes for Windows 11 version 24H2.
Windows 11 2024 Update common problems and fixes
When it's time to upgrade to a new version, you may encounter problems related to the new feature update. However, it's also possible to come across issues during and after the upgrade that are not related to the latest version of the operating system.
This guide outlines the troubleshooting steps for both types of issues.
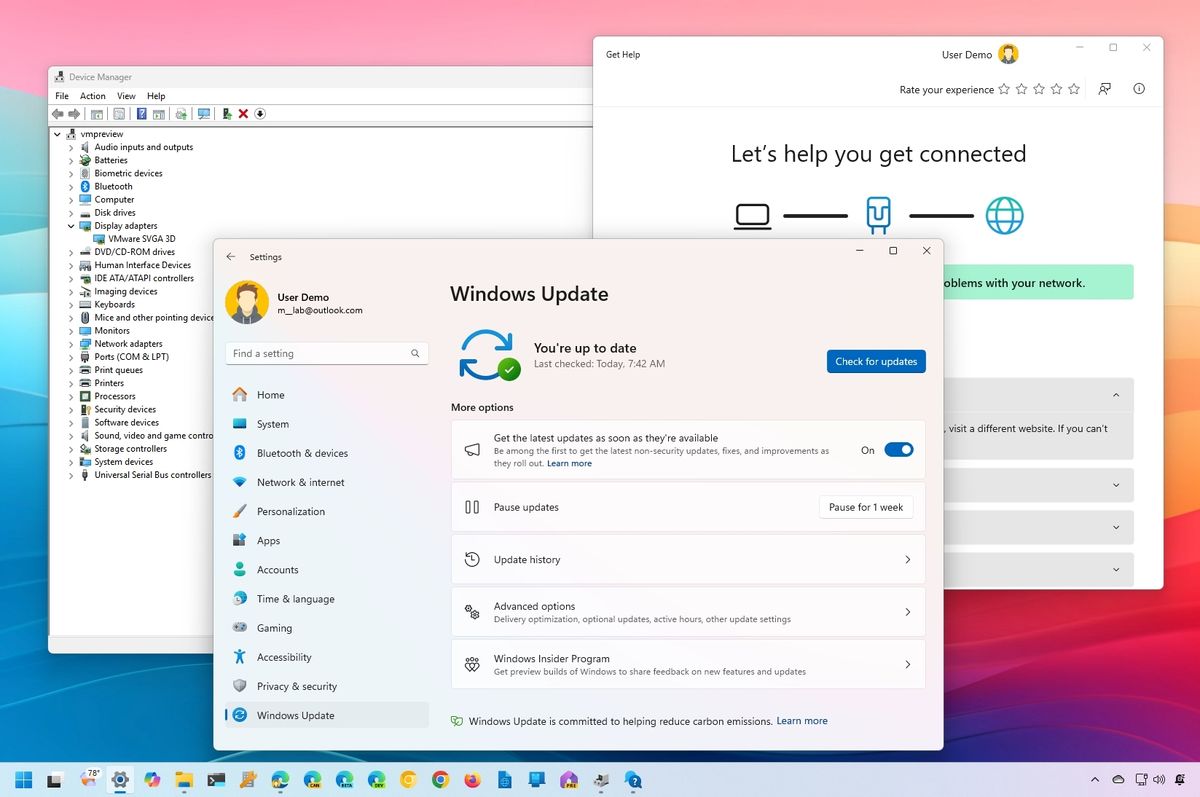
Windows Update troubleshooting
Although Microsoft recommends upgrading to a new version of Windows 11 through the "Windows Update" settings, sometimes this mechanism won't work.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
In these cases, you can use the system troubleshooter feature and the storage settings to remove damaged or missing files.
Update Troubleshooter
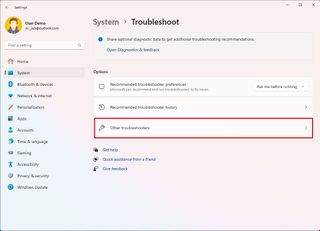
To fix the "Windows Update" mechanism to upgrade to version 24H2, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Troubleshoot page on the right side.
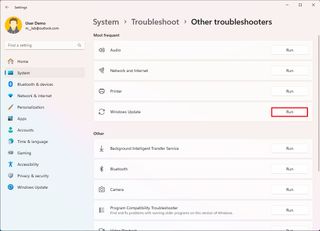
- Click the Other troubleshooters setting.
- Click the Run button for the "Windows Update" troubleshooter.
- Click the "Apply this fix" option (if applicable).
- Quick note: The option will only appear if, after running, the series of fixes and something else you need to repair.
- Continue with the on-screen directions (if applicable).
- Click the Close button.
- Restart the computer.
Once you complete the steps, the feature update should apply successfully the next time you try to upgrade.
The error code 0xc1900223 refers to the problem downloading the update. You can fix this issue by trying to upgrade at a different time.
Error code 0x80073712
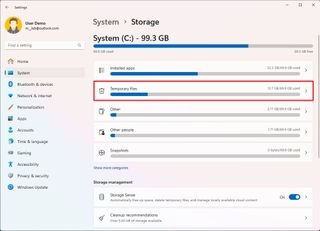
The error 0x80073712 indicates that installation files are missing or damaged. You can resolve this issue by deleting the temporary files and redownloading the feature update with these steps:
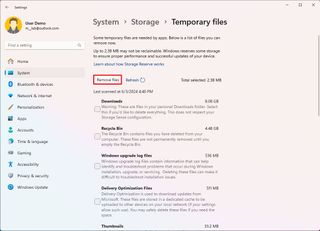
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Storage page on the right side.
- Click the Temporary files setting.
- Clear the current selections.
- Check the "Temporary Windows Installation files" or "Windows Setup temporary files" item.
- Click the Remove files button.
After you complete the steps, the system will download and try to upgrade to version 24H2 one more time.
While it's not recommended to rush the upgrade, you should consider using the Installation Assistant if you have to install the new version.
Error code 0x800F0922
This error indicates that the computer is having difficulties connecting to the Microsoft servers to download the files, or that the system-reserved partition doesn't have enough space.
In this case, you may have to use third-party software to change the reserved partition size. If the problem is the connection, you may want to disconnect from the VPN connection or wait for a later time to upgrade.
Setup troubleshooting
When using any of the available methods to upgrade, including the Installation Assistant and ISO file, if the setup appears stuck and results in the error code 0x8007042B or 0x800700B7 because of another running process, you have multiple ways to resolve this issue.
You must identify and terminate the process through Task Manager, clean boot, or remove a conflicting app.
Terminate process
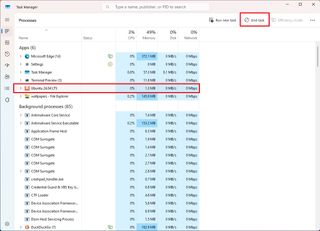
To terminate a process with Task Manager, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
- Select the conflicting app or process.
- Click the End task button.
- Repeat the steps (if applicable).
Once you complete the steps, you can proceed with the upgrade again.
Uninstall apps
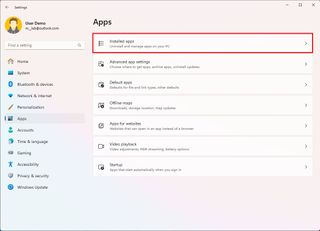
To remove an app, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Click the Installed apps page on the right side.
- Click the menu button for the app and select the Uninstall button.
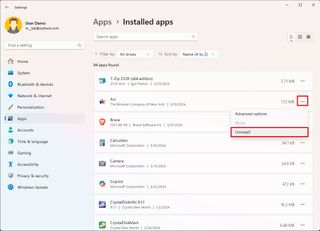
- Click the Uninstall button again.
- Repeat the steps (if applicable).
After you complete the steps, you can continue with the upgrade again.
Installation media troubleshooting
When using the USB bootable media to install Windows 11 version 24H2 and the setup fails, it usually indicates that some installation files are missing or damaged.
In this case, you must recreate the USB installation media or use another method, such as the Installation Assistant.
Media Creation Tool
To create a USB flash drive to install version 24H2, use these steps:
- Open Microsoft download page.
- Click the Download Now button under the "Create Windows 11 installation media" section.
- Double-click the executable file to launch the tool.
- Click the Accept button.
- Click the Next button.
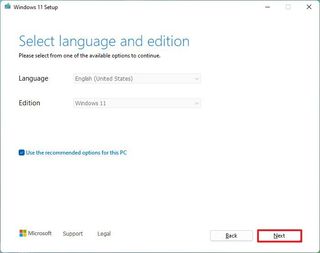
- Select the USB flash drive option.
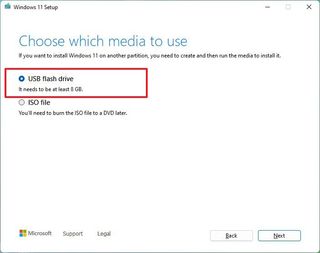
- Click the Next button.
- Select the USB flash drive from the list.
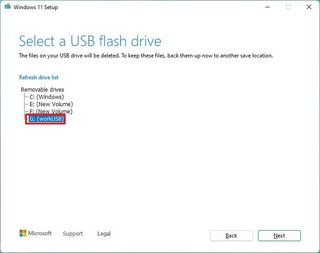
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Finish button.
Once you complete the steps, you can try the upgrade one more time.
Installation Assistant
Alternatively, if the problem persists, you can use another upgrade method, such as the Installation Assistant.
- Open Microsoft download page.
- Click the Download Now button under the "Windows 11 Installation Assistant" section.
- Double-click the executable file to launch the tool.
- Click the "Accept and install" button.
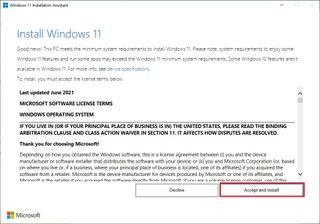
After completing the steps, the tool will download and install the feature update.
Hard drive space troubleshooting
If you plan to upgrade to a newer version of Windows 11, you may also receive the error code 0x80070070 – 0x50011, 0x80070070 – 0x50012, or 0x80070070 – 0x60000. These codes mean that the device does not have enough storage to continue with the installation. Using the storage settings to free up space can fix the problem.
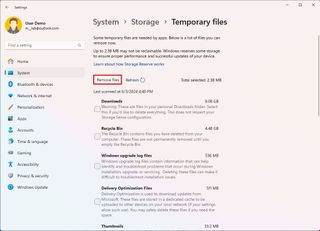
To free up space on your computer, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Storage page on the right side.
- Click the Temporary files setting.
- Check the items to clear from the hard drive.
- Quick note: When selecting the items, do not choose the "Windows Setup temporary files" or "Windows ESD installation files" options since these are the upgrade files.
- Click the Remove files button.
Once you complete the steps, continue with the upgrade process. You can also try these other methods to free up even more space on Windows 11.
In addition, you may get the error code 0x80070002 0x20009 during the installation wizard, which indicates that the setup can't find one or more of the setup files.
In this case, disconnect the external drives, except the USB installation media, and restart the process.
Drivers troubleshooting
If you encounter driver problems, you may receive the error code 0x800F0923 or experience a black screen.
Error code 0x800F0923
The error code 0x800F0923 can be a problem with an application, but it's usually something wrong with the graphics driver.
If you're getting this error and this is a known issue, the setup will give you more specific details.
When dealing with driver issues, the first thing you want to do is update the driver in question. You can try the latest update available from your manufacturer or the latest beta release, which may include a fix for the problem.
If you are unable to resolve the driver issue, you can uninstall the device before proceeding with the installation.
Also, the error code 0xC1900208 – 0x4000C also indicates a conflict with an application.
Uninstall driver
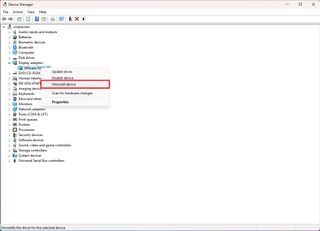
To uninstall a driver from your computer, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Device Manager, and click the top result to open the app.
- Expand the branch category containing the device that is having issues.
- Right-click the component and select the Uninstall device option.
- Click the Uninstall button again.
After completing the steps, the feature update should install without issues.
Uninstall app
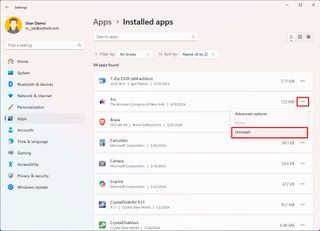
To remove a problematic app, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Click the Installed apps page on the right side.
- Click the menu button for the app and select the Uninstall button.
- Click the Uninstall button again.
Once you complete the steps, you can continue with the feature update setup.
Fix black screen
On Windows 11, a black screen can appear during and after an installation, and it can be due to a graphics driver or an error during the process.
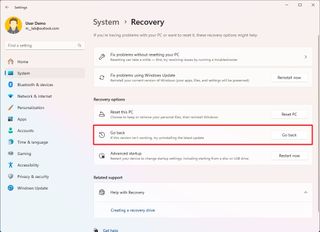
You could spend the time to troubleshoot and resolve the issue, but the quickest way to deal with this problem is to roll back to the previous version of the operating system with these instructions:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Recovery page on the right side.
- Click the Go back button in the "Previous version of Windows" settings under the "Recovery options" section.
- Click the Next button.
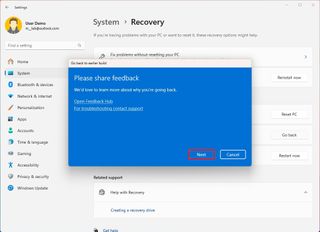
- Click the Next button again.
- Click the No, thanks button.
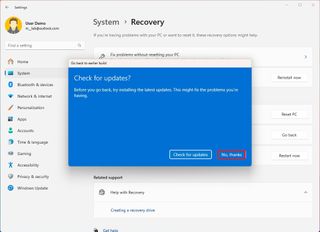
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Next button again.
- Click the "Go back to earlier build" button.
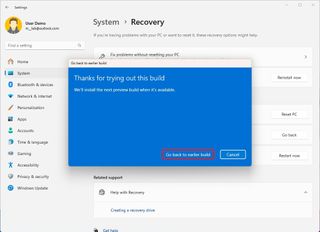
- Quick note: The description of the button may be worded slightly differently.
After completing the steps, it would be a good idea to wait until a patch fixes the problem from Microsoft or the hardware manufacturer before upgrading again.
Error code 0XC1900101 troubleshooting
The error 0XC1900101 has at least seven different variants (including 0xC1900101 - 0x2000c, 0x20017, 0x30017, 0x30018, 0x3000D, 0x4000D, and 0x40017), and they indicate different problems during the upgrade alongside the error 0x80090011.
You can troubleshoot this error by disconnecting peripherals, freeing space, uninstalling apps and drivers, and repairing logical and physical errors.
Disconnect devices
If the problem is one of the peripherals (such as external drives, printers, Bluetooth devices, USB devices, and cameras), you can disconnect them from your computer to resolve the issue. After the upgrade process, you can reconnect the devices again.
Cleanup storage space
Updating Windows 11 to a new version usually requires around 20GB of storage. If the computer runs out of space during the upgrade, the system will pop one of the above errors.
In this case, you can use this guide to find the best tips to free up storage space on your computer.
Uninstall apps
When the problem is a third-party security program, you will most likely encounter one of the 0xC1900101 0x20017 or 0xC1900101 0x30017 error codes.
Usually, the easiest workaround is to uninstall the antivirus or any other security application until after the upgrade.
To temporarily remove security software, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Click the Installed apps page on the right side.
- Click the menu button for the app and select the Uninstall button.

- Click the Uninstall button again.
- Continue with the on-screen directions (if applicable).
Once you complete the steps, you should be able to upgrade to version 24H2.
Update drivers
If the issue is a driver, you will likely see an error code that starts with 0xC1900101 or 0x80090011. You can always update the driver in question to resolve the issue.
It's always best to use the manufacturer's instructions when updating a device driver. If you can't find them, you can refer to these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Click the Advanced options page on the right side.
- Click the Optional updates setting under the "Additional options" section.
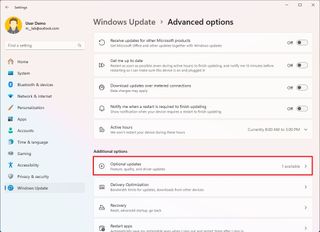
- Select the available driver update.
- Click the "Download and install" button.
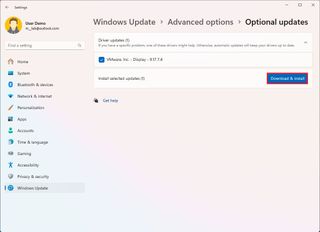
After completing the steps, you should be able to upgrade without issues.
Repair installation
An error code 0xC1900101 can also indicate a problem with the current installation. In this situation, you can use the Deployment Servicing and Management (DISM) and the System File Checker (SFC) tools to repair the installation.
To fix problems with DISM and SFC, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command and press Enter: dism /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth
- Type the following command to repair the installation and press Enter: SFC /scannow
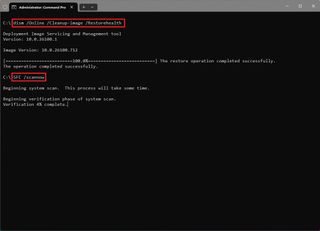
Once you complete the steps, the DISM command will repair the files of the local Windows image, and the SFC command will use the local image files to repair the current installation. (You can find additional instructions in my previous guide.)
Repair physical drive
You can also use the CHKDSK command to fix logical and specific physical errors on the installation drive with these instructions:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command and press Enter: chkdsk/f c:
- Type Y and press Enter to schedule a scan.
- Restart the computer.
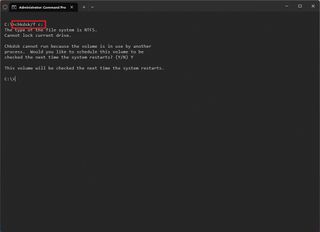
Once you complete the steps, the computer will restart in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) and run the Check Disk command to fix issues.
Clean installation
When you can't find a fix for the problem, performing a clean installation with an ISO file or USB flash drive to upgrade to the Windows 11 2024 Update is best.
Install failure troubleshooting
When installing a new version of the operating system, the setup can fail for many reasons. Sometimes, you may receive a message describing the issue, and other times, the installation will fail without any error.
If either of these things happens, depending on whether you receive an error, you can use the update history settings or the SetupDiag tool to find clues that can help you resolve the issue.
Error messages troubleshooting
You may also receive at least two different error messages during the upgrade process, including:
- Error: We couldn't complete the updates. Undoing changes. Don't turn off your computer.
- Error: Failure configuring Windows Updates. Reverting changes.
Although these errors try to give you a description of the problem, they are very generic responses. In this case, you will have to check the Windows Update history settings to find out the exact error and research online for a possible resolution.
To find the error code blocking the installation of the Windows 11 2024 Update, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Click the Update history setting under the "More options" section.
- Confirm the error code under the update that failed to install.
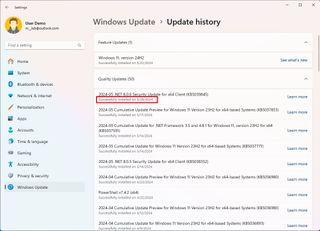
- Copy the code and research online for a possible solution.
After you complete the steps, use your research to resolve the problem.
SetupDiag troubleshooting
If the installation process rolls back to the previous version without any error message, you can use the SetupDiag tool to diagnose and determine the exact reason why the new version failed to install.
To run the SetupDiag tool on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
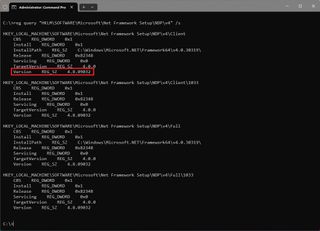
- Type the following command to reveal the version of .NET installed and press Enter: reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Net Framework Setup\NDP\v4" /s
- Confirm that the "Version" field reads something higher than 4.6.xxxxx, you can run the tool.
- Open SetupDiag download page.
- Click the Download SetupDiag button.
- Select an empty folder to download the files.
- Click the Save button.
- Open File Explorer.
- Browse to the downloaded file location.
- Right-click the "SetupDiag.exe" and select the Run as administrator option.
- Open File Explorer.
- Browse to the downloaded file location.
- Right-click the SetupDiagResults.log file and select the Open option.
Once you complete the steps, the log file will open with the results that the tool was able to identify based on the known rules.
You can find even more details about the SetupDiag in my previous instructions.
Network troubleshooting
If the computer loses local or internet access, this can happen for a number of reasons, such as problems with drivers, configuration, wireless signal, network cable, router, switch, access point, or internet providers, or it could also be an issue with the new version.
If the problem is a configuration or something wrong with the networking components, you can use the network troubleshooter or reset option on Windows to resolve this problem.
Network adapter troubleshoot
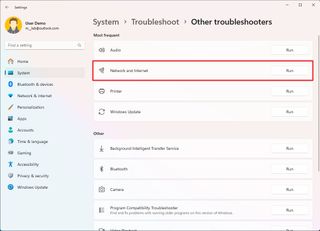
To fix network adapter problems after upgrading to the new version of Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Troubleshoot page on the right side.
- Click the Other troubleshooters setting.
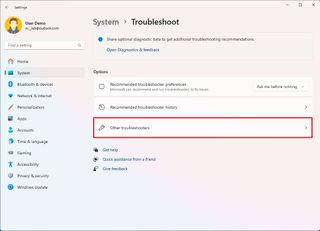
- Click the Run button for the "Network and internet" under the "Most frequent" section.
- Continue with the on-screen directions with the Get Help app.
After you complete the steps, the device should connect to the network again.
Network adapter reset
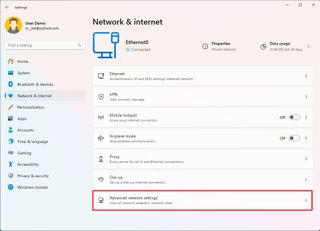
To reset network adapters to their default settings, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Network & internet.
- Click the Advanced network settings page on the right side.
- Click the Network reset setting under the "More settings" section.
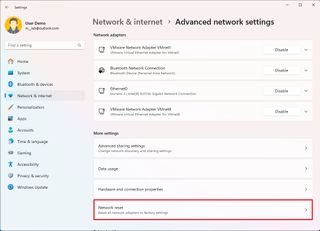
- Click the Reset now button.
- Click the Yes button.
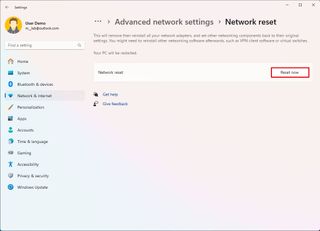
Once you complete the steps, the system will reinstall the network adapters to reset the settings. If you have a wireless connection, you may need to re-enter the password to connect to the network again.
Unsupported hardware troubleshooting
If you plan to upgrade a device running Windows 10, you may receive the "Error this PC doesn't currently meet Windows 11 system requirements" message, which indicates a compatibility problem.
Typically, this means that the setup has failed to detect the TPM and Secure Boot components or the processor is incompatible. Sometimes, you may even receive the error codes 0xC1900200 – 0x20008 and 0xC1900202 – 0x20008, indicating that the device doesn't meet the minimum requirements.
These are the minimum requirements to install any version of Windows 11:
- Processor: 1GHz or faster CPU or System on a Chip (SoC) with two or more cores.
- Memory: 4GB.
- Storage: 64GB or larger.
- System firmware: UEFI with Secure Boot enabled.
- Graphics: Compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.0 driver.
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0.
- Display resolution: High definition (720p) display greater than 9 inches diagonally, 8 bits per color channel.
If you want to access the new AI features available on version 24H2, you will typically have a computer featuring at least a Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite processor, 16GB of RAM, and at least 256GB of SSD storage.
Enable TPM and Secure Boot
If the computer supports TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot, you can enable these features in the UEFI firmware of the motherboard with these instructions.
- Open Settings.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Click on Recovery.
- Click the Restart now button under the "Advanced startup" section.
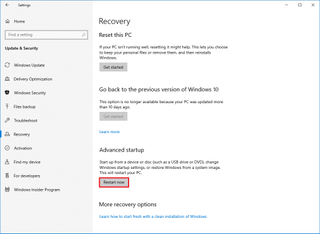
- Click on Troubleshoot.
- Click on Advanced options.
- Click the "UEFI Firmware Settings" option.
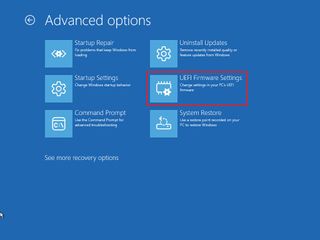
- Click the Restart button.
- Open the security or boot settings and enable TPM and Secure Boot (as necessary).
If the motherboard doesn't include the TPM chip, it may be available on the processor. On AMD processors, the feature may appear as "fTPM" or "AMD fTPM switch," and on Intel processors as "PPT."
Blue Screen of Death troubleshooting
Although the initial rollout of Windows 11 version 24H2 is off to a good start, a small number of devices may encounter a Blue Screen of Death if they are using Intel Smart Sound Technology (Intel SST) on Intel 11th Gen Core processors and or the Easy Anti-Cheat software.
According to the company, after installing version 24H2, devices with Intel SST drivers will receive a bugcheck error if the IntcAudioBus.sys file is version 10.29.0.5152 or 10.30.0.5152.
Microsoft is currently blocking the feature for devices known to encounter this issue, and it's not recommending users upgrade until the problem has been fixed.
One way to prevent this issue is to update the Intel SST Audio Controller drivers before upgrading to the Windows 11 2024 Update. You have to make sure that the driver version is 10.29.00.5714 or 10.30.00.5714 or higher.
To update the affected drivers through Windows Update, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Click the "Check for updates" button.
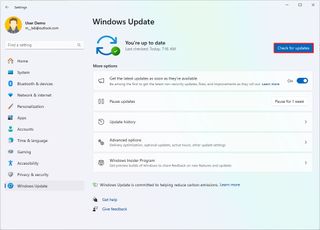
- (Optional) Click on Advanced options.
- Click the "Optional updates" setting under the "Additional options" section.
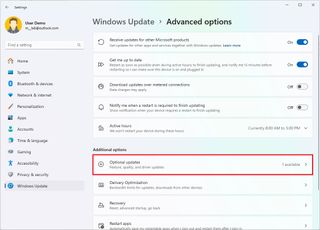
- Select the driver (if applicable).
- Click the "Download & install" button.
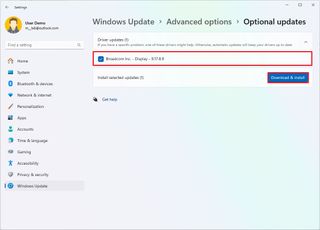
If you're not able to update the drivers, it's recommended to check with your manufacturer support website to download and install the latest update.
Alternatively, you can roll back to the previous version of Windows 11 with these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Recovery page on the right side.
- Click the Go back button in the "Previous version of Windows" settings under the "Recovery options" section.

- Click the Next button.

- Click the Next button again.
- Click the No, thanks button.

- Click the Next button.
- Click the Next button again.
- Click the "Go back to earlier build" button.

After completing the steps, you shouldn't upgrade again, instead wait until a patch fixes the problem from Microsoft or the hardware manufacturer before upgrading again.
The feature update also has issues with the Easy Anti-Cheat app that installs automatically with some games to prevent cheating during online gameplay. According to the company, devices may stop responding with a blue screen that includes the "MEMORY_MANAGEMENT" message.
It's also important to note that this is only happening for devices with Alder Lake+ processors and vPro processors.
Microsoft is currently blocking the feature for devices known to encounter this issue, and it's not recommending users upgrade until the problem has been fixed.
As part of the resolution, the company recommends updating the game if it includes a newer version of the Easy Anti-Cheat app. You can also choose to remove the game until the problem has been resolved, and as a last resort, you can roll back to the previous version of the operating system.
You can use the steps mentioned above to uninstall the feature update from your computer.
Fingerprint sensor troubleshooting
If you upgrade to version 24H2, you may also experience problems with the fingerprint sensor, causing your computer to become unresponsive after locking the current session.
Microsoft is currently blocking the feature update for devices known to encounter this issue, and it's only recommending users upgrade once the problem is resolved. However, you may be able to fix this issue by updating the firmware of the fingerprint device so you can upgrade without issues.
You can check with your device manufacturer's support website to download and install the updated fingerprint firmware. If you have a fingerprint adapter that connects through a USB port, uninstalling the driver and disconnecting the adapter may resolve the conflict until the problem has a permanent solution. As a last resort, you can roll back to the previous version of the operating system.
To uninstall a fingerprint driver, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Device Manager, and click the top result to open the app.
- Expand the branch category containing the device that is having issues.
- Right-click the fingerprint device and select the Uninstall device option.
- Click the Uninstall button again.

After completing the steps, the driver will be removed and you can disconnect the fingerprint device.
Alternatively, you can uninstall the feature update from your computer with these instructions:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Recovery page on the right side.
- Click the Go back button in the "Previous version of Windows" settings under the "Recovery options" section.

- Click the Next button.

- Click the Next button again.
- Click the No, thanks button.

- Click the Next button.
- Click the Next button again.
- Click the "Go back to earlier build" button.

After completing the steps, the computer will revert to previous version, fixing the problem with fingerprint reader.
Apps incompatible troubleshooting
Although applications should work without issues, Microsoft is aware that some apps are having problems with the Windows 11 2024 Update, such as the Safe Exam Browser, Asphalt 8, and some apps designed to change the desktop wallpaper.
You should roll back to the previous version if you must use these applications. However, the best action in this case is to remove the application until there's an update for the system or app that resolves the issues.
To remove an app, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Click the Installed apps page on the right side.

- Click the menu button for the app and select the Uninstall button.

- Click the Uninstall button again.
Once you complete the steps, the incompatible app will be removed from the system.
Storage drive undeletable 8.63GB troubleshooting
After upgrading to the latest operating system version, many users started reporting that the "Temporary Files" settings and the "Disk Cleanup" tool would leave behind 8.63GB of data on the computer.
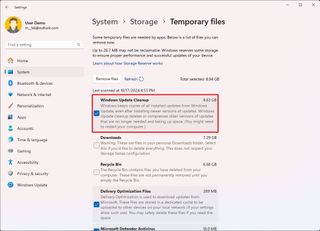
According to the company, this is, in fact, a problem with the feature update, but it's a reporting problem, and it's not the case that the system cannot delete those 8.63GB.
This is an issue you can safely ignore. The company is currently working on a resolution.
Western Digital NVMe Blue Screen of Death troubleshooting
Shortly after the release of the Windows 11 2024 Update, some users began reporting Blue Screen of Death errors on devices equipped with NVMe drives from Western Digital.
If you're experiencing this issue, Western Digital has identified and resolved the problem in the latest firmware update.
According to the company, the root of the problem was an issue with the HMB (Host Memory Buffer) of several drive 2TB NVMe models, including WD_BLACK SN770, WD_BLACK SN770M, WD Blue SN580, WD Blue SN5000, and SanDisk Extreme M.2.
Warning: Updating the firmware of a storage drive can cause data loss in some cases. As such, it's important to create a backup before proceeding.
To update the firmware of your Western Digital drive, use these steps:
- Open the SandDisk download page.
- Click the Download button for the Western Digital Dashboard (Offline Installer) app.
- Right-click the DashboardSetup.exe file and choose the Run as administrator option.
- Click the Install button.
- Click the Finish button.
- Open the Western Digital app.
- Click on Update available or Tools.
- Click the Update firmware button.
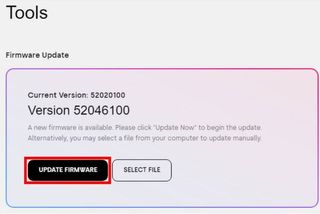
- Click the Proceed button.
- Click the Shutdown now button.
Once you complete the steps, restart the computer to start the drive with the new firmware on the drive.
Clipboard history troubleshooting
In the latest version of Windows 11, a small group of users have also noticed that the Clipboard history appears empty after copying content to the clipboard. According to a report from Windows Latest, users have been reporting this issue even before version 24H2 was officially available.
Although Microsoft hasn't confirmed this as an official, the workaround to fix it is straightforward:
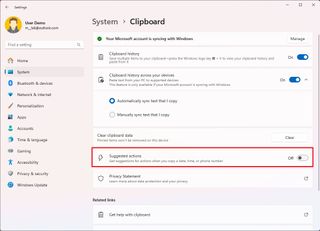
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Clipboard page on the right side.
- Turn off the Suggested Actions toggle switch.
- Open the Clipboard history using the "Windows + V" keyboard shortcut.
- Turn on the Suggested Actions toggle switch (as needed).
After you complete the steps, the history should appear normally.
Mouse pointer disappearing troubleshooting
If you upgrade to version 24H2, you may also notice that the mouse pointer and cursor may disappear on the screen (especially while trying to interact with the text field) on applications based on the Chromium engine, such as Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and others.
To get around the mouse issue, use these steps:
- Open Start.
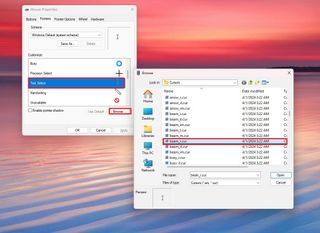
- Search for main.cpl and click the top result to open the Mouse Properties in Control Panel.
- Click the Pointers tab.
- Select the "Text Select" item under the "Customize" section.
- Click the Browse button.
- Choose the "beam_r" cursor file.
- Click the Open button.
- Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the system will use the default pointer, which addresses the symptom until an update becomes available to fix the problem permanently.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
