What is DISMTools, and how do you get started? Windows 11 (and 10) image GUI manager explained.
The DISMTools app lets you interact with DISM through a GUI instead of using commands, and here's how to get started.
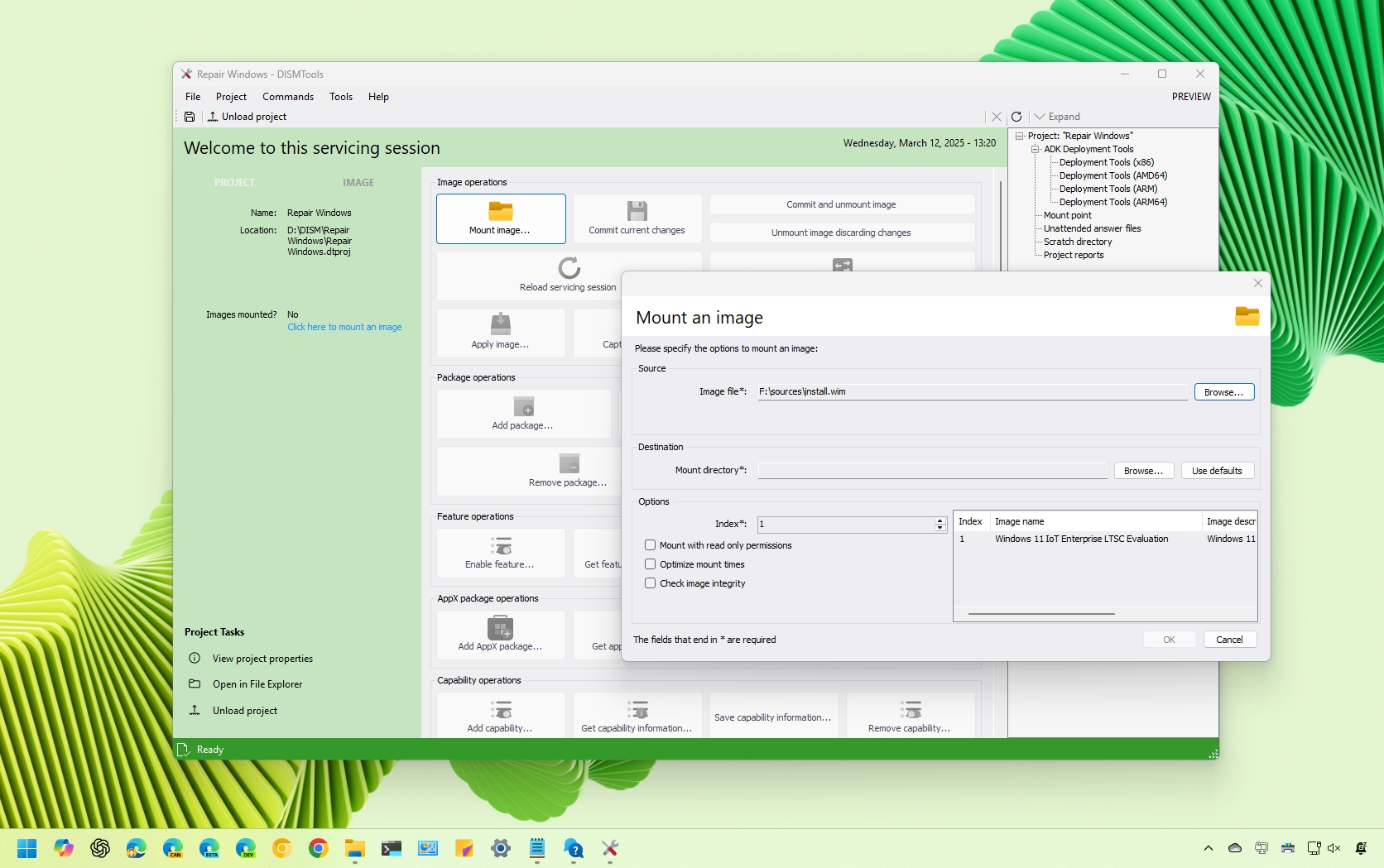
On Windows 11 (and 10), DISMTools is a free, non-Microsoft open-source graphical user interface (GUI) designed to enhance and simplify the use of Microsoft's Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM).
The DISM tool is primarily available as a command-line utility for servicing and preparing Windows images, but its complexity can be a barrier for many users. DISMTools tries to overcome this complexity friction by providing an accessible front-end that streamlines the management of Windows Imaging (WIM) files and related tasks.
In addition, the developer aims to provide an alternative to other solutions that may lack functionality or reserve certain features for paid customers.
DISMTools key features
DISMTools introduces a project-based approach, allowing you to manage mounted images, create unattended answer files, convert images, and more, which improves organization and workflow when working with the DISM command-line tool.
You can also work with the image locally available on your computer (online) or another location (offline), giving you an easy way to manage any installation of the operating system.
This tool also uses the DISM API and DISM executable to improve performance while scanning an image, and this approach allows you to use any version of a Windows image from 7 through 10 and 11.
In addition, the tool shines in the more intuitive interface and rich information when serving an image compared to using the command-line option.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
You can easily get image information and add and remove app packages, features, drivers, and more.
It's even possible to generate and print image information for future reference.
Furthermore, you can perform operations like image conversion from ".esd" to ".wim," you can create a custom Windows 11 ISO file, and it even offers a wizard to create unattended answer files, which you can use to install the operating system hands-free.
How to install DISMTools
To install DISMTools on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and choose the Run as administrator option.
- (Option 1) Type the following command to install the tool (preview) and press Enter: winget install CodingWondersSoftware.DISMTools.Preview
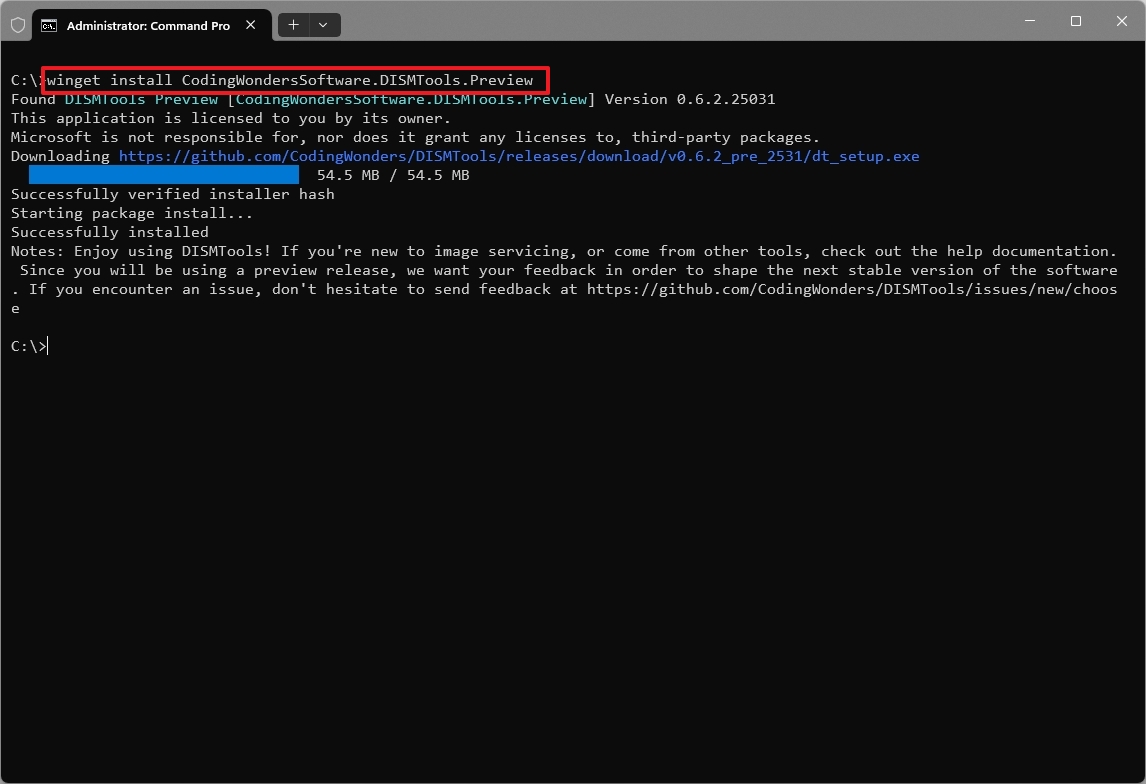
- (Option 2) Type the following command to install the tool (stable) and press Enter: winget install CodingWondersSoftware.DISMTools.Stable
Once you complete the steps, the tool will be available like any other app from the Start menu.
How to get started with DISMTools
The DISMTools allows you to perform many different operations, but these are the basics:
- Open Start.
- Search for DISMTools and click the top result to open the utility.
- Click the Next button.
- Choose the tool preferences, such as color, language, font, etc.
- (Optional) Select the location to save the logs and choose the level of errors and warning messages.
- Click the Next button.
- Continue with the on-screen directions.
After you complete the steps, you will find different options for starting to work with DISMTools. For example, you can create a new or resume working on an existing project.
Working with projects
You can also go directly to manage an online or offline image. The "Manage online installation" opens the Windows image locally available on the current installation.
If you choose the "Manage offline installation" option, you will have the option to select one of the available images.
To start with a new project, click the "New project" option, choose the name and a location to store the project, and click the "OK" button.
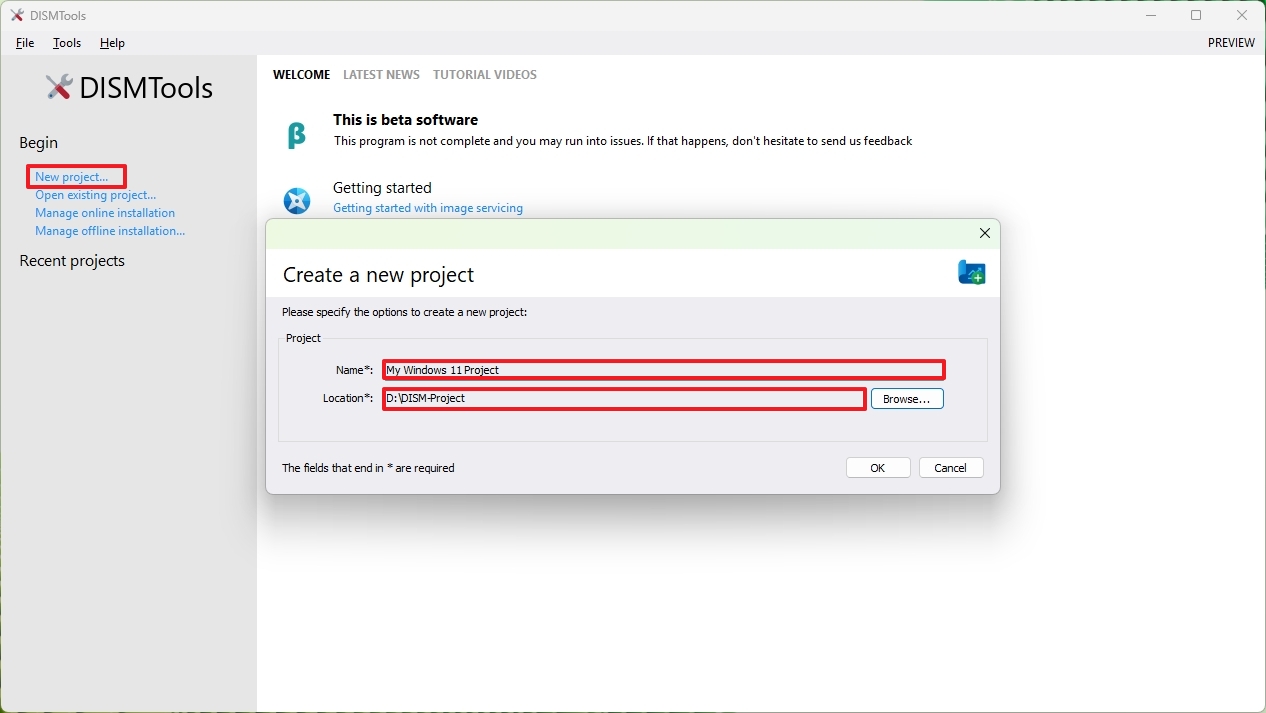
Inside the project, click the "Mount image" button. On the page, choose the install.wim (or install.esd) image using the "Source" setting. You also have to specify the destination mount directory in the "Destination" setting.
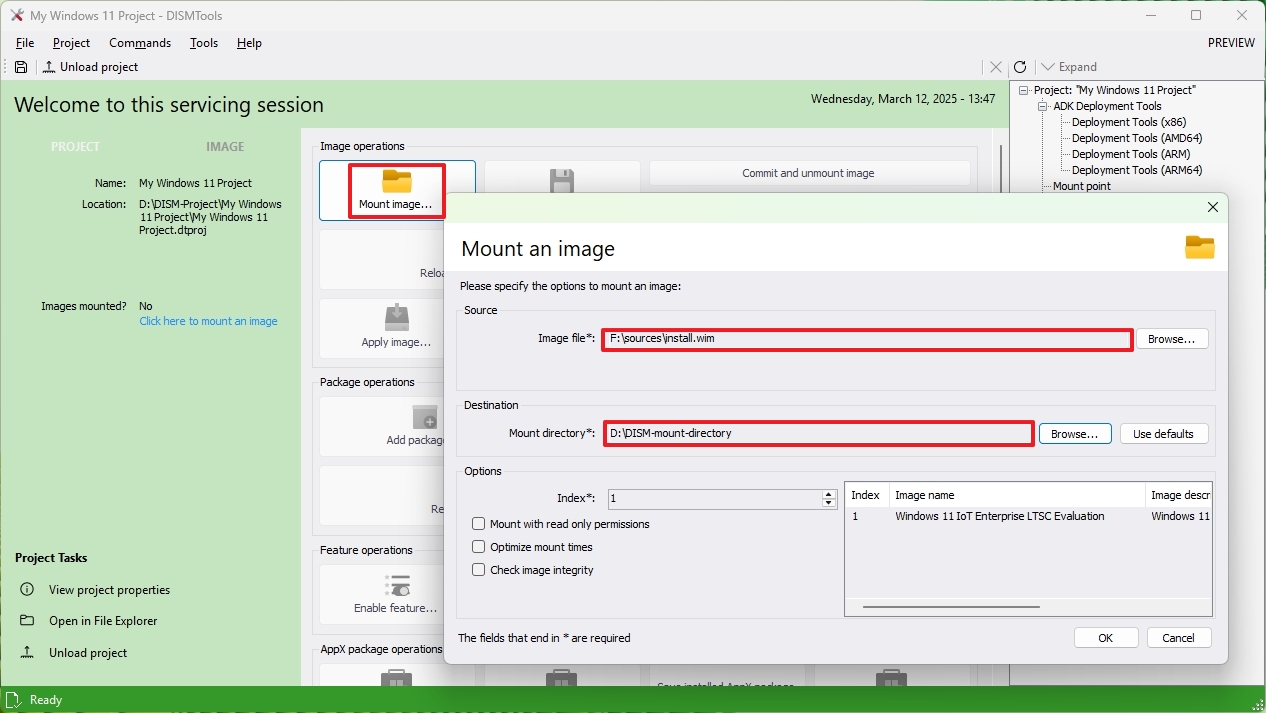
In addition, in the "Options" section, you need to select the edition of the operating system that you want to customize by specifying the index number (if applicable).
If you're mounting an ISO file, you may want to check the "Mount with read only permissions" option. Otherwise, you may not be able to mount the image.
Finally, click the "OK" button to mount the image.
On the main project page, you have different tools to perform a number of operations, including adding and removing packages, features, apps, drivers, and more.
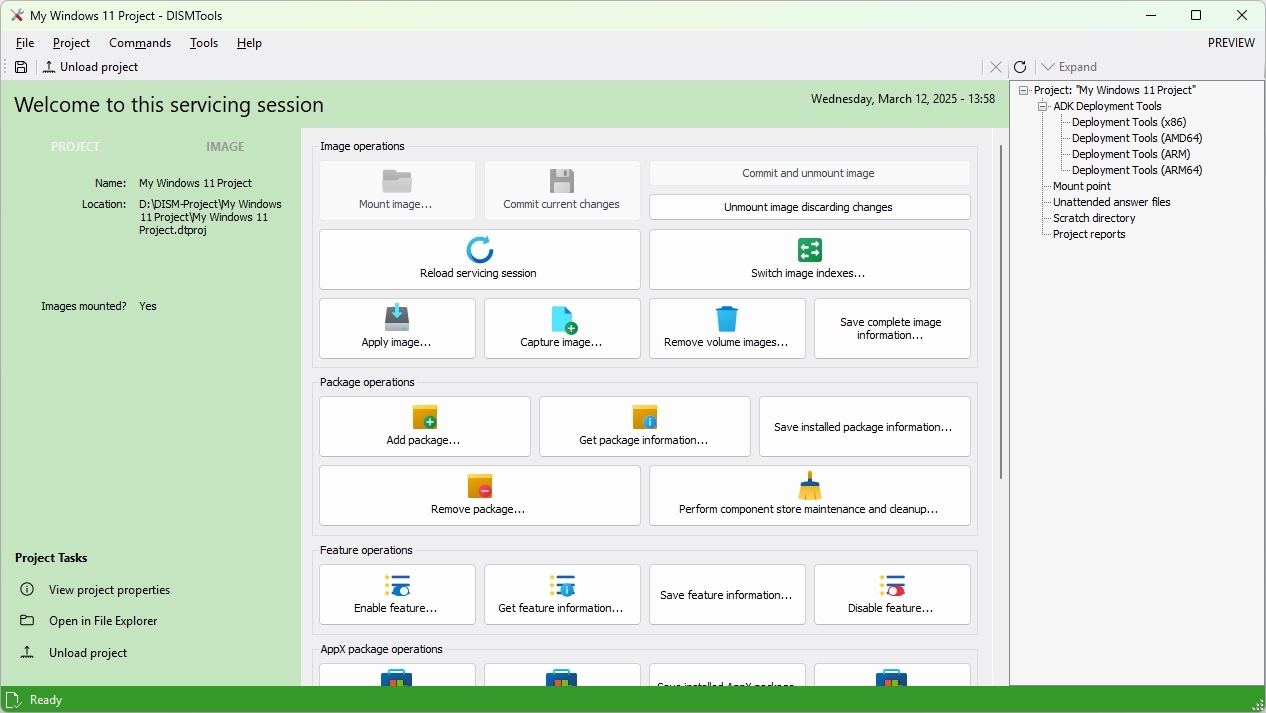
It's important to note that making changes to the locally available image doesn't make changes to the current installation. You're only modifying the operating system image. Any modifications will be applied when the image is deployed to the system. Therefore, changes made to the offline image do not affect your current installation.
Available tools
In addition to working on projects, the DISMTools includes a number of tools to perform different actions, such as converting an image using the ESD format to WIM.
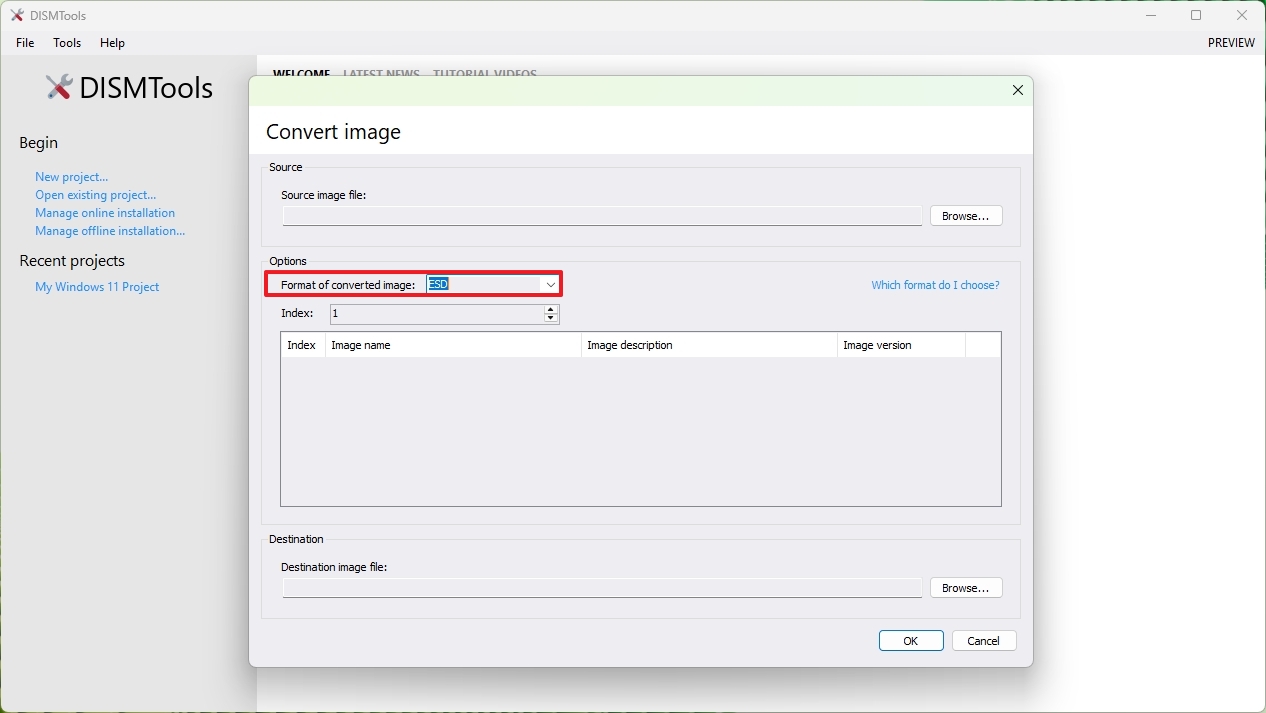
The install.ESD (Electronic Software Download) is a highly compressed and encrypted version of the install.WIM (Windows Imaging Format) file. As a result, directly opening and manipulating an install.ESD file is not possible. However, the DISMTools provides a functionality to convert the install.ESD format to install.WIM enables users to modify the Windows image.
One of the tools (I personally find interesting) is the option to create an unattended file. The "unattended file" (typically named autounattend.xml) allows for automating the Windows 11 setup process. This eliminates the need for user interaction during installation, making it ideal for large-scale deployments or users who want a streamlined installation experience.
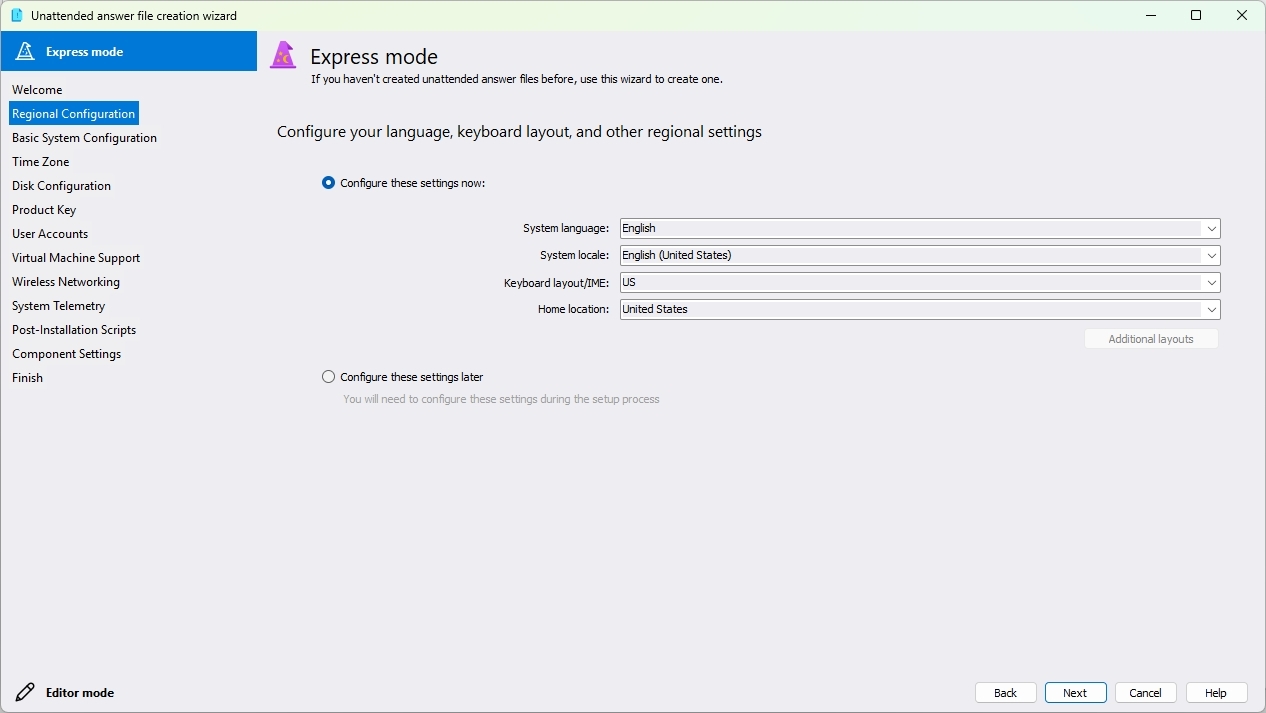
The only caveat is that the creation of the file can be a tedious process. However, the DISMTools includes an easy-to-follow wizard to create the autounattend.xml file.
Other things
DISMTools, though still under development, offers a comprehensive graphical interface for interacting with the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) command-line tool. It enables you to manage both online and offline Windows images, making it easier to complete tasks such as adding or removing features, packages, and drivers. However, as of its current version, DISMTools does not seem to support the 'RestoreHealth' functionality, which is used to repair the operating system image (a capability available through specific DISM command-line operations).
This tool is designed primarily for network administrators and developers who require efficient management of images. Regardless, its user-friendly interface makes it accessible to a broader audience, allowing anyone interested to utilize its features.
More resources
Find in-depth guides, troubleshooting tips, and the latest updates on Windows 11 and 10 here:
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.

