How to configure a static IP on Windows 10 or 11
Do you need to switch from a dynamic to a static IP address configuration on Windows 11 or 10? Here's how.
On Windows, the router's Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is (usually) responsible for assigning a dynamic Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) configuration to every device in the network, including to your computer running Windows 11 or Windows 10.
Although a dynamic IP address is the recommended configuration for most situations, you may need to change to a static IP address if you're thinking about setting up a printer or file sharing, or you have to configure port forwarding on the router to your computer.
The reason is that a dynamic network configuration can change at any time after the lease from the DHCP expires and if the address changes, network resources you may have configured will stop working. Setting a static IP address will always stay the same on the computer, allowing a more reliable experience sharing resources in the network or forwarding ports.
Whatever the reason, on Windows 10 and 11, you have many ways to configure a static TCP/IP address, including using the Settings app and Command Prompt.
This guide will walk you through the different ways to configure a static network configuration on Windows 11 and 10.
How to set a static TCP/IP network configuration on Windows 11
On Windows 11, you can change your computer's dynamic IP configuration to static in at least two ways through the Settings app or commands.
Configure IP from Settings app
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
To assign a permanent TCP/IP configuration on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
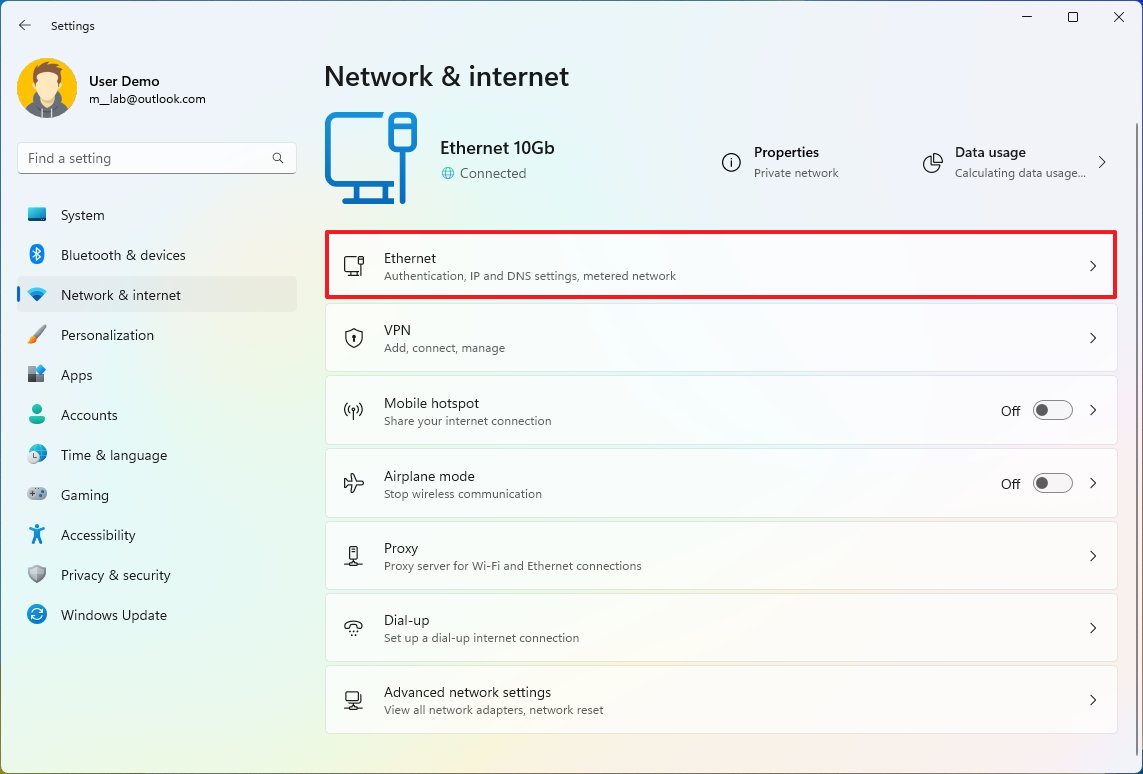
- Click on Network & internet.
- (Optional) Click on Advanced network settings.
- Under the "More settings" section, click on Hardware and connection properties.
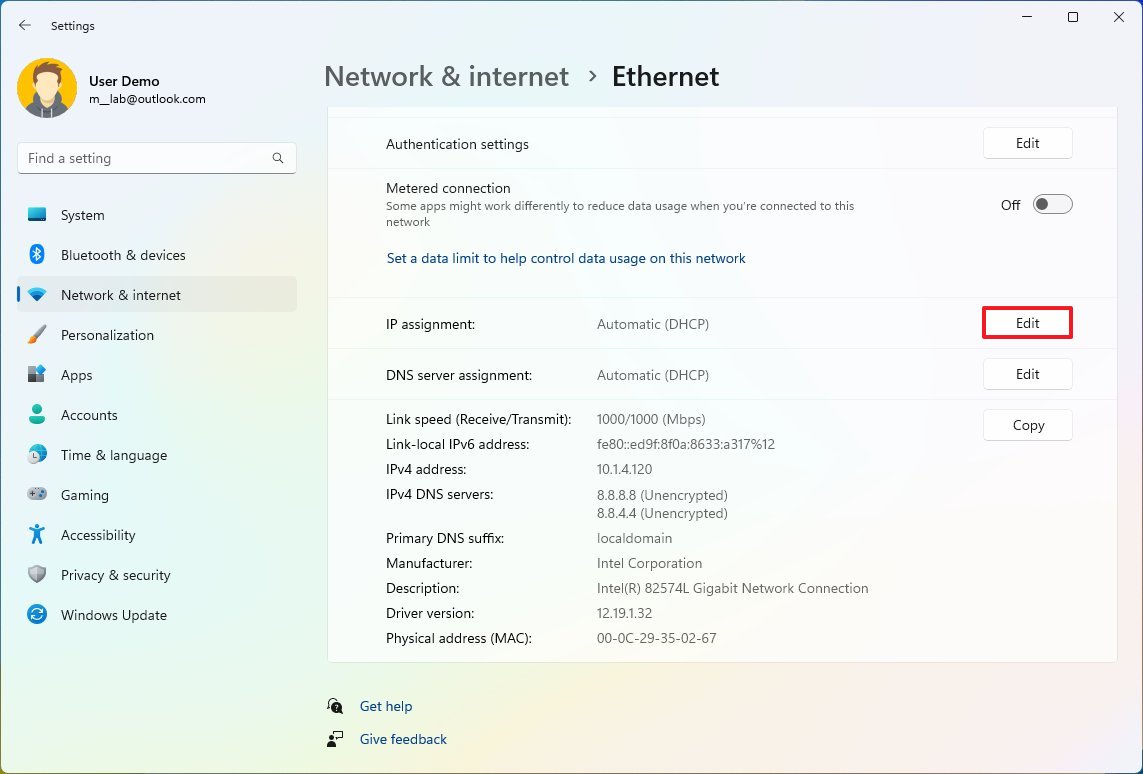
- Note the current IPv4, Subnet mask, Default Gateway, and DNS server addresses to determine the new configuration, as it has to be in the same network scope.
- Click the Ethernet or Wi-Fi page on the right side from the "Network & internet." page.
- Quick note: If you select the Wi-Fi page, you need to click on the connection properties to access the network settings.
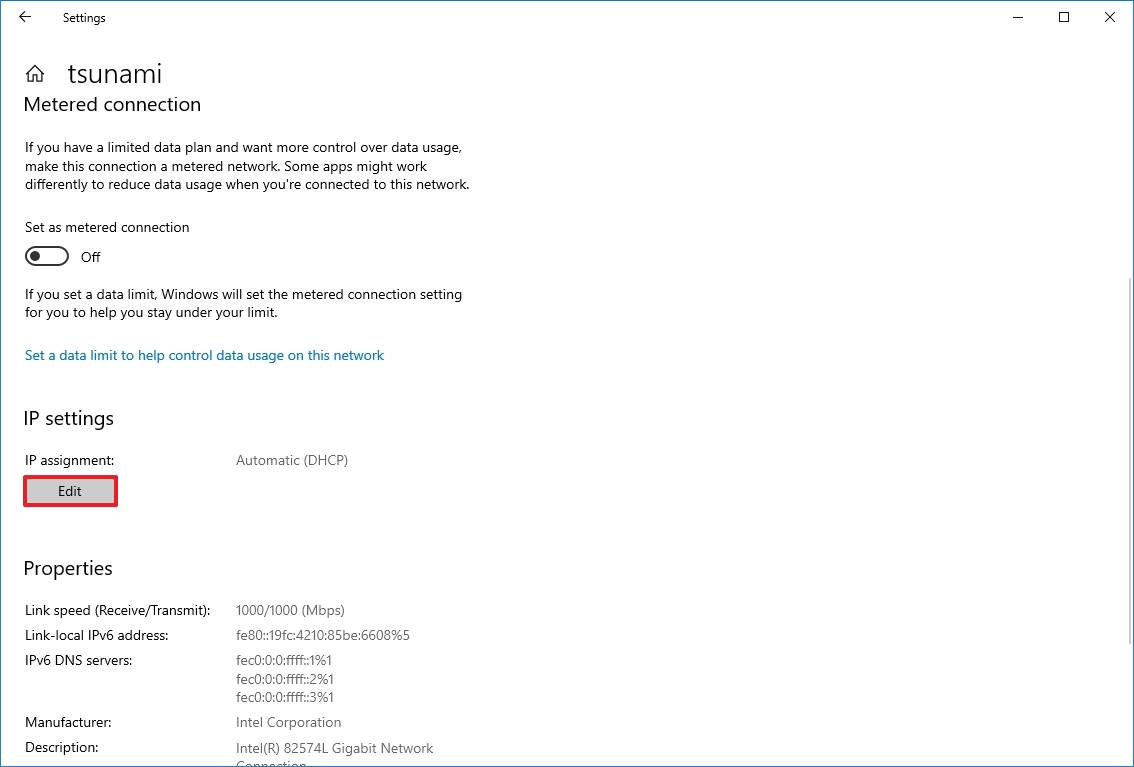
- Click on the Edit button for the "IP assignment" setting.
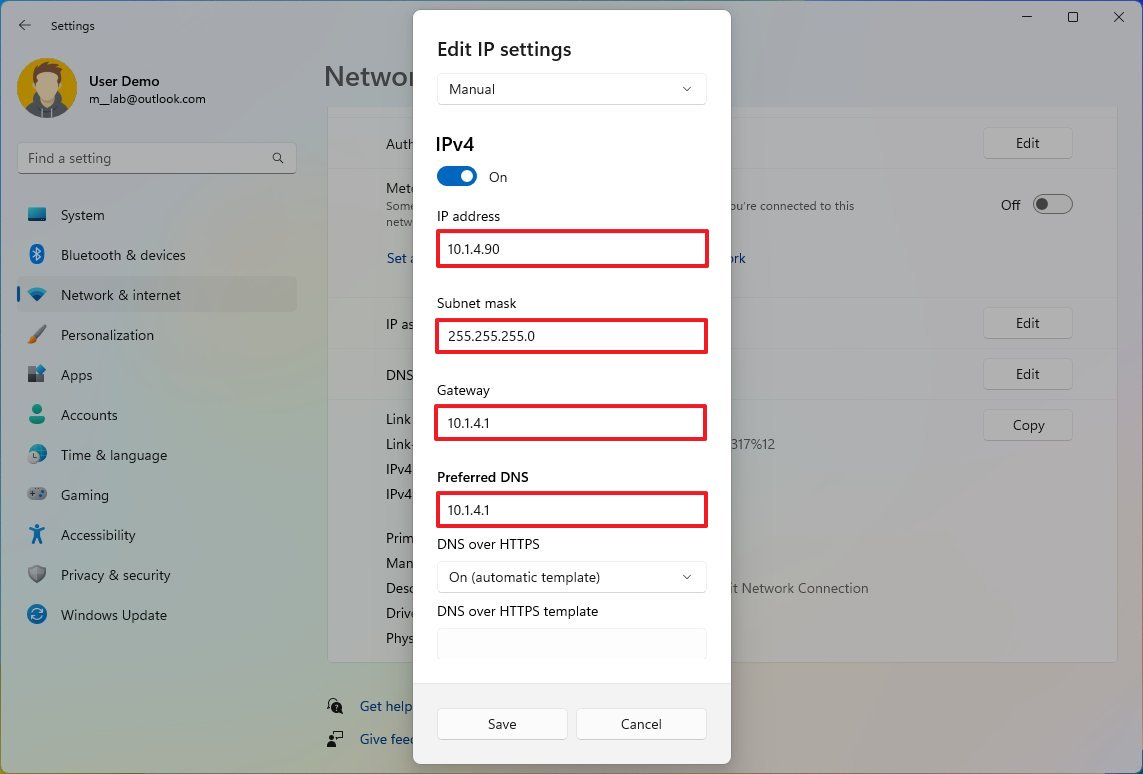
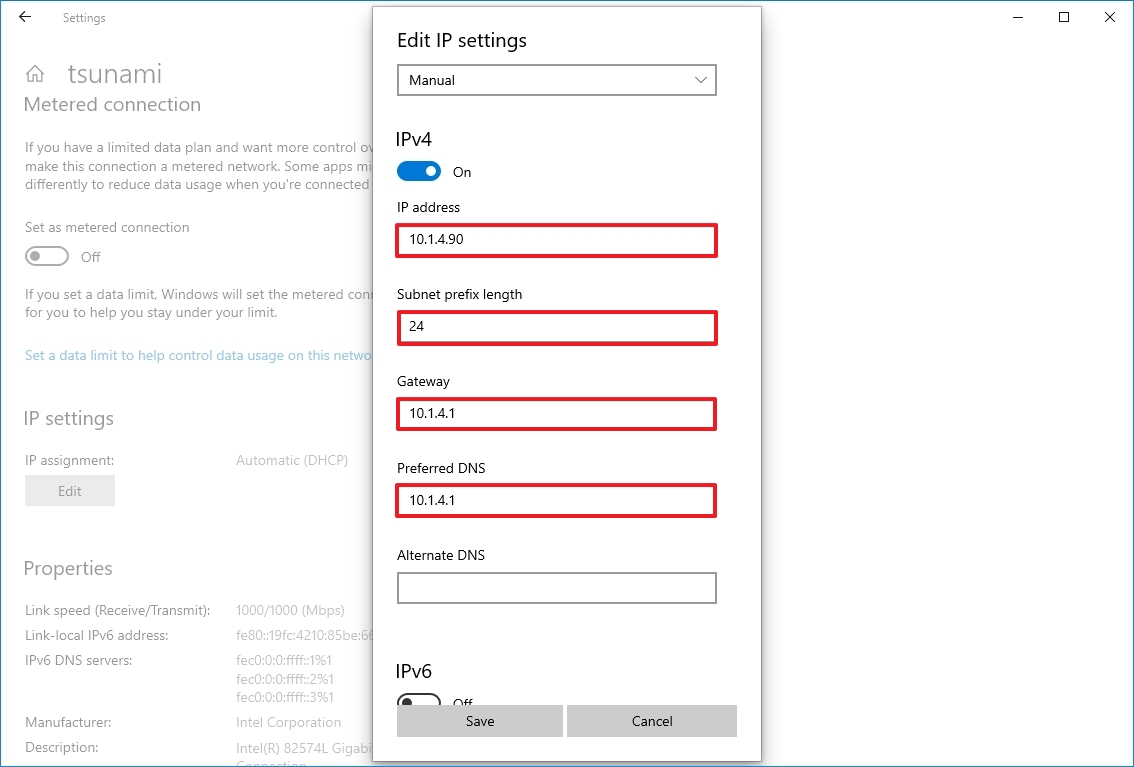
- Select the Manual option from the drop-down menu.
- Turn on the IPv4 toggle switch.
- Confirm the IP address for the computer – for example, 10.1.4.90.
- Confirm the subnet mask for the configuration – for example, 255.255.255.0.
- Confirm the default gateway address (usually your router's IP) – for example, 10.1.4.1.
- Confirm the preferred DNS address – for example, 10.1.4.1.
- Quick note: In a home network, you may also be able to use the router's IP address for the DNS configuration. You can also use third-party DNS services like Google Public DNS, Cloudflare, Cisco's OpenDNS, and others.
- (Optional) Select the "On (automatic template)" option for the "DNS over HTTPS" setting and leave the "Fallback to plaintext" option disabled unless you want to encrypted as well as unencrypted traffic or you're troubleshooting connectivity.
- Quick note: DNS over HTTPS (DoH) is a feature that encrypts the DNS queries over the HTTPS protocol to improve security and privacy on the internet. You only want to enable this feature if the DNS server supports this feature.
- Confirm the alternate DNS address (if applicable).
- (Optional) Select the "On (automatic template)" option for the "DNS over HTTPS" setting and leave the "Fallback to plaintext" option disabled.
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, the computer will start using the static network configuration. If everything has been configured correctly, you should be able to open the web browser to access the internet.
If you entered an address (such as the DNS address) and then changed it, you probably won't be able to save the settings. If this is the case, cancel the configuration, start over, enter the correct configuration, and then try to save the settings.
Configure IP from Command Prompt
To set a static TCP/IP configuration on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
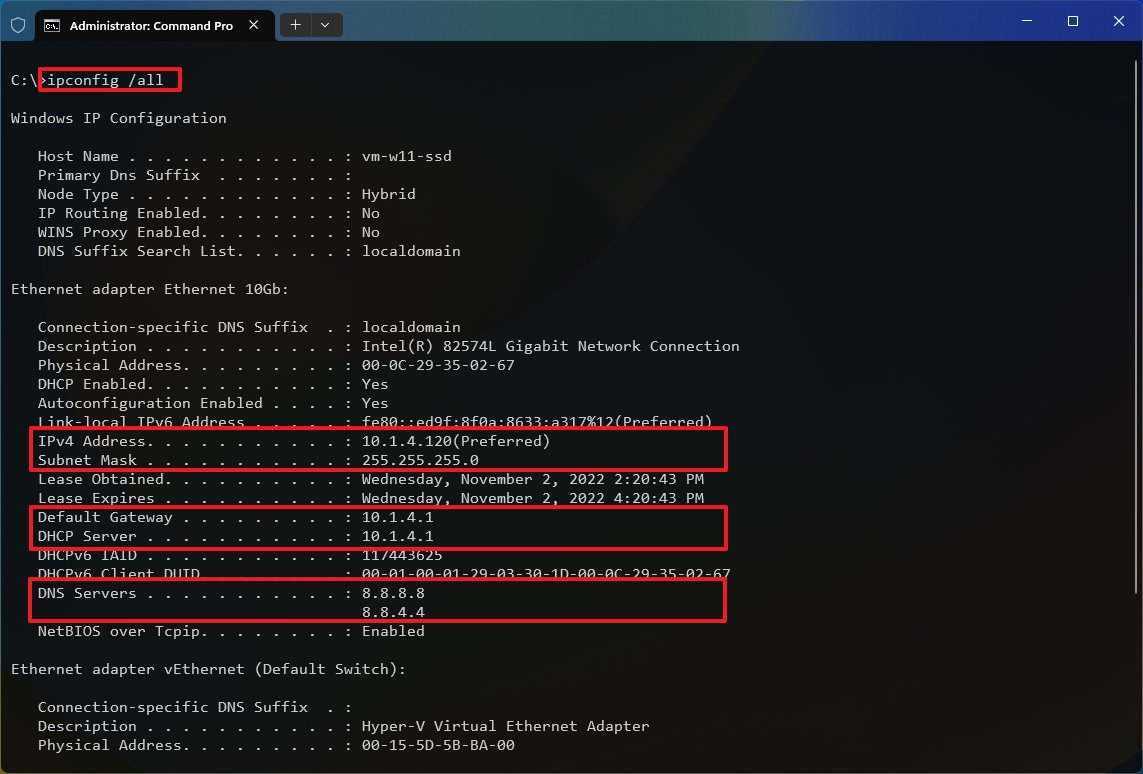
- Type the following command to see your current networking configuration and press Enter: ipconfig /all
- Confirm the name of the adapter and the networking configuration, including the IPv4, Subnet mask, Default Gateway, and DNS Servers.
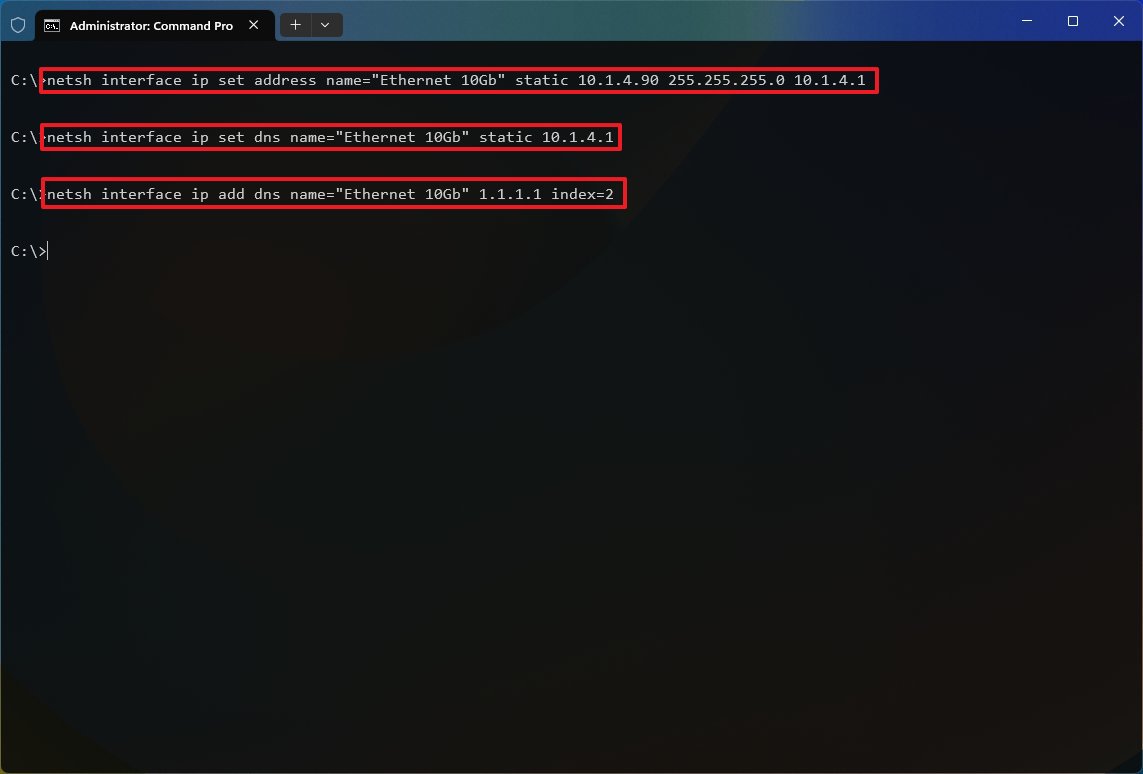
- Type the following command to configure a static TCP/IP address and press Enter: netsh interface ip set address name= "ADAPTER-NAME" static IP-ADDRESS SUBNET-ADDRESS DEFAULT-GATEWAY-ADDRESS
In the above command, replace ADAPTER-NAME with the name of your network adapter. Change IP-ADDRESS SUBNET-ADDRESS DEFAULT-GATEWAY-ADDRESS with the device IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway addresses you want. For example, this command sets the 10.1.4.90, 255.255.255.0, 10.1.4.1 configuration: netsh interface ip set address name="Ethernet 10Gb" static 10.1.4.90 255.255.255.0 10.1.4.1
- Type the following command to set a DNS server address and press Enter: netsh interface ip set dns name="ADAPTER-NAME" static DNS-ADDRESS
In the command, change ADAPTER-NAME with your adapter's name and DNS-ADDRESS with the DNS server address of the network. For example, this command sets the local router as the DNS server: netsh interface ip set dns name="Ethernet 10Gb" static 10.1.4.1
- Type the following command to set an alternate DNS server address and press Enter: netsh interface ip add dns name="ADAPTER-NAME" DNS-ADDRESS index=2
In the command, change ADAPTER-NAME with the adapter's name and DNS-ADDRESS with an alternate DNS server address. For example, netsh interface ip add dns name="Ethernet 10Gb" 1.1.1.1 index=2
After you complete the steps, the commands will set a static network configuration on Windows 11.
How to set a static TCP/IP network configuration on Windows 10
On Windows 10, you can also use the Settings app and Command Prompt to set up a static IP network configuration.
Configure IP from Settings app
To assign a permanent TCP/IP configuration on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Network & internet.
- Click on Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
- Click on the active connection on the right side.
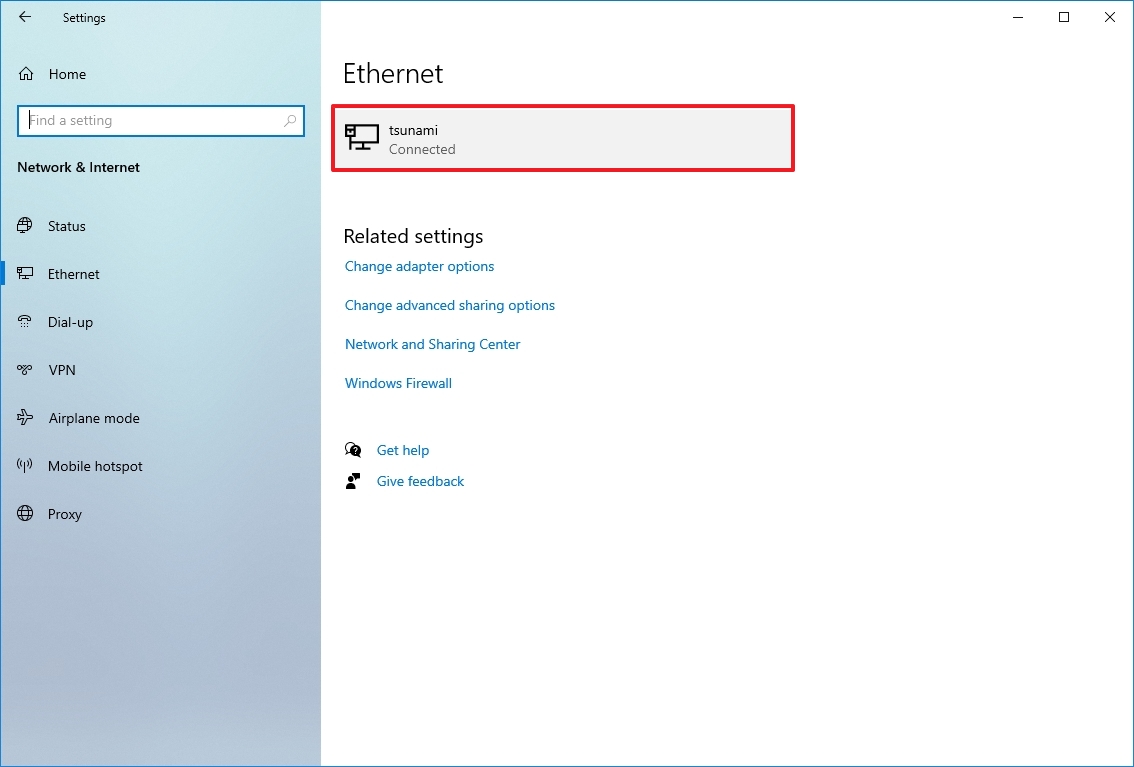
- Click the Edit button for the "IP assignment" setting.
- Select the Manual option.
- Turn on the IPv4 toggle switch.
- Confirm the IP address for the computer – for example, 10.1.4.90.
- Confirm the subnet prefix length (subnet mask) for the configuration – for example, 24 to specify the 255.255.255.0 subnet mask.
- Quick tip: It's important to use the number that represents the network instead of the subnet mask. Otherwise, the configuration won't save. If you don't know the subnet prefix length for your subnet mask, you can use any online subnet calculator to find out.
- Confirm the default gateway address (usually your router's IP) – for example, 10.1.4.1.
- Confirm the preferred DNS address – for example, 10.1.4.1.
- Quick note: In a home network, you may also be able to use the router's IP address for the DNS configuration. You can also use third-party DNS services like Google Public DNS, Cloudflare, Cisco's OpenDNS, and others.
- Confirm the alternate DNS address (if applicable).
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, Windows 10 will start using the static IP configuration. If you lose network connectivity, restart the computer to regain access to the local network and internet.
Configure IP from Command Prompt
To change from dynamic to static IP address with commands on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to see your current networking configuration and press Enter: ipconfig /all
- Confirm the name of the adapter and the networking configuration, including the IPv4, Subnet mask, Default Gateway, and DNS Servers.
- Type the following command to configure a static TCP/IP address and press Enter: netsh interface ip set address name= "ADAPTER-NAME" static IP-ADDRESS SUBNET-ADDRESS DEFAULT-GATEWAY-ADDRESS
In the above command, replace ADAPTER-NAME with the name of your network adapter. Change IP-ADDRESS SUBNET-ADDRESS DEFAULT-GATEWAY-ADDRESS with the device IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway addresses you want. For example, this command sets the 10.1.4.90, 255.255.255.0, 10.1.4.1 configuration: netsh interface ip set address name="Ethernet 10Gb" static 10.1.4.90 255.255.255.0 10.1.4.1
- Type the following command to set a DNS server address and press Enter: netsh interface ip set dns name="ADAPTER-NAME" static DNS-ADDRESS
In the command, change ADAPTER-NAME with your adapter's name and DNS-ADDRESS with the DNS server address of the network. For example, this command sets the local router as the DNS server: netsh interface ip set dns name=" Ethernet 10Gb" static 10.1.4.1
- Type the following command to set an alternate DNS server address and press Enter: netsh interface ip add dns name="ADAPTER-NAME" DNS-ADDRESS index=2
In the command, change ADAPTER-NAME with the adapter's name and DNS-ADDRESS with an alternate DNS server address. For example, netsh interface ip add dns name="Ethernet0" 1.1.1.1 index=2
After you complete the steps, the network configuration will switch from dynamic to static on Windows 10.

Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 22 years of combined experience in IT and technical writing. He holds various professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA and has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.