How to use Search instead of Cortana on Windows 10 May 2019 Update
The classic search experience is coming back with the May 2019 Update, and with new features — Here are the steps to get started.
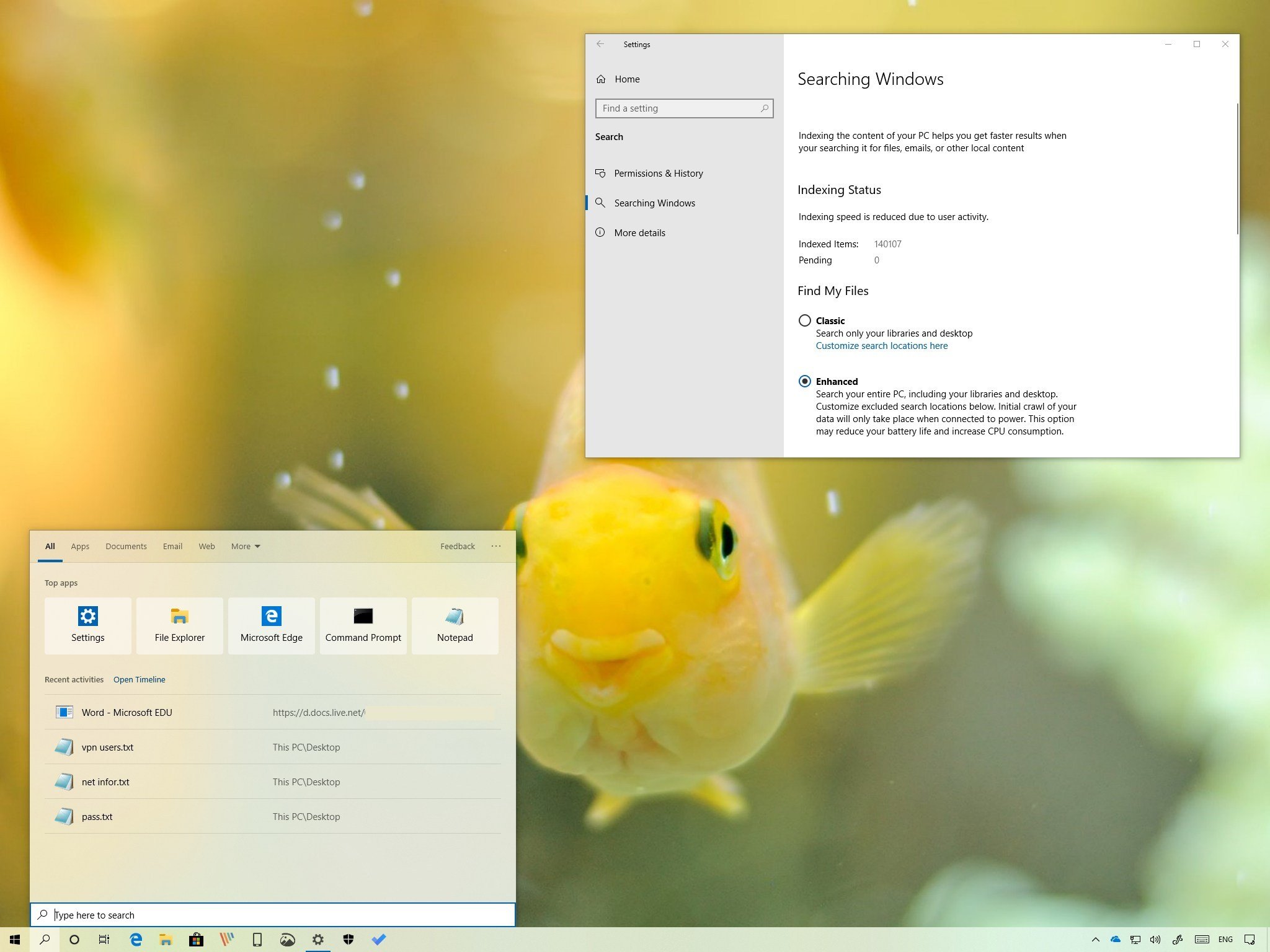
Once you upgrade to the Windows 10 May 2019 Update (version 1903), you'll notice something different in the taskbar. You'll see a search box and a Cortana button next to it. This is because starting with this new major release, Cortana and Search are becoming two separate features, which means that the classic search is coming back.
In this new version of Windows 10, the overall experience to search files, folders, and the web remain similar to previous versions, but there are a few interesting changes. For instance, you can now control the aspects of search from the new dedicated Search section available in the Settings app. You can enable a new enhanced option to expand the search capability to your entire device. The search interface in taskbar gets a bunch of tweaks, and a lot more.
In this Windows 10 guide, we'll walk you through the steps to manage the new Search settings and the instructions to use the experience with the May 2019 Update.
- How to manage permissions settings for Search
- How to manage index settings for Search
- How to find files and apps with Search
- How to manage taskbar button for Search
Windows 10 May 2019 Update full reviewHow to get the May 2019 Update ASAPMay 2019 Update common problems and how to fix themFull list of changes in the May 2019 UpdateAll of our May 2019 Update resources in one place
How to manage permissions settings for Search
In the past, the Permissions & History page was part of the Cortana experience, but starting with the May 2019 Update, the page has been relocated to the new "Search" section, and it allows you to control many privacy and feature settings to improve your search experience.
Restricting search results
Alongside files and apps results, Windows 10 can also provide results for web searches. However, because web previews can include unsuitable content, you can adjust the settings to specify a custom filter level.
To change the search preview restriction level, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Permissions & History.
- Under the "SafeSearch" section, select one of the search filter levels:
- Strict — doesn't show results that may contain adult text, images, and videos for web searches.
- Moderate — filters out videos and images that may contain adult content (default).
- Off — search results are shown without restrictions.
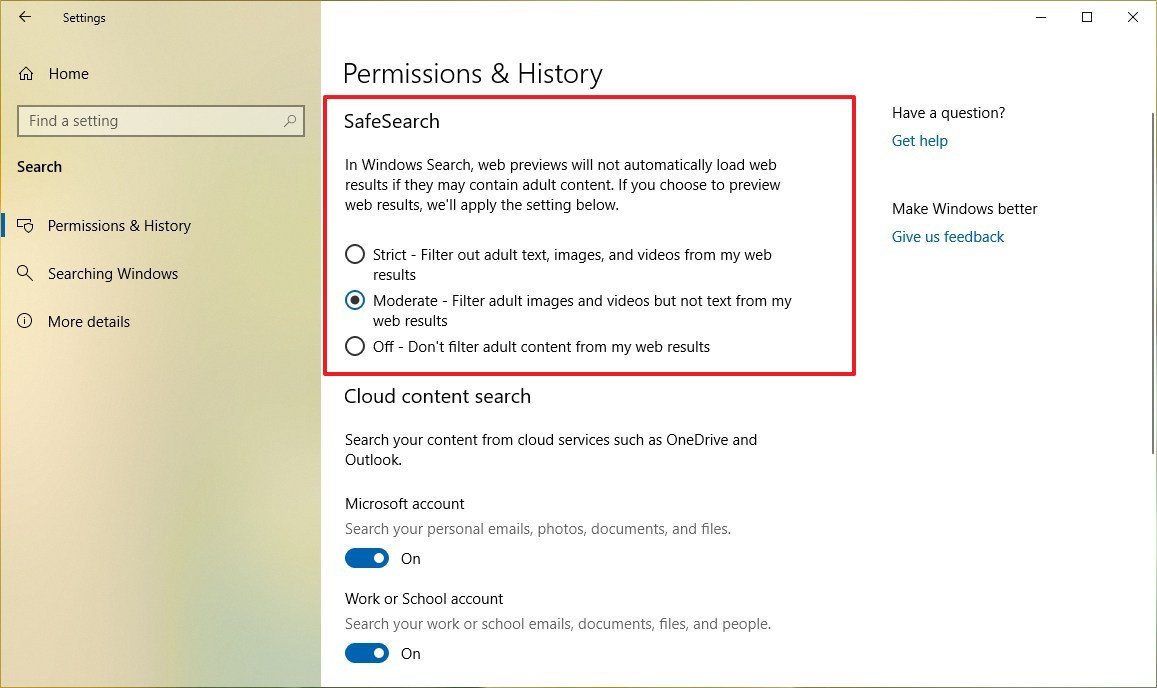
Once you complete the steps, search results will be restricted depending on your settings.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
Getting cloud search results
Windows 10 can not only provide search results for files and folders stored locally on your device but also from content stored in the cloud (OneDrive or OneDrive for Business).
To allow or deny cloud search within Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Permissions & History.
- Under the "Cloud content search" section, select and turn on or off the toggle switch to allow or deny cloud search on Windows 10:
- Microsoft account — allows you to search files, images, and emails stored in the cloud.
- Work or School account — allows you to make your files, images, and emails stored in your organization cloud searchable in your computer.
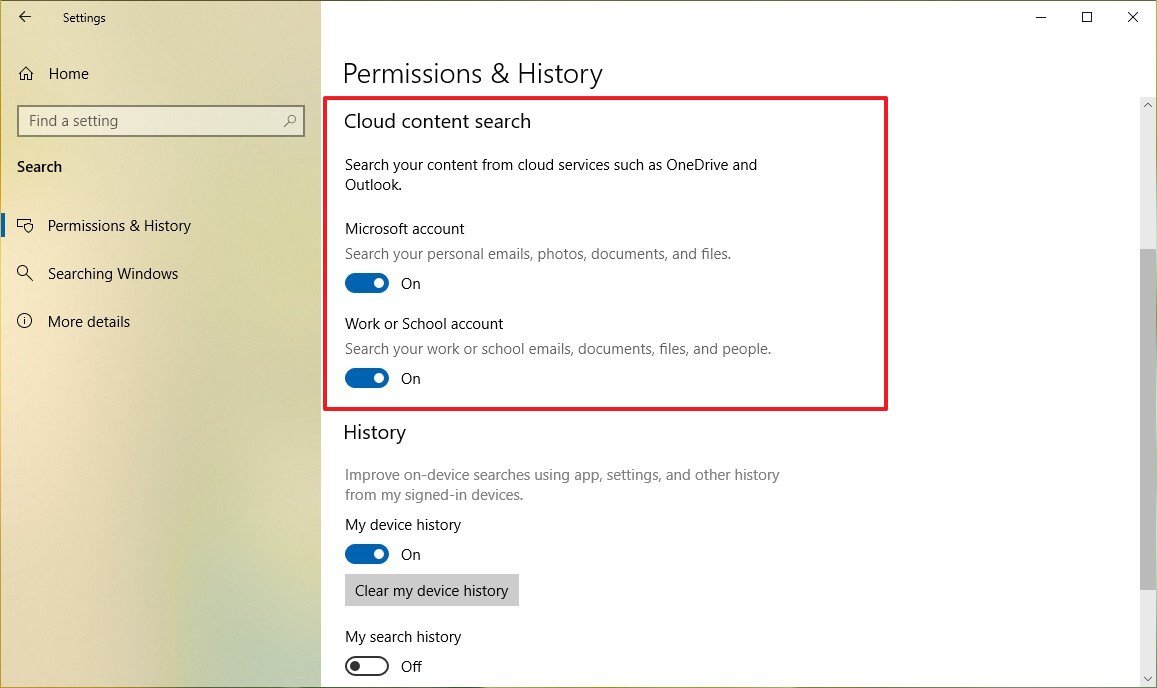
After completing the steps, depending on your configuration, you'll be able to run a query in the Search interface, and the results will now include content stored locally on your device and from those files, emails, and images stored in the cloud.
Managing search history
Windows 10 can collect searches from one or multiple devices that you own to provide a more personalized experience. If you're not interested in this functionality, you can use the history settings to control your search experience.
To manage search history on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Permissions & History.
- Under the "History" section, turn off the My device history toggle switch to prevent the system from collecting search information to improve results.
- Click the Clear my device history button to delete searches using apps and settings.
- Turn on the My search history toggle switch if you want Windows 10 to collect your searches to improve your search experience across devices. (The default state of this setting is off.)Quick note: You can also click the "Search history" settings option to open your Microsoft account online to customize your search experience further.
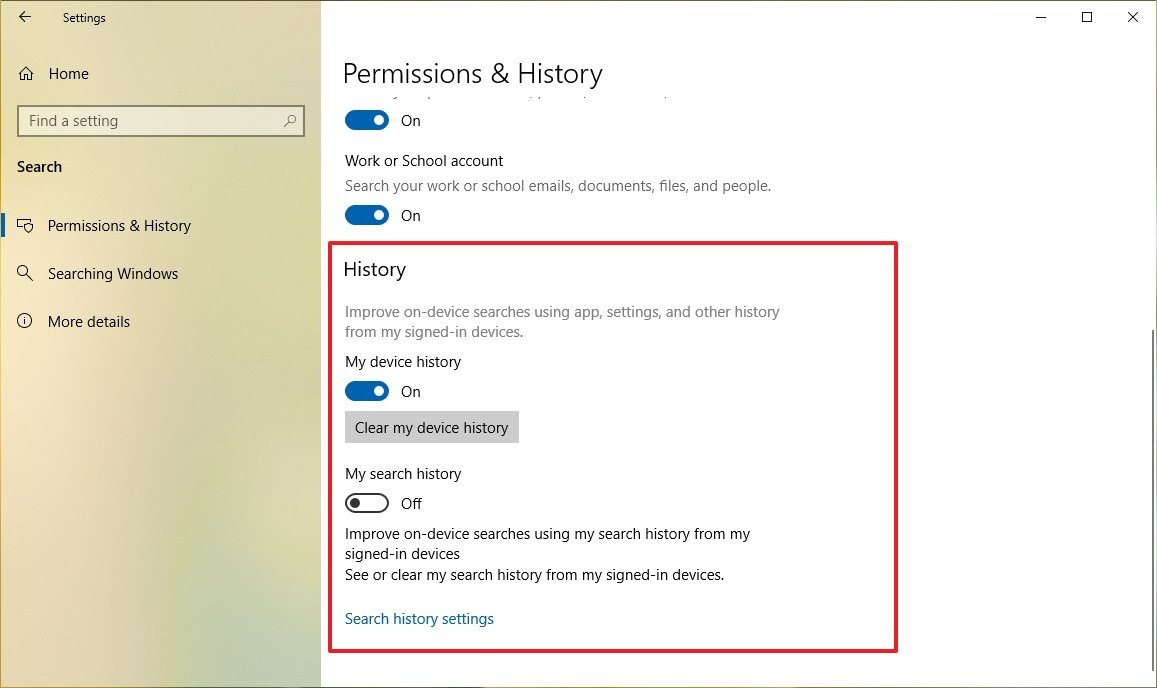
Once you complete the steps, depending on your settings, search results will improve over time when searching for apps and settings on your computer or across your devices.
How to manage index settings for Search
Search Windows is a new page available in the Settings app, and it includes new features and options previously available through Control Panel to manage various aspects of the indexing process on Windows 10.
Viewing indexing stats
To view the current indexing status starting with the May 2019 Update, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Searching Windows.
- See Indexing Status section.
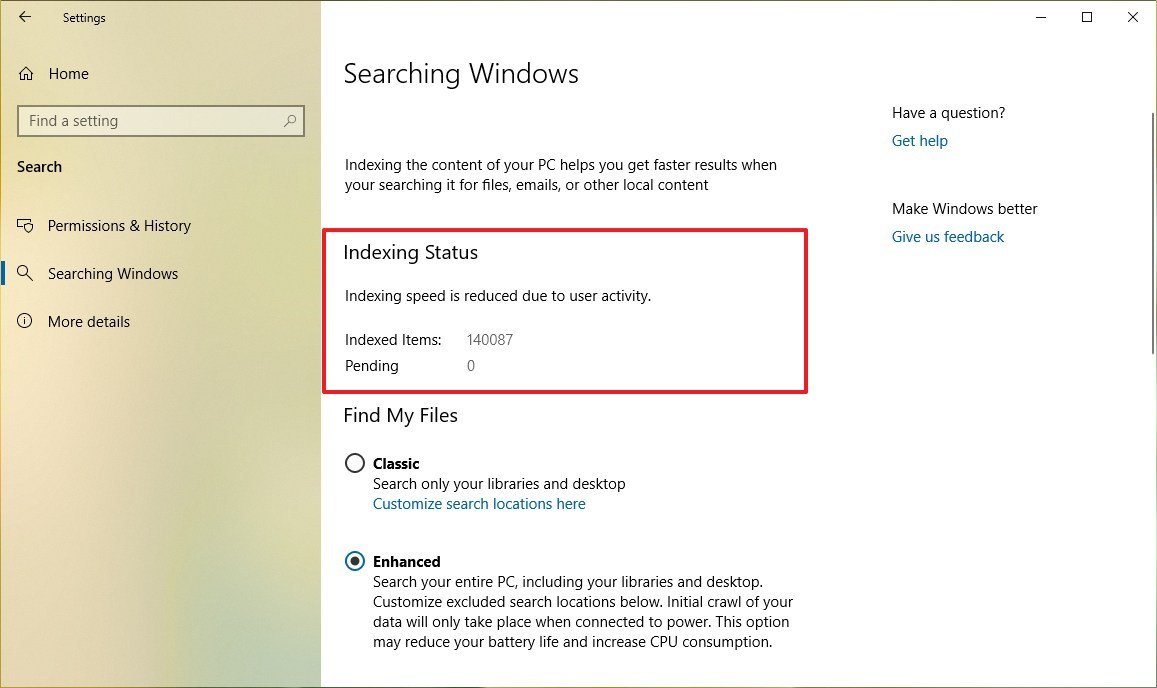
Once the in the settings page, at the top, you'll notice the indexing status of your device, which shows you the number of items that have been indexed and those items yet to be added to the searchable list.
Using Enhanced mode
In addition to the features previously available, starting with version 1903, Windows 10 is also introducing a new Enhanced search mode that allows you to search your entire device, and not just your Documents, Videos, Pictures, Music, and Desktop folders.
To enable the new Enhanced search feature on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Searching Windows.
- Under the "Find My Files" section, select the Enhanced option.
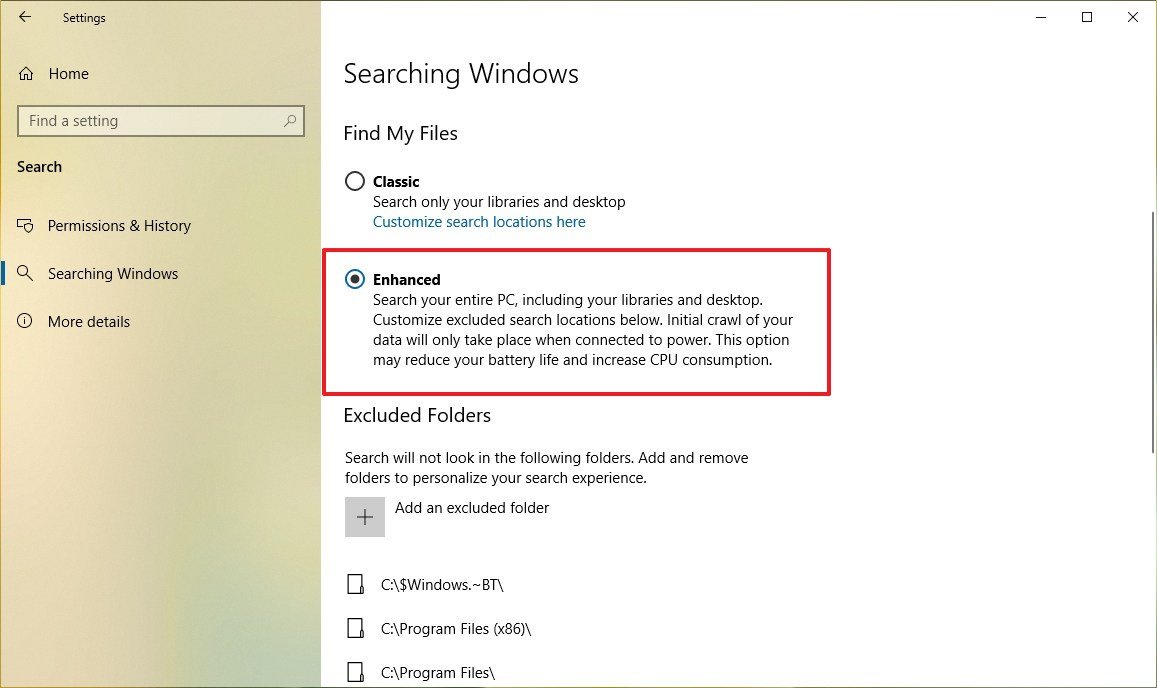
After completing the steps, when you perform a search, Windows 10 will look into all the folders and drives (not just your libraries and desktop) to find the item that you want.
Excluding folders
If there are specific folders that you wish not to be searchable, the new Search Windows settings have an option to exclude folders from search.
To include or exclude folders from search, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Searching Windows.
- Under the "Excluded Folders" section, click the Add an excluded folder button.
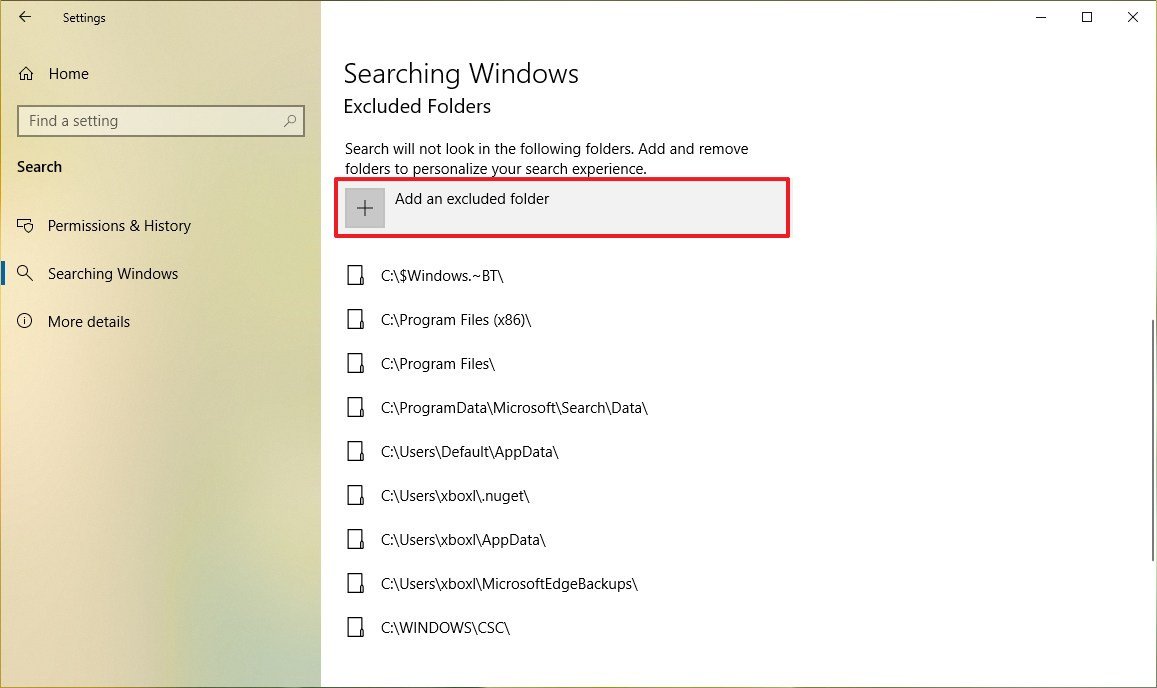
- Select the folder that you don't want to index.
- Click the Select Folder button.
Once you complete the steps, the folder and its content will not participate in the search experience on your device.
Although the enhanced option has been designed to search your entire system, Windows 10 automatically removes specific folders from the search index, including the $Windows.~BT, Programs Files (x86), Program Files, Windows, and other folders. If you want to make these and other folders searchable, make sure to select the folder and click the Remove excluded folder button.
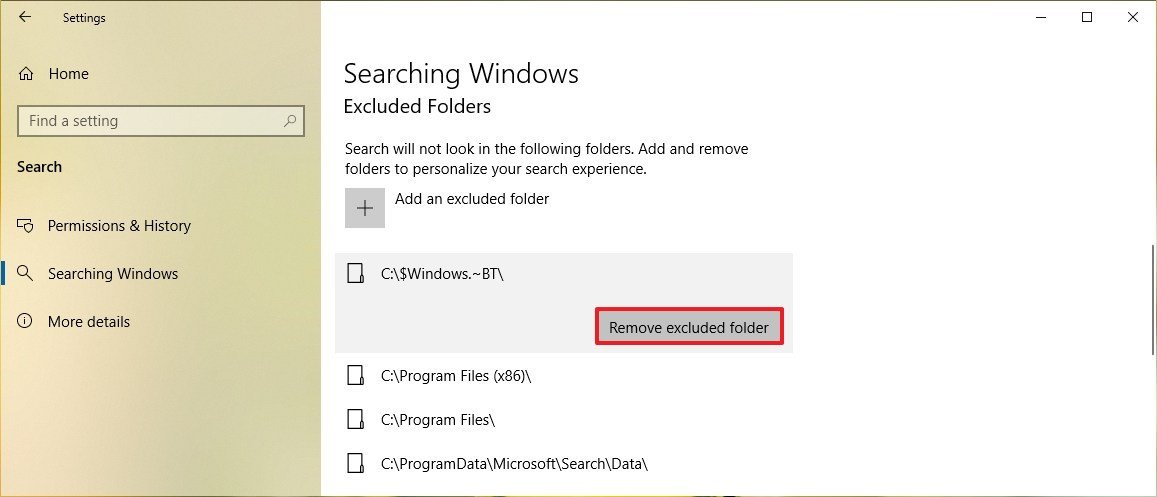
Customizing advanced settings
If you need to tweak the indexing settings even further, you can customize the experience using the advanced settings to index encrypted files, rebuild the index database, make new file formats searchable, and more.
To change the search index advanced settings on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
- Click on Searching Windows.
- Under the "More Search Indexer Settings" section, click the Advanced Search Indexer Settings option.
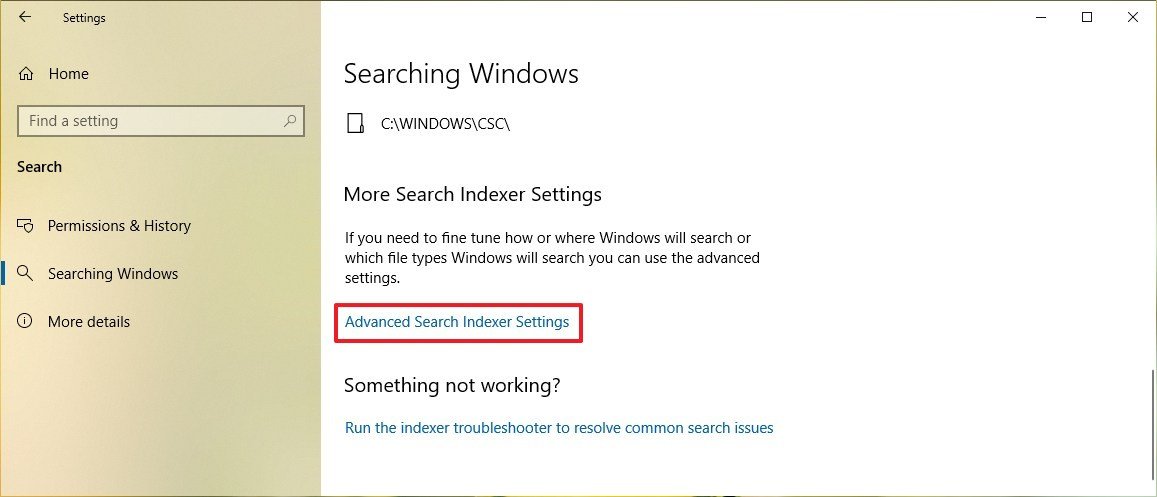
- Click the Advanced button.
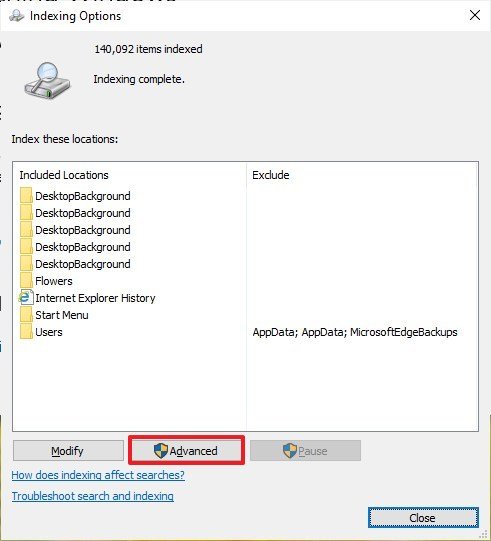
- Click the Index Settings tab.
- Under the "File Settings" section, you can enable two features:
- Index encrypted files — makes files and folders using encryption searchable.
- Treat similar words with diacritics as different words — recognizes two words as similar if one other is similar but it has an accent, and the other doesn't.
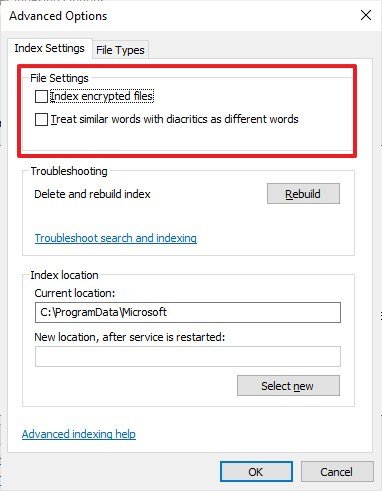
- Under the "Troubleshooting" section, you can click the Rebuild button to delete and recreate the index database when Search isn't working correctly.
- Under the Index location section, you can specify another folder or driver to relocate the index database.
- Click the File Types tab.
- Check or clear the file formats that are searchable on Windows 10.
- Under the "How should this file be indexed" section, you can select two settings:
- Index Properties — Only indexes metadata information.
- Index Properties and File Contents — indexes the metadata information and the content inside the file.
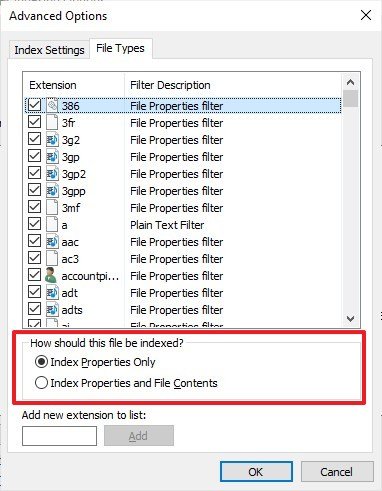
- The Add new extension to list option allows you to includes new file formats to the list to make them searchable.
In addition, while in the "Indexing Options" page (part of the old Control Panel experience), you can use the Modify button to add and remove locations, but it's similar to using the "Exclude folders" settings. However, you'll notice a Pause button, which allows you to temporarily stop Windows 10 from trying to index files and folders.
Fixing search problems
If files or emails don't appear in results, Search is causing your device to run slow, or any other problem, you can use the indexer troubleshooter to resolve most common issues.
To run the indexer troubleshooter on Windows 10 version 1903, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Search Windows.
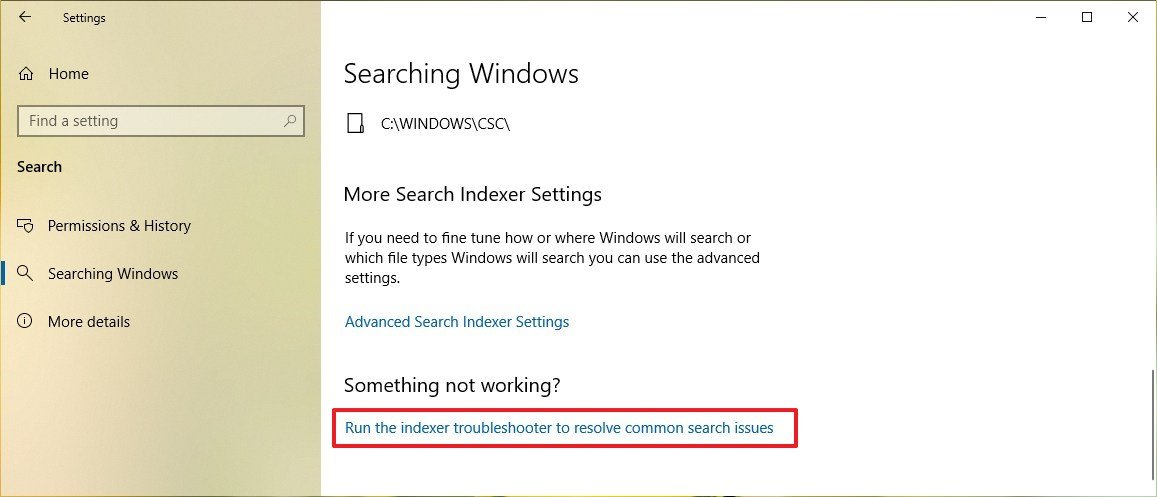
- Click on Searching Windows.
- Under the "Something not working" section, click the Run the indexer troubleshooter to resolve common search issues option to fix problems.
- Select one or multiple problems that you want to troubleshoot.
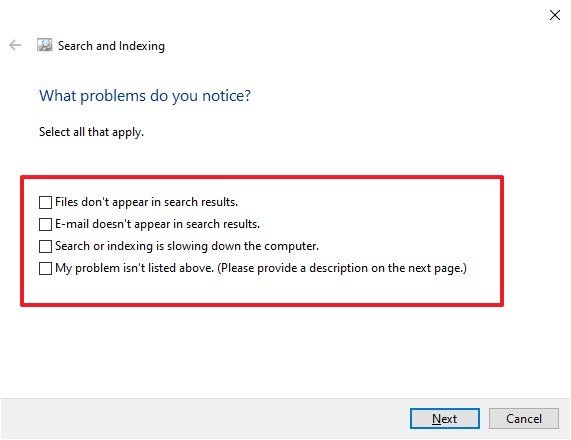
- Click the Next button.
- Continue with the on-screen directions.
After completing the steps, Search experience should start working normally.
How to find files and apps with Search
Alongside the new features and improvements, starting with the May 2019 Update, you're also getting a new Search interface in the taskbar. The new interface introduces a new landing page that uses improved spacing to display your recent activities from Timeline.
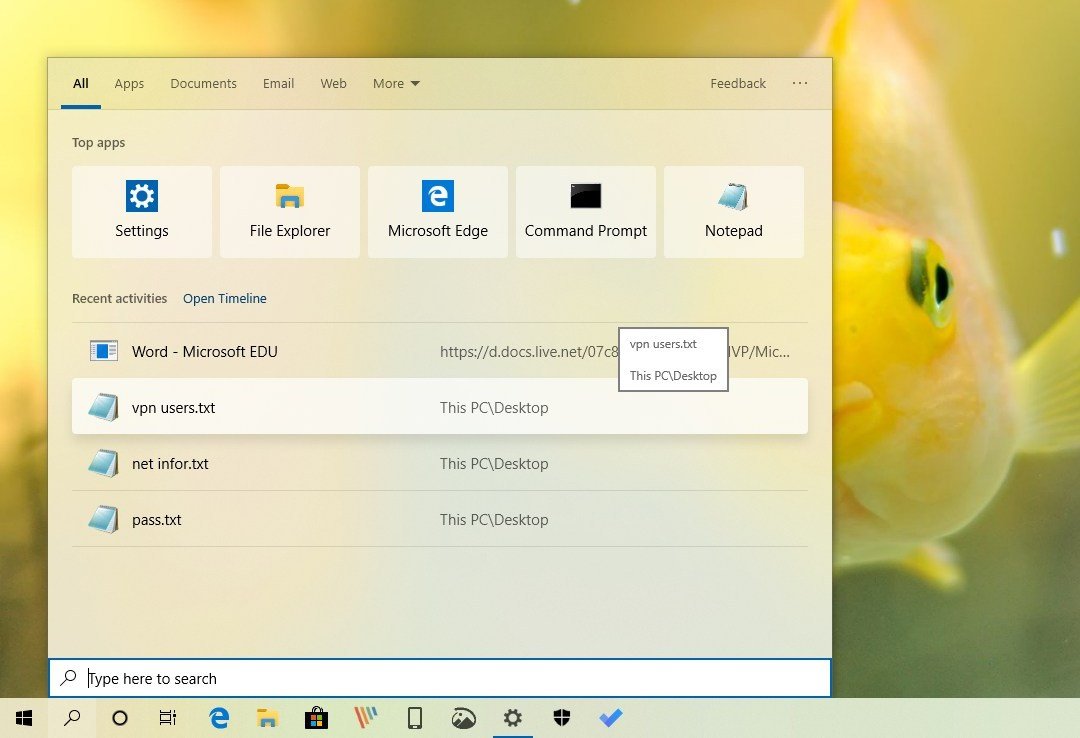
You'll also notice a "Top apps" section which lists your most frequently accessed applications using tiles with rounded corners.
As you type a search query, the results will appear in a similar layout as the search experience available with the Windows 10 October 2018 Update, which shows results in the left pane with additional options (Open, Run as administrator, Open file location, etc.) in the right side.
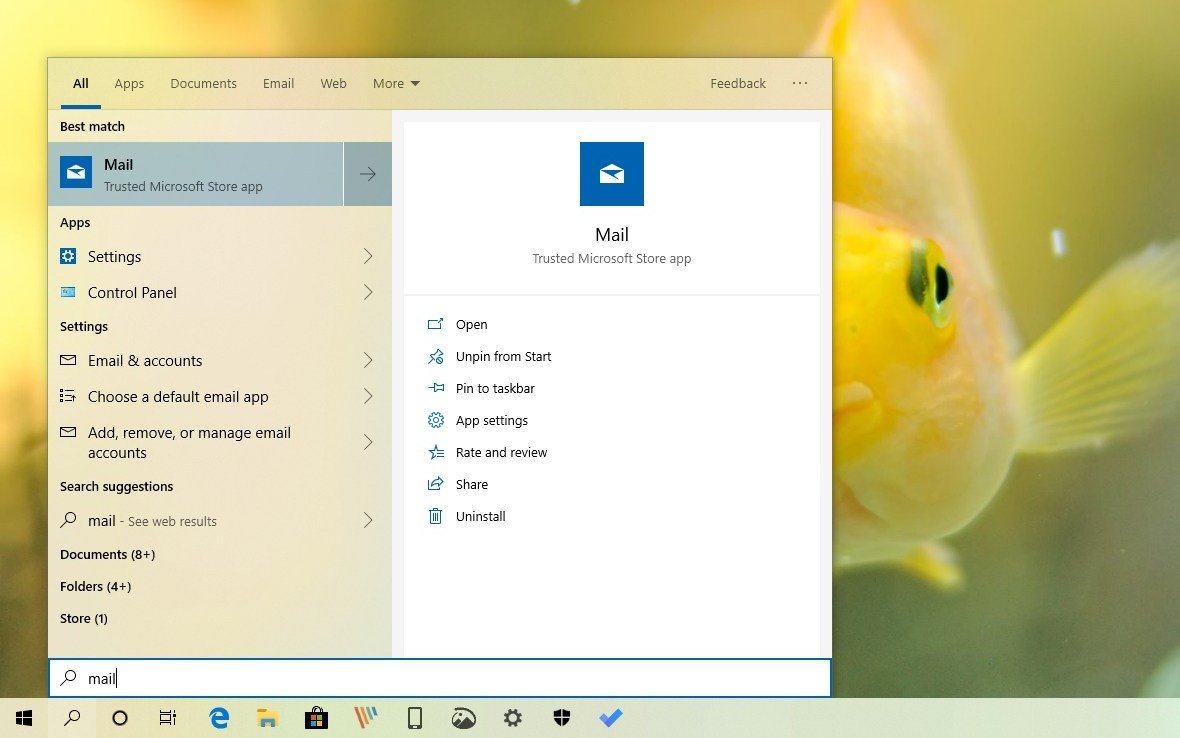
In this feature update, you'll find the same search filters like in previous versions, but with the difference that this time around, the "Apps" filter is getting an update with a new landing page that includes two lists that surfaces your frequent and most recent applications.
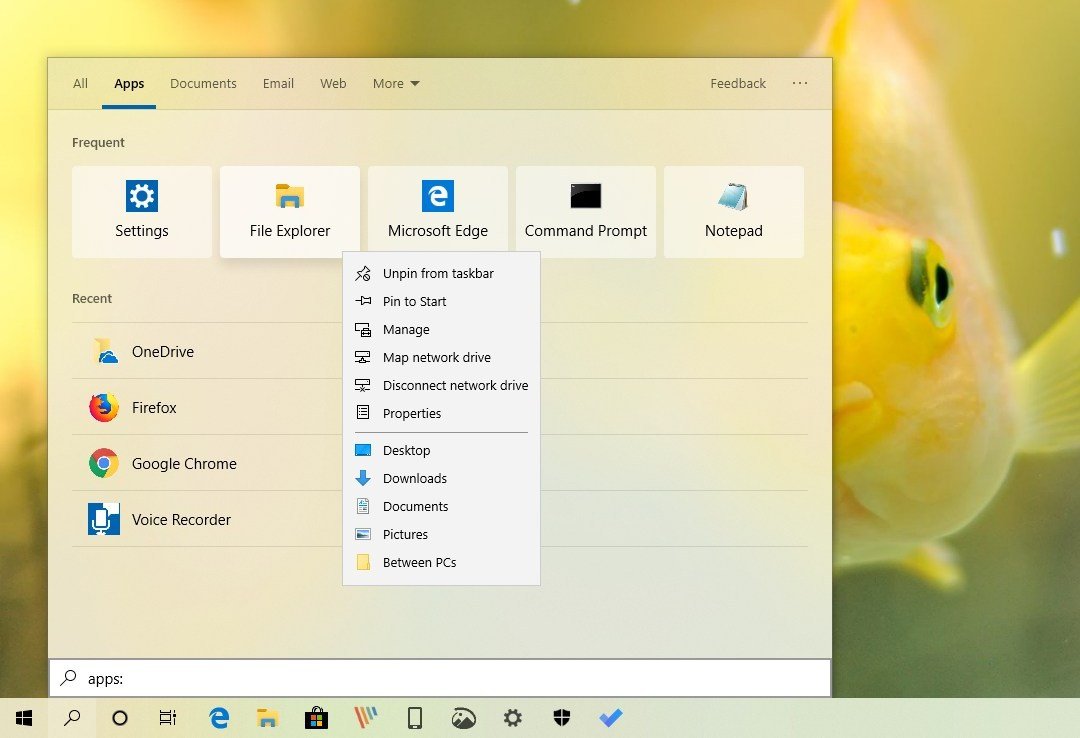
The new Search experience also features some Fluent Design visual improvements, including acrylic and shadow effects as well as full support for the dark and new light system mode.
How to manage taskbar button for Search
The May 2019 Update, by default, ships with the full Search box pinned to the taskbar. However, if you want to reclaim taskbar space, you can customize the experience.
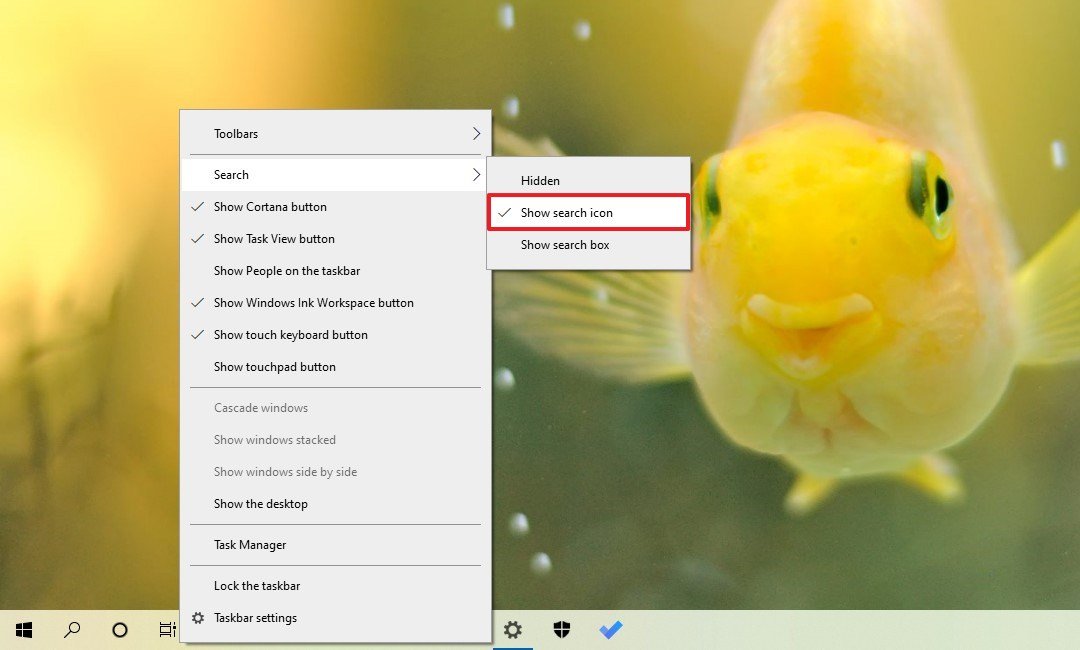
If you want to remove the search box while still having quick access to Search, use these steps:
- Right-click the taskbar.
- Select the Search submenu.
- Choose the option that you want to use:
- Hidden — removes the search box from the taskbar, but you can still use search on Windows 10 by opening the Start menu and just starting typing the query.
- Show search icon — replaces the box for a search button, which you can click to access the experience faster.
- Show search box — default option, shows the big search box in the taskbar.
Once you complete the steps, depending on your configuration, you'll have more space to pin apps in the taskbar.
What are your thoughts in the updated search experience? Tell us in the comments.
More Windows 10 resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10, visit the following resources:
- Windows 10 on Windows Central – All you need to know
- Windows 10 help, tips, and tricks
- Windows 10 forums on Windows Central
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.

