How to install the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL 2) on Windows 10 and Windows 11
The most recent version of the Windows Subsystem for Linux is a significant upgrade; for most, and it's now easier than ever to install.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Microsoft dropped plenty of jaws way back when it launched the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), a way to run actual Linux inside Windows without the need to set up a virtual machine. The project has seen a ton of support, and WSL 2 is the latest and greatest.
It takes things a little further and adds yet more awesomeness to the Linux experience on Windows 10 and Windows 11. WSL 2 uses a proper Linux kernel compared to the virtualized one from the first version, and it has significantly better performance.
More recent developments also reduce the reliance on the Microsoft Store for serving up distro images, and official support is inbound from the likes of Fedora and Arch Linux, too. But before all of that, let's walk through how you get set up.
Simplified setup of WSL2 on Windows 10 and Windows 11
There is now an extremely simplified way to get WSL 2 up and running on your Windows 10 and Windows 11 PC. To get the very latest version using the simplified method you need to be running Windows 10 version 2004 or higher, or Windows 11.
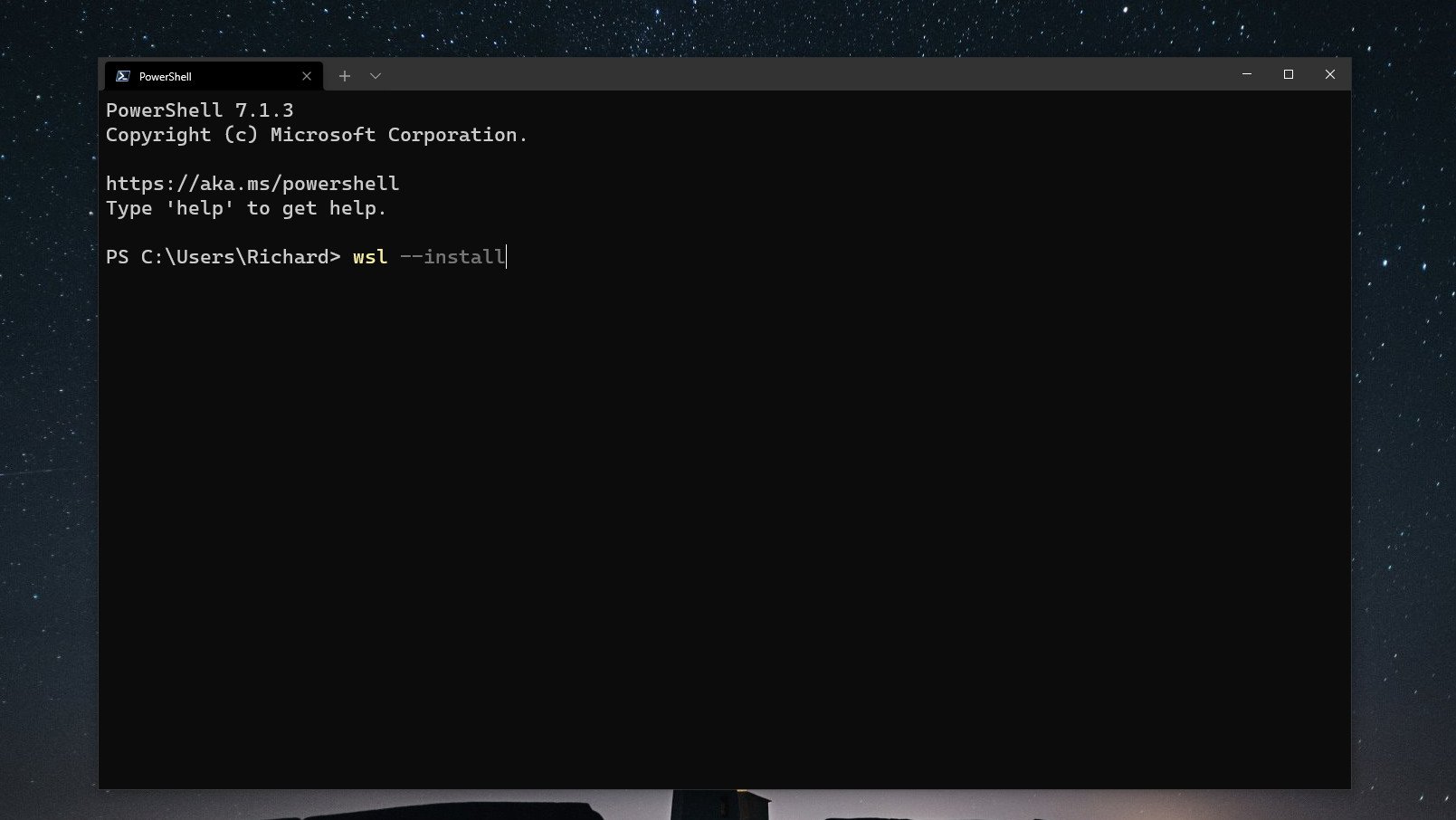
Once this is in place, open up PowerShell and enter this command:
wsl --installThat's it. The setup process will begin, and you can relax until it's finished. By default, WSL will enable all system features required and it will download and install Ubuntu. If you don't want a distribution installed during setup, you can add the --no-distribution tag to the installation command.
Alternatively, if you want a non-Ubuntu distribution installed, you can add its name after the install command. For example, wsl --install Debian.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
WSL is also distributed through the Microsoft Store, and the simplified installation process will pull this version in. Alternatively, you can download it directly from its Microsoft Store listing.
You will also require the optional Windows Subsystem for Linux component if you wish to also use WSL 1 alongside WSL 2.
How to enable Windows Subsystem for Linux optional component for WSL 1
WSL 2 is now the standard, but if for any reason you also want to use WSL 1 alongside it, you'll need the optional Windows Subsystem for Linux component enabling. Fortunately, you can do this in two ways. The first is by adding --enable-wsl1 to the install command used above.
But you can also enable the component at any time, even after you already have WSL 2 up and running. Open PowerShell as administrator and enter this command:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestartEventually, you will need to reboot your PC, adding norestart means you won't be immediately kicked out of whatever you're doing. If you want to reboot immediately, simply omit this from the end of the command.
Setting WSL 2 for your Linux distros
The good thing about WSL 2 is that it doesn't replace WSL 1. It just runs alongside it. This means you can run Linux installs with a combination of different versions. You're able to set either as default, as well as setting a version specifically to each Linux distro you have on your PC.
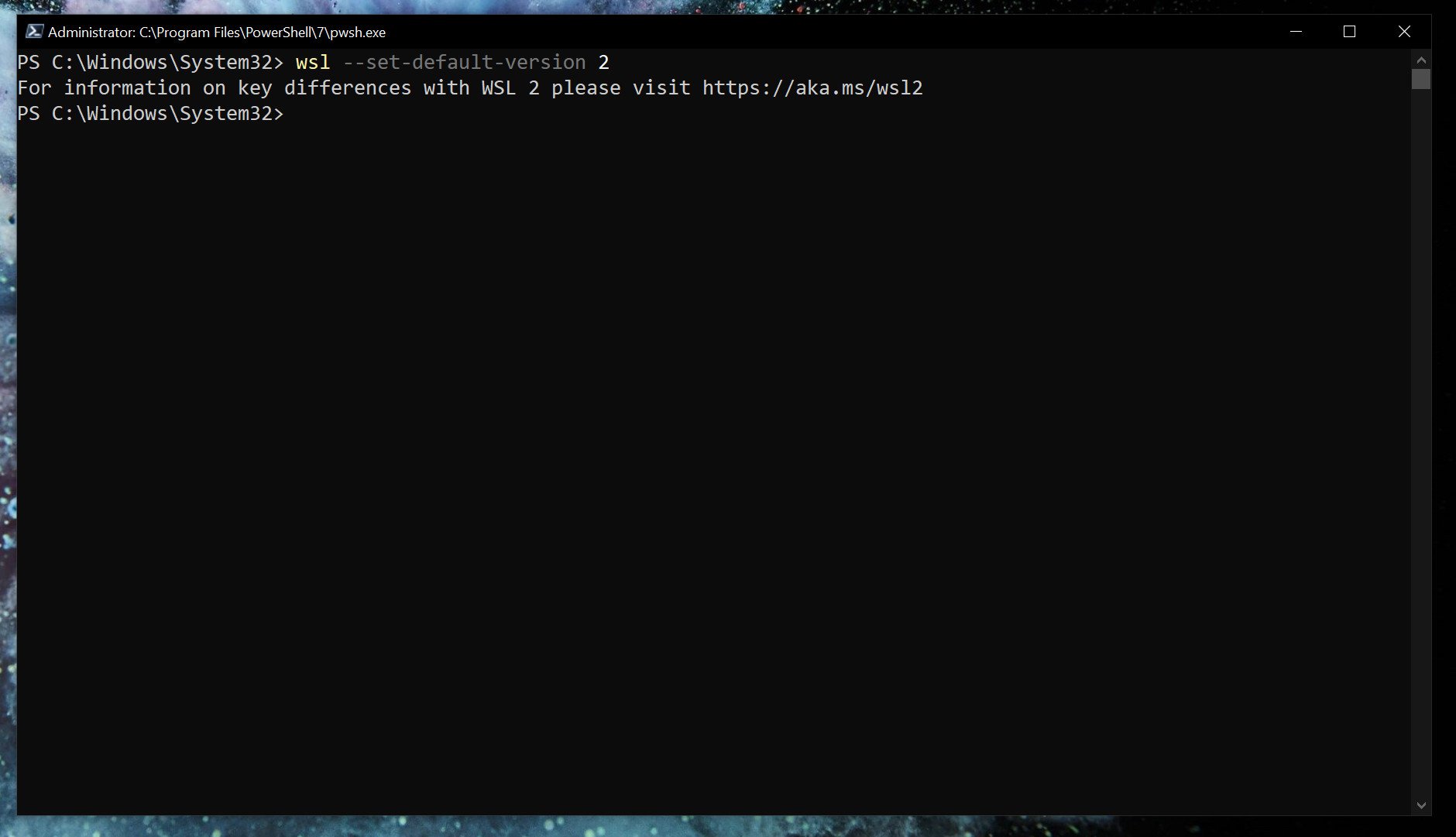
If you want everything to run on WSL 2 as soon as you install it, you can set it as the default version.
wsl --set-default-version 2Listing installed Linux distros and their WSL version
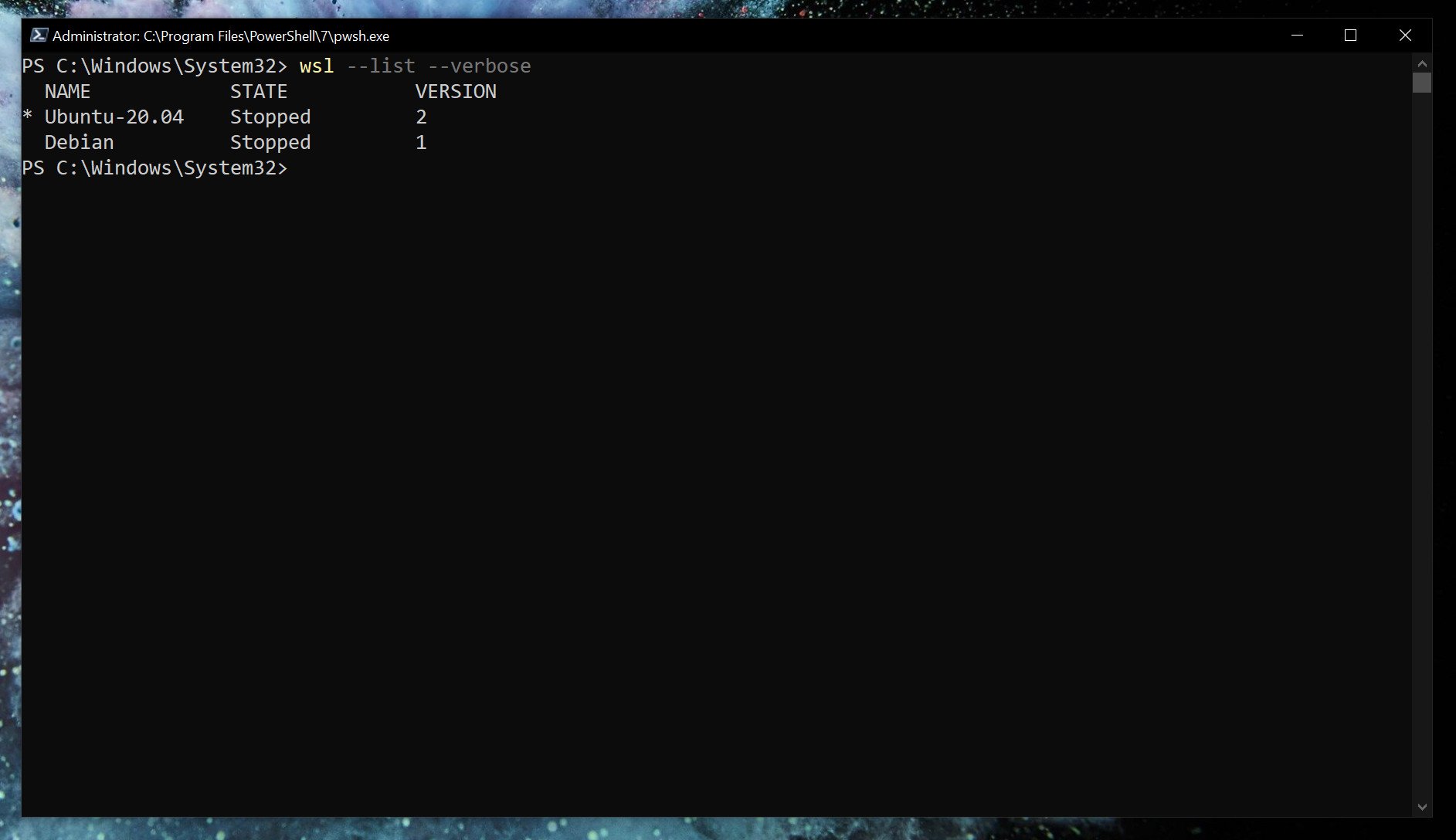
With WSL 2 set as default, any Linux installs after that will use it automatically. You can easily check which version of WSL your installed Linux distros are using.
wsl --list --verbose Using the verbose flag will give you the breakdown of which version of WSL is attached to which Linux installation. Without it, you'll simply get a list of the versions of Linux you have installed.
Changing the version of WSL per Linux installation
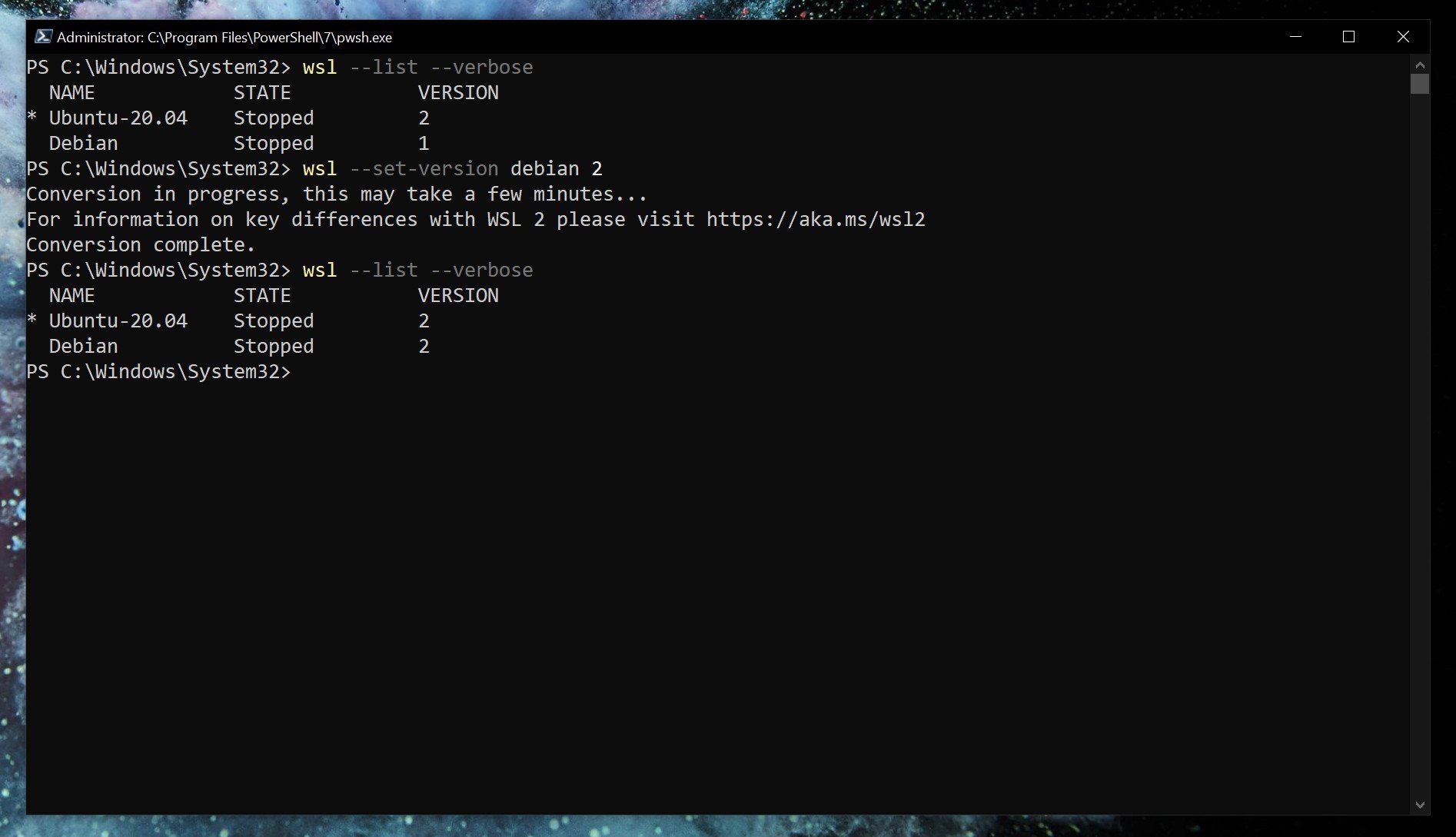
While setting WSL 2 as default will apply it to anything you install afterward. If you're already set up, you'll need to manually convert. Likewise, if you wish to go between versions 1 and 2 or run a mixture on your system, you can do that.
wsl --set-version <distribution name=""> <versionnumber></versionnumber></distribution>So, as an example, if you have a Debian installation on WSL that you need to convert to WSL 2, you'd enter
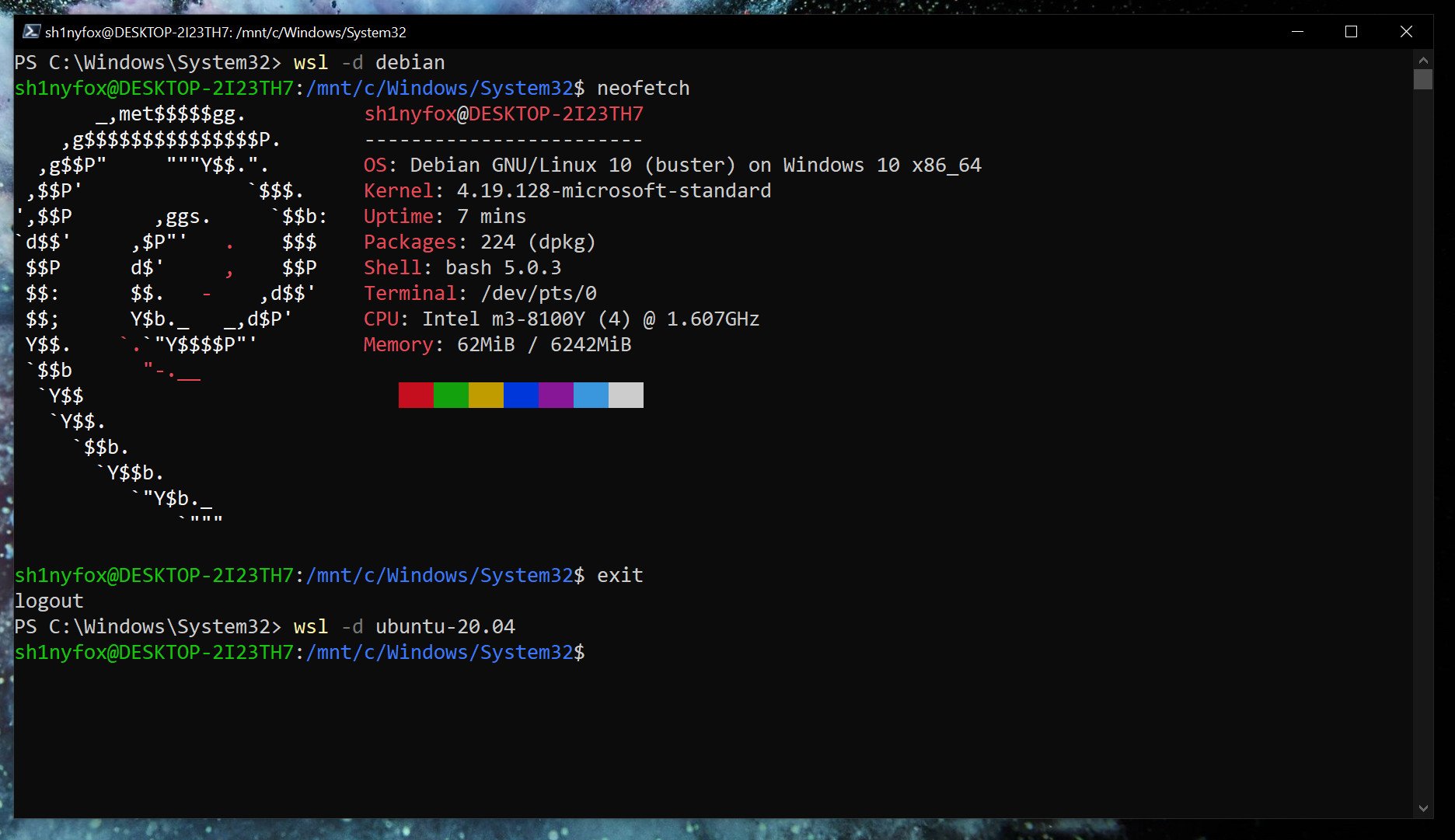
wsl --set-version debian 2Launch specific Linux installations in PowerShell
If you only have one version of Linux installed, simply typing
wslin PowerShell will launch you into the associated bash shell. But if you have multiple, you can launch a specific distro with this command.
wsl -d <distribution name=""></distribution>Once you're done and want to go back to PowerShell, typing
exitwill take you back.
From here on out, you're ready to go forth and install all the Linux you want. Our full guide will help you along the way, but once WSL 2 is set up how you like it, it just fades into the background.
It's also worth grabbing the Windows Terminal app from the Microsoft Store if you're using WSL. While you can just use the standard terminal installed with each or launch through PowerShell as shown above, Windows Terminal has a neat, tabbed interface that lets you run multiple shells at once. Have PowerShell, Linux, Azure Cloud Shell, and even Command Prompt, all open together side-by-side in one window.

Richard Devine is the Managing Editor at Windows Central with over a decade of experience. A former Project Manager and long-term tech addict, he joined Mobile Nations in 2011 and has been found in the past on Android Central as well as Windows Central. Currently, you'll find him steering the site's coverage of all manner of PC hardware and reviews. Find him on Mastodon at mstdn.social/@richdevine
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.