How to get full PC memory specs (speed, size, type, part number, form factor) on Windows 10
Use these commands to quickly find memory module information without taking the computer apart or using third-party apps.
On Windows 10, the ability to check the tech specs of the RAM (Random Access Memory) installed on your computer can come in handy in many situations. For example, when troubleshooting hardware and software-related problems, and details like the manufacturer name, part number, and serial number can be useful when contacting technical support.
If your device's performance is degrading due to memory-demanding apps or games, upgrading the memory can improve it, and knowing the RAM specs can help determine the right size, speed, and brand to purchase a compatible upgrade kit.
In addition, when adjusting the memory settings in the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) or Basic Input/Output System (BIOS), memory information can also help you determine whether the configuration has been applied correctly.
Whatever the reason might be, Windows 10 provides the necessary information using Command Prompt without the need to open the device or install third-party tools.
In this how-to guide, I will explain the steps to find the technical specifications of the RAM installed on your computer, including part number, manufacturer, serial number, speed, capacity, form factor, memory type, etc.
How to check RAM specification from Command Prompt
While you can use Task Manager to view the memory specs information, if you want to determine more specific details, such as manufacturer, part number, serial number, and more, then you can use several commands.
Check memory manufacturer
To determine the memory modules brand installed on the computer, use these steps:
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to check the memory manufacturer name and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, manufacturer
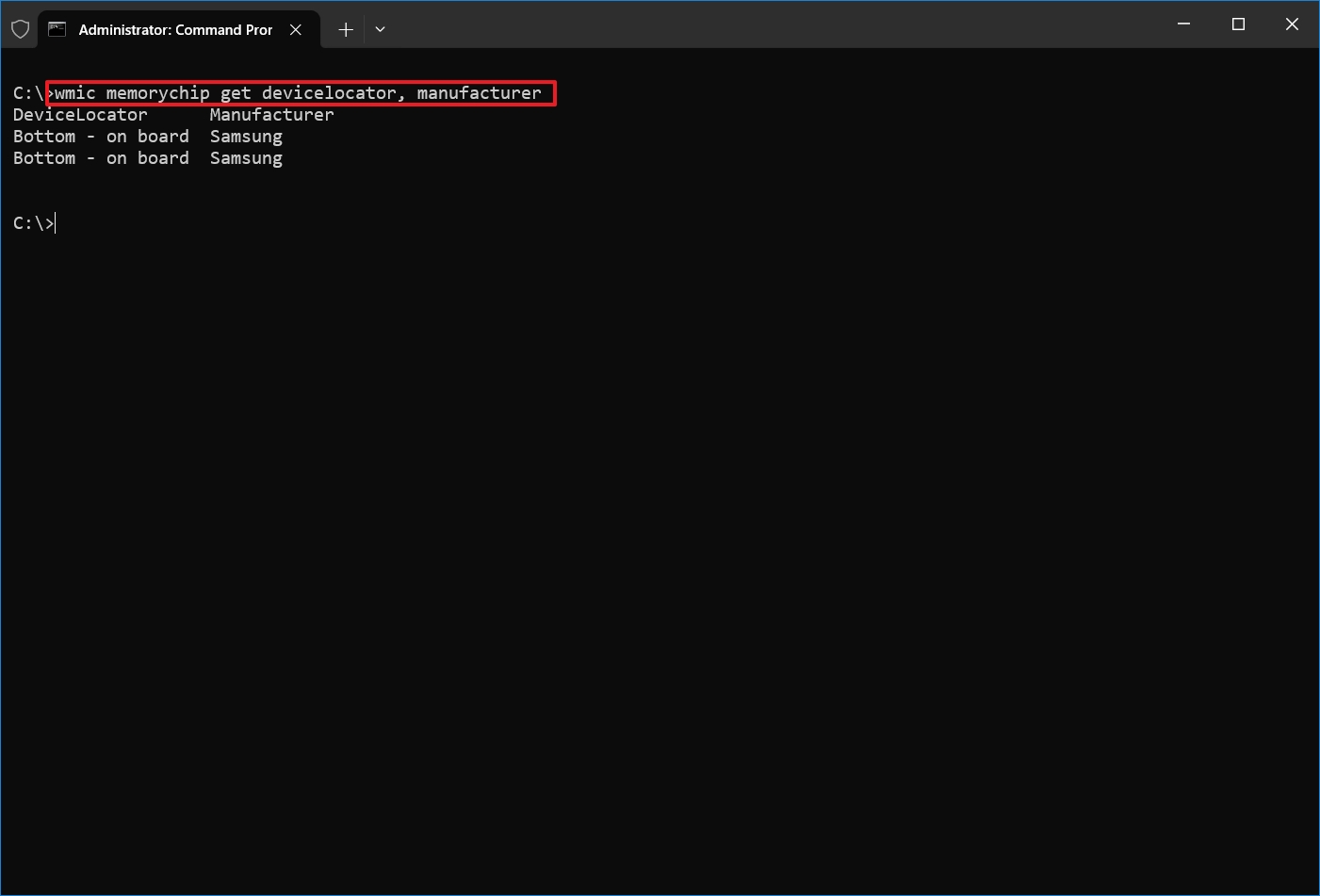
- Confirm the memory brand under the "Manufacturer" column.
Check memory part number
To find out the part number of each memory module on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to determine the part number of the memory module and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, partnumber
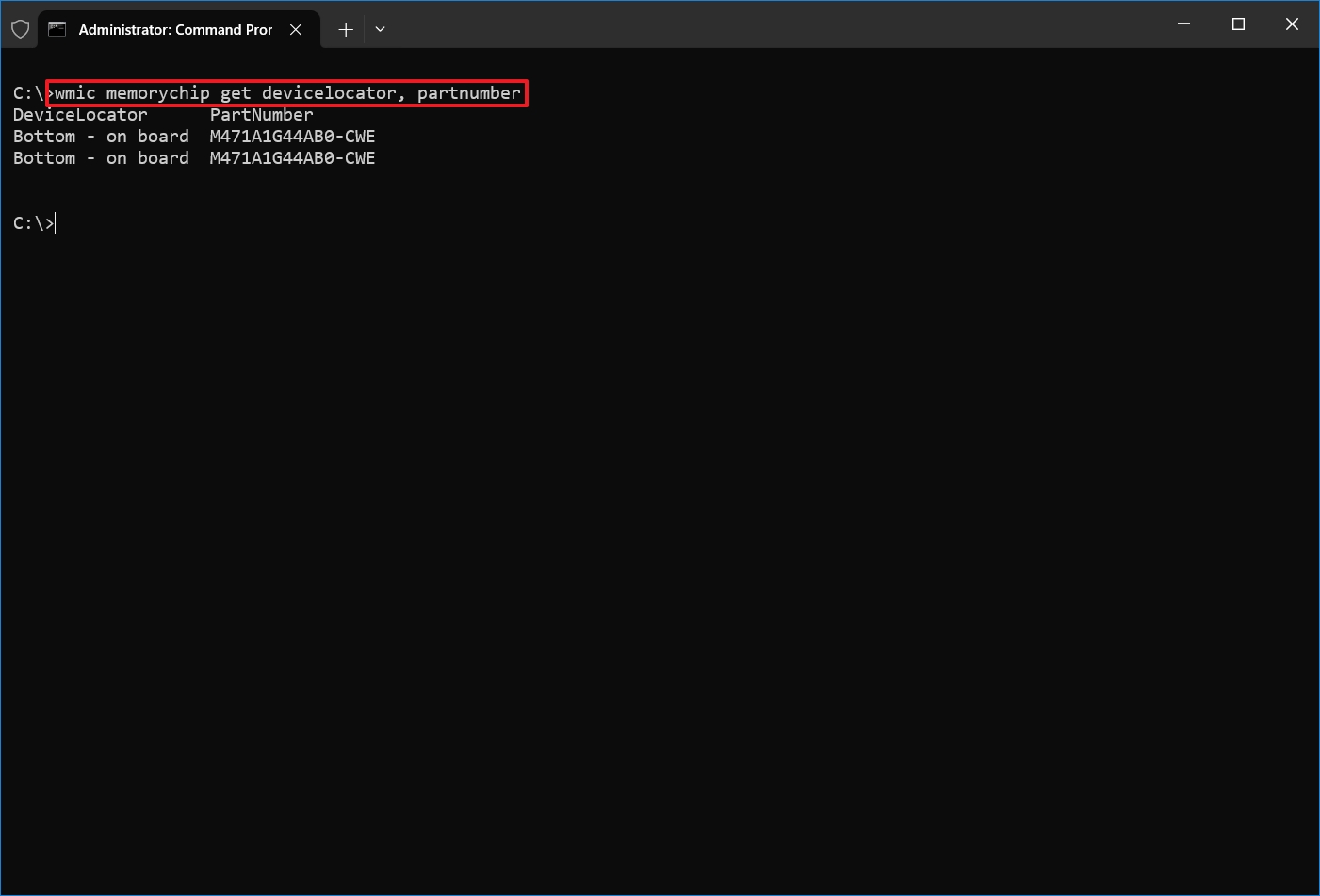
- Confirm the product number under the "PartNumber" column.
Check memory serial number
To find out the RAM serial number on your computer, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to view the serial number for each memory stick and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, serialnumber
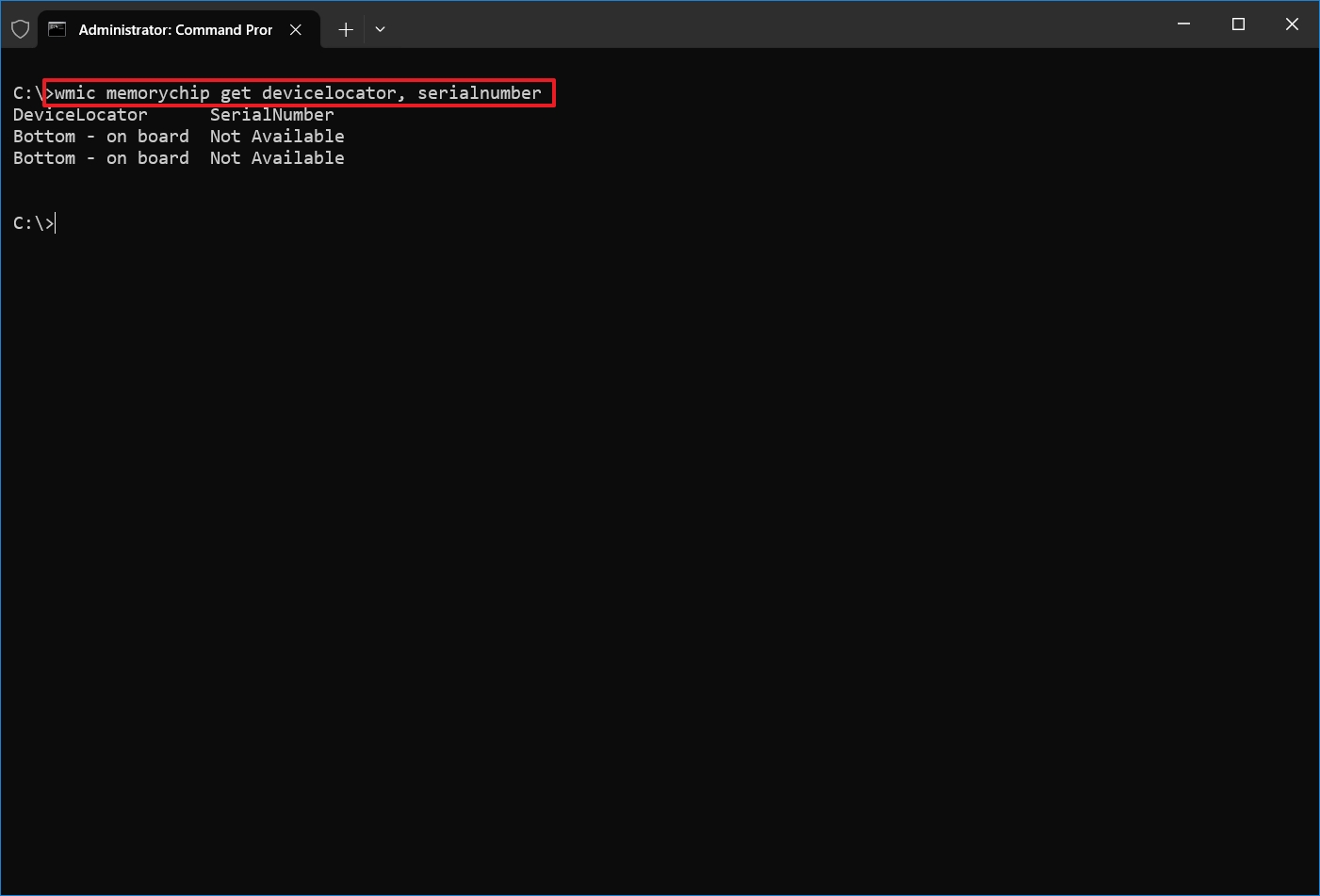
- Quick tip: In the command, you can also replace "devicelocator" with "banklabel" to list the serial number showing the bank's physical label where the memory is located on the motherboard. For example, wmic memorychip get banklabel, serialnumber.
- Confirm the product identifier under the "SerialNumber" column.
Check memory capacity
Using Command Prompt, you can determine the total capacity per module and the entire system.
Determine capacity per memory module
To check each memory module capacity on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to determine the memory capacity and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, capacity
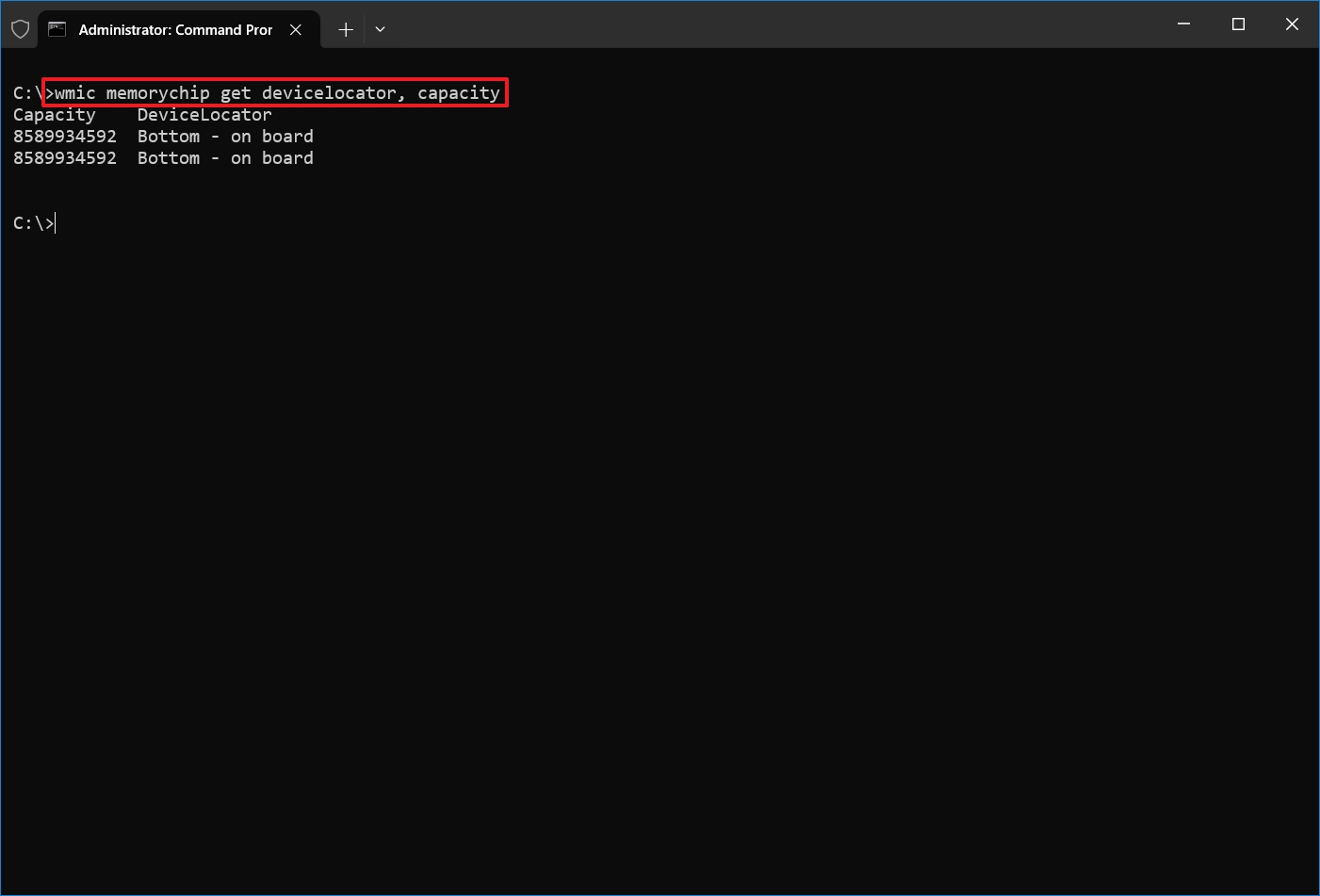
- Confirm the size of each memory module under the "Capacity" column.
- Quick tip: The capacity information is displayed in bytes, but you can divide the number by 1,073,741,824 (1 gigabyte in bytes) to convert the data into gigabytes.
Determine total system memory capacity
To find out the total amount of memory installed on the computer, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to determine the total physical memory and press Enter: systeminfo | findstr /C:"Total Physical Memory"
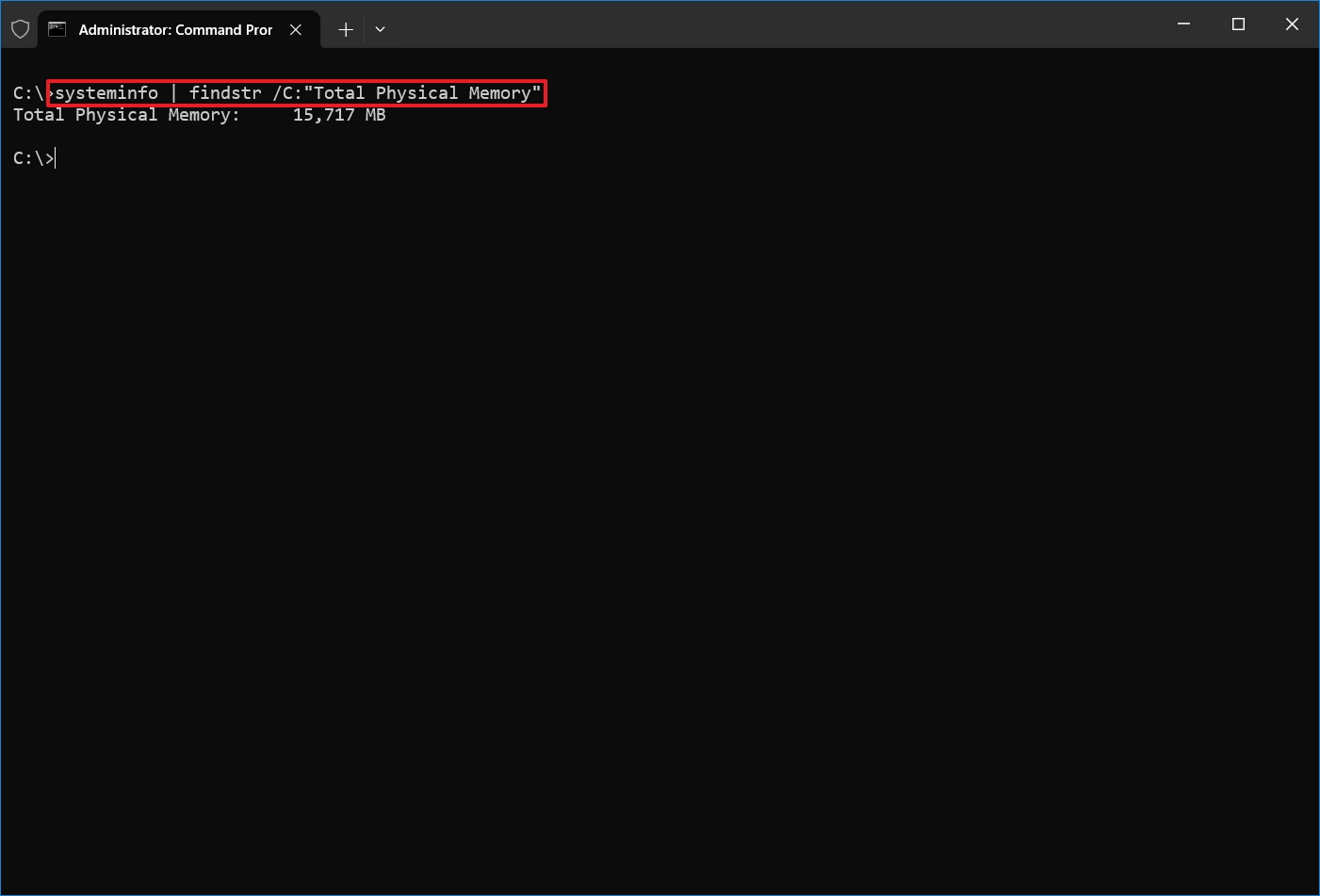
- Confirm the total amount of physical memory (in megabytes) installed on the device.
Check memory module speed
To confirm the operating module speed, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to determine the memory speed and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, speed
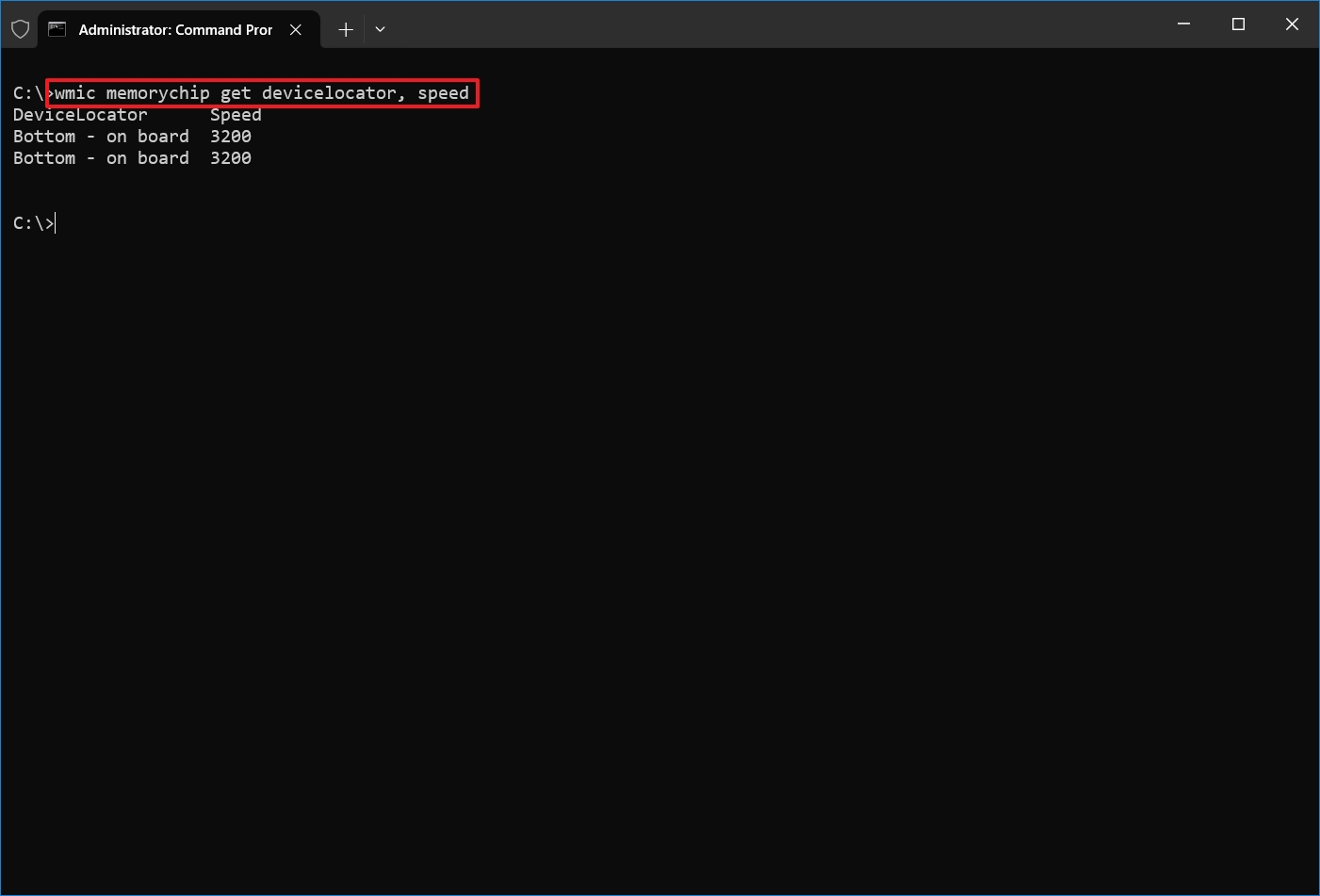
- Confirm the speed of the memory modules (in MHz) under the "Speed" column
Check memory type
To check the system memory type on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to determine the memory type and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, memorytype
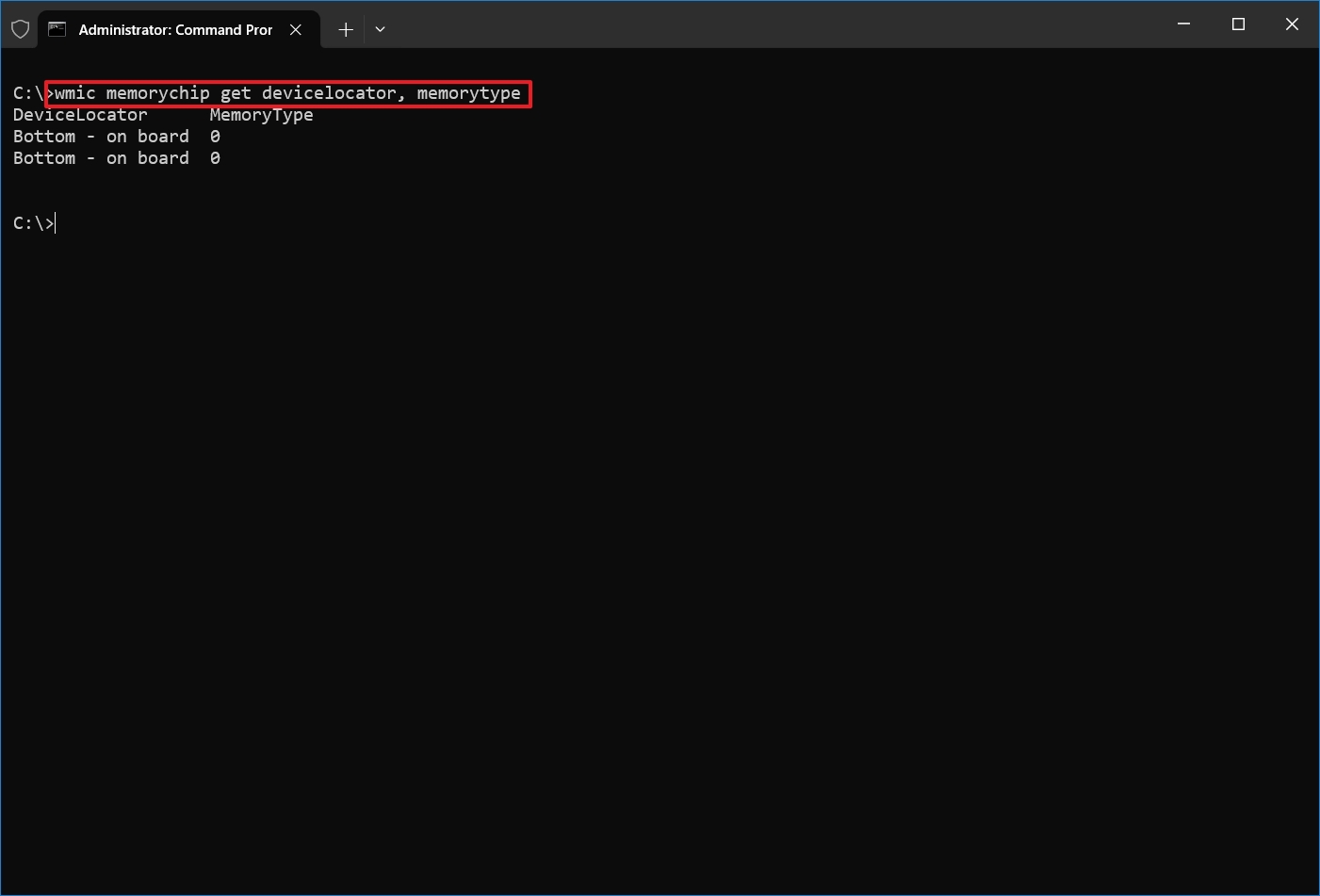
- Under the "MemoryType" column, confirm the number that identifies the type of memory. (See list below.)
Supported types
Memory types the command can identify:
- 0: Unknown.
- 1: Other.
- 2: DRAM.
- 3: Synchronous DRAM.
- 4: Cache DRAM.
- 5: EDO.
- 6: EDRAM.
- 7: VRAM.
- 8: SRAM.
- 9: RAM.
- 10: ROM.
- 11: Flash.
- 12: EEPROM.
- 13: FEPROM.
- 14: EPROM.
- 15: CDRAM.
- 16: 3DRAM.
- 17: SDRAM.
- 18: SGRAM.
- 19: RDRAM.
- 20: DDR.
- 21: DDR2.
- 22: DDR2 FB-DIMM.
- 24: DDR3.
- 25: FBD2.
- 26: DDR4.
Check memory form factor
To check whether the modules are DIMM or SODIMM, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to check the memory form factor and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, formfactor
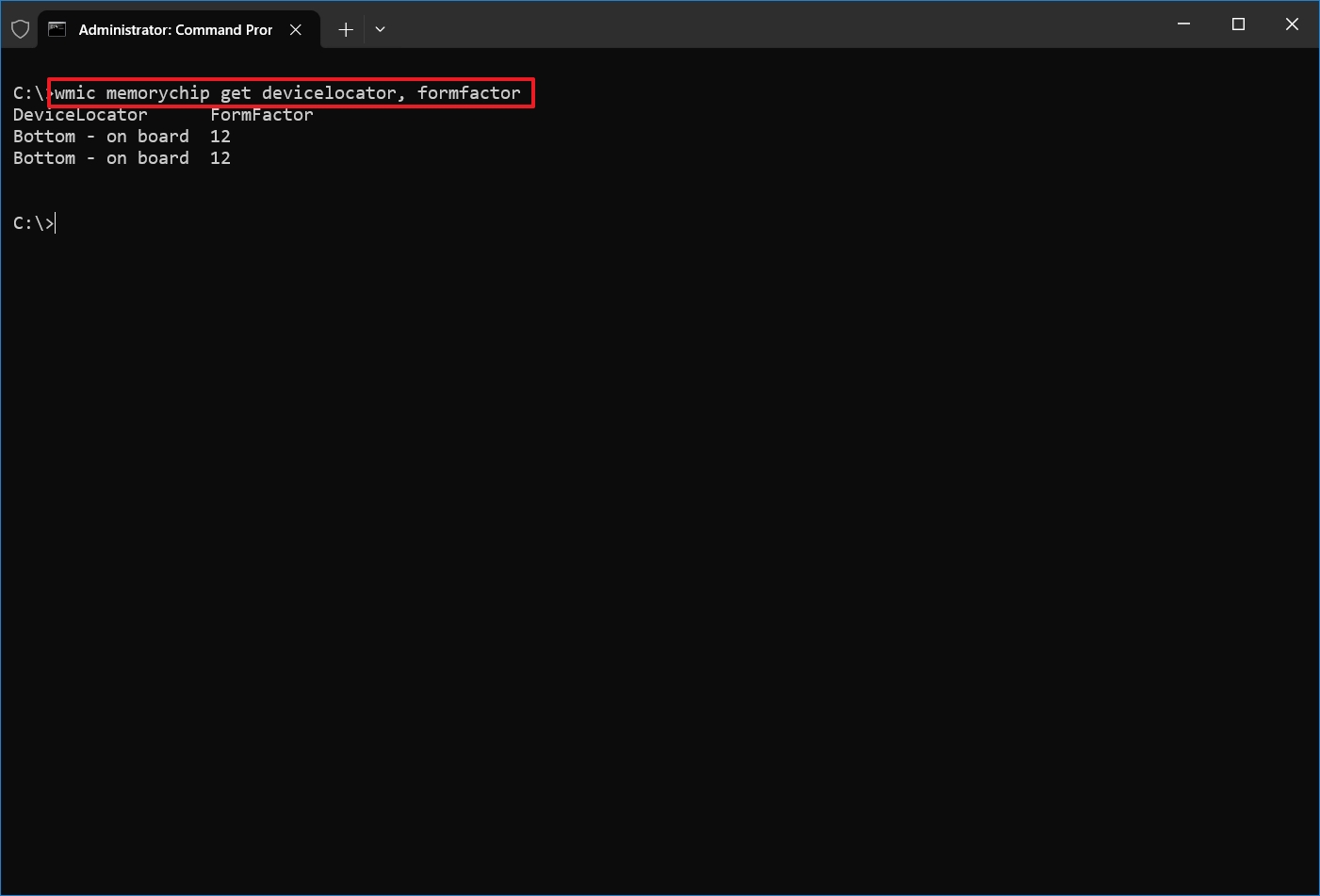
- Under the FormFactor column, confirm the form factor information.
- Quick note: If the output is 8, the device uses DIMM modules (typically available on desktops). Otherwise, if the command output the number 12, the computer uses SODIMM modules (usually available on laptops).
Supported form factors
Form factors the command can identify:
- 0: Unknown.
- 1: Other.
- 2: SIP.
- 3: DIP.
- 4: ZIP.
- 5: SOJ
- 6: Proprietary.
- 7: SIMM.
- 8: DIMM.
- 9: TSOP.
- 10: PGA.
- 11: RIMM.
- 12: SODIMM.
- 13: SRIMM.
- 14: SMD.
- 15: SSMP.
- 16: QFP.
- 17: TQFP.
- 18: SOIC.
- 19: LCC.
- 20: PLCC.
- 21: BGA.
- 22: FPBGA.
- 23: LGA.
- 24: FB-DIMM.
Check all memory details
The above commands help you determine the most useful information about the RAM installed on your computer. However, there is another command you can use to query all the available details at the same time.
To view all the memory details on Windows 10, then use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Type Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to list every memory detail possible and press Enter: wmic memorychip list full
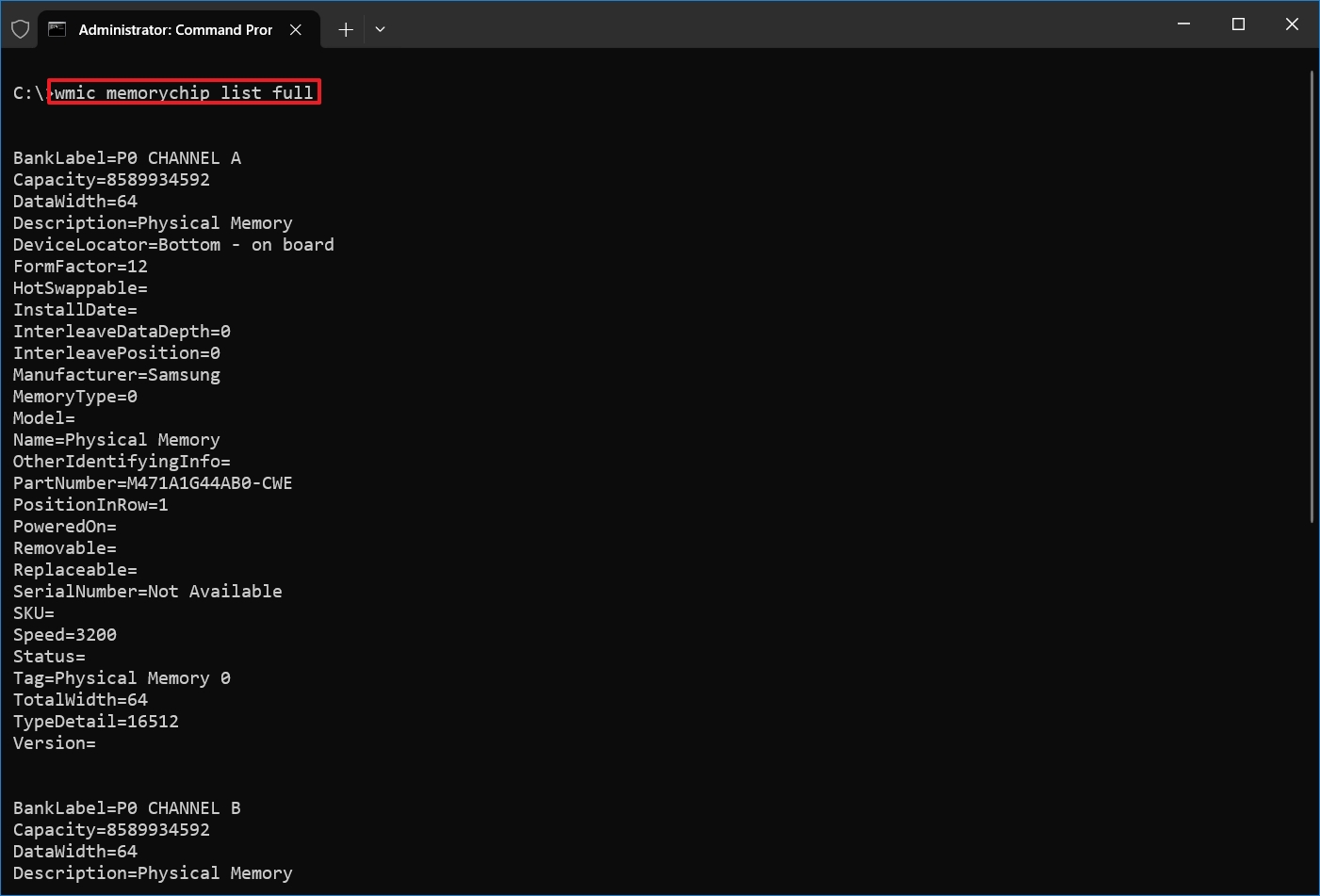
- Confirm the available information for each memory module installed on the device.
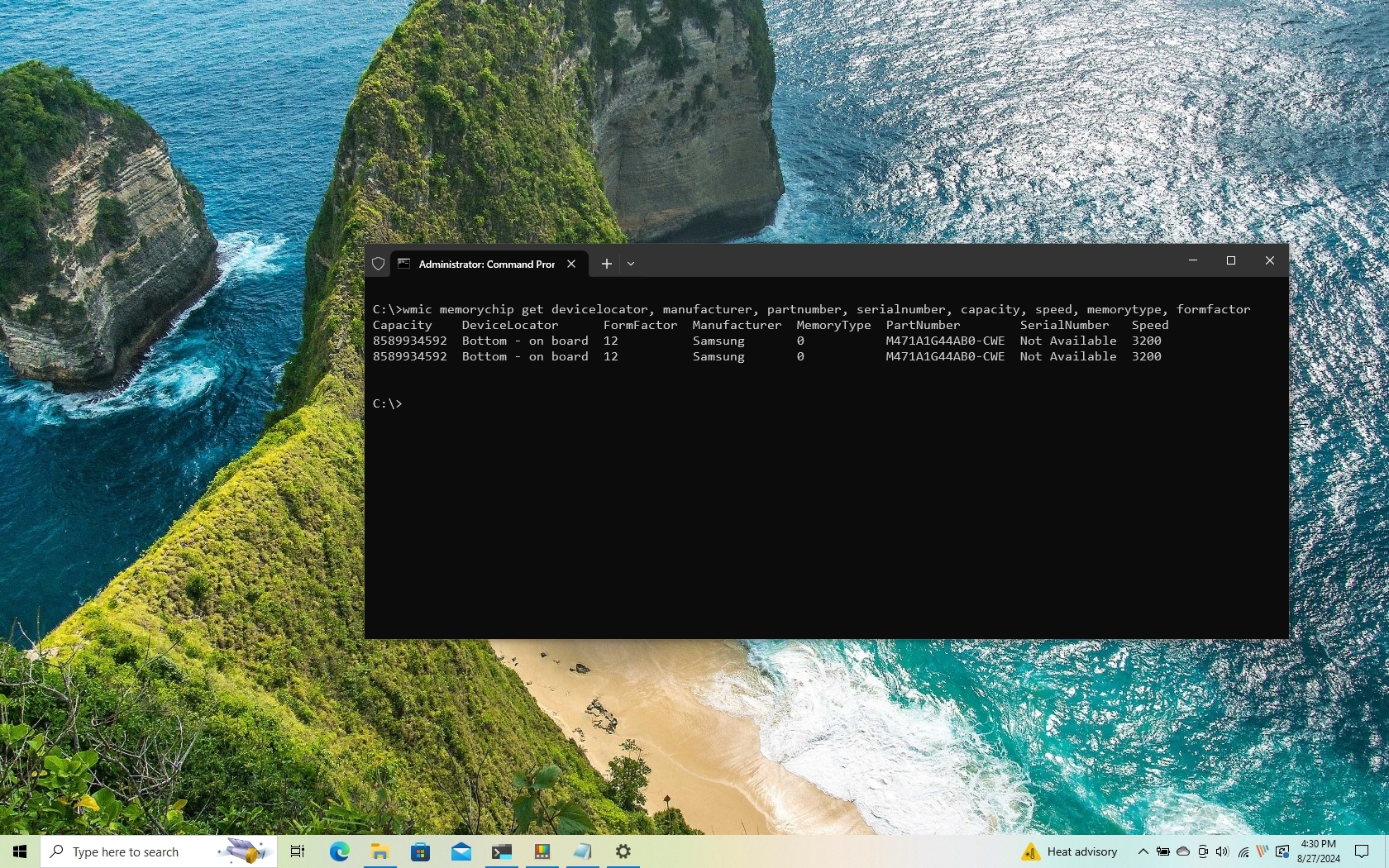
- (Optional) Type the following command to view only the specific details and press Enter: wmic memorychip get devicelocator, manufacturer, partnumber, serialnumber, capacity, speed, memorytype, formfactor
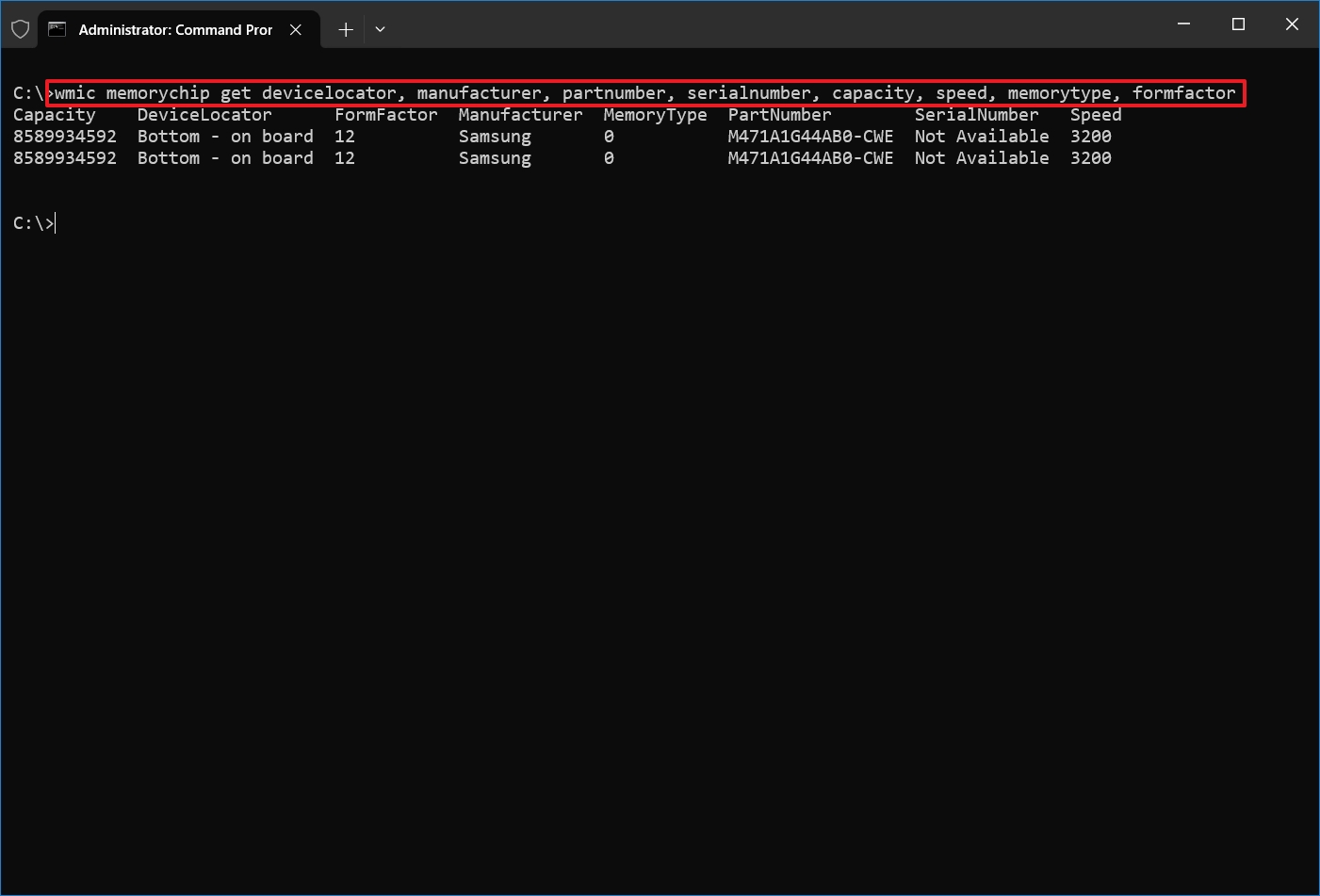
- Confirm the memory information.
Once you complete the steps, you will have many details about the memory modules installed on your Windows 10 device.
While you can use Command Prompt to query many details about your computer's RAM specifications, some information may not be available depending on the system's hardware.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.