How to determine Wi-Fi and Ethernet connection speed on Windows 10
Are you wondering about the connection speed of the network adapter? Here are four ways to find out on Windows 10.
On Windows 10, the network adapter is an essential component that offers the means to connect to the network and internet using a wired or wireless connection, and understanding the current link speed can come in handy in many scenarios.
For example, checking the link speed is helpful to find out whether the adapter is operating according to its technical specifications and can help you diagnose performance problems. If you're upgrading your internet service to a faster tier, knowing the maximum speed of the Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter will help to confirm whether you'll be able to take advantage of all the bandwidth. If you plan to upgrade the network to 10Gbps, you can quickly determine if you need to change the card. Or if you use a USB network adapter that doesn't include any information, checking the speed connection will reveal if you're using a 100Mbps or 1Gbps chipset.
Whatever network card you use, Windows 10 provides different features to confirm the link speed of a connection using Settings, Control Panel, and command lines with PowerShell and Command Prompt.
This guide will walk you through several ways to determine the speed of the adapter connected to the network, whether you're using a wired or wireless connection.
How to check network adapter speed from Settings
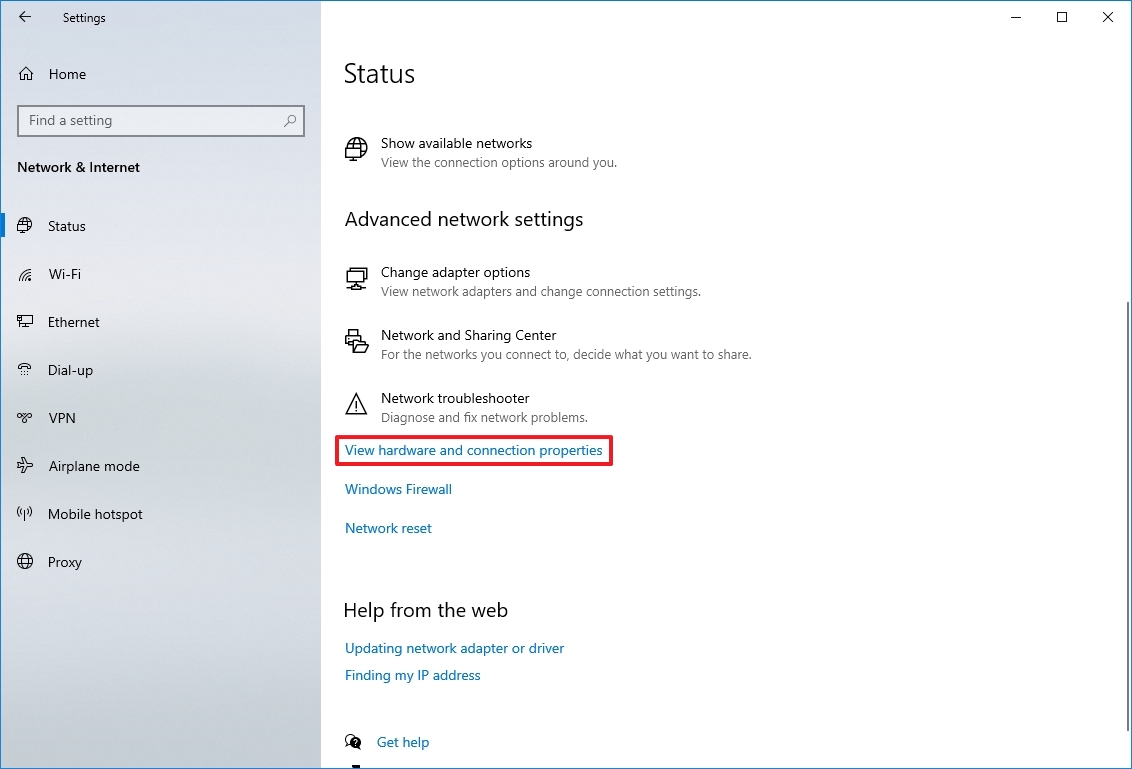
To view the connection speed for a Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Network & Internet.
- Click on Status.
- Under the "Change your network settings" section, click the "View your network properties" option.
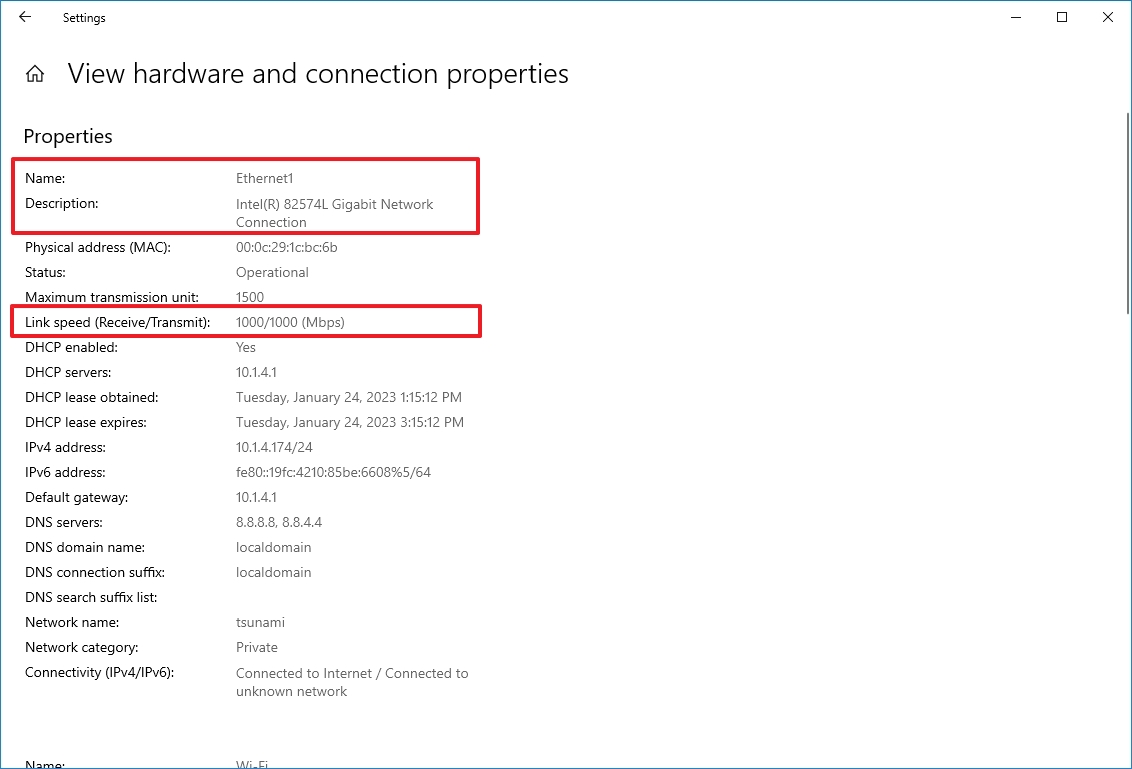
- Under the "Properties" section, find the network adapter (Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Determine the connection speed in the "Link speed (Receive/Transmit)" field.
Once you complete the steps, the Settings app will reveal the speed the adapter uses to connect to the network.
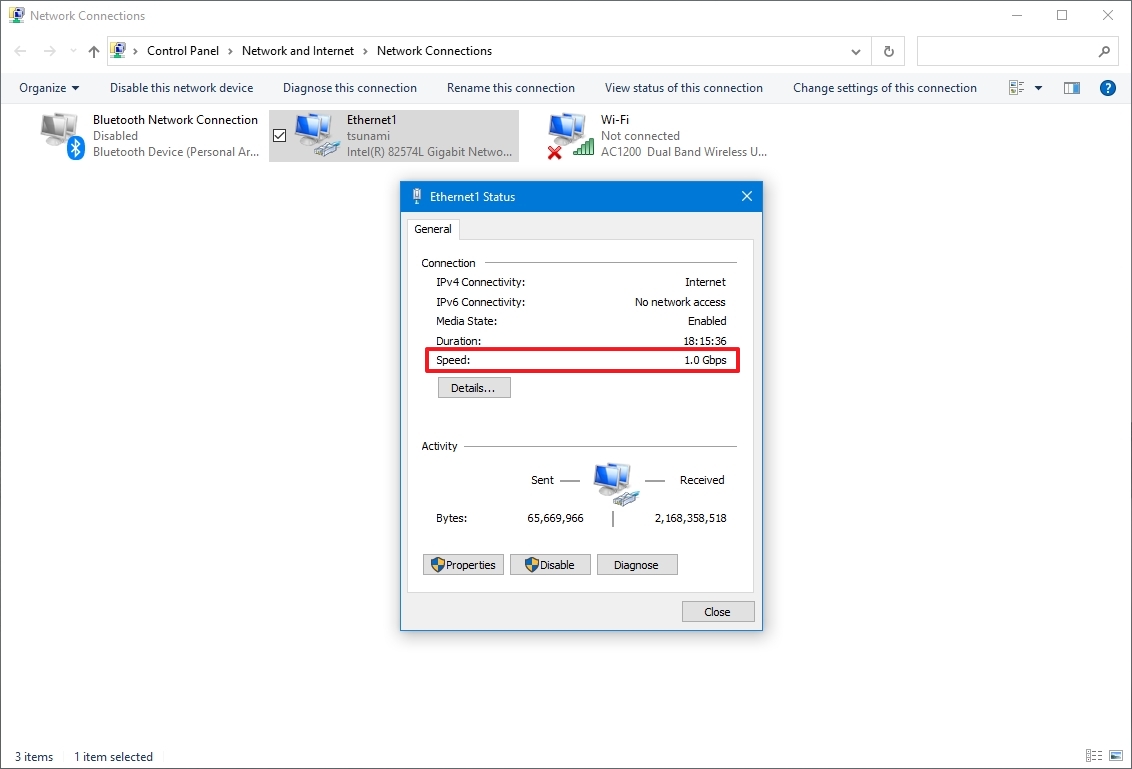
How to check network adapter speed from Control Panel
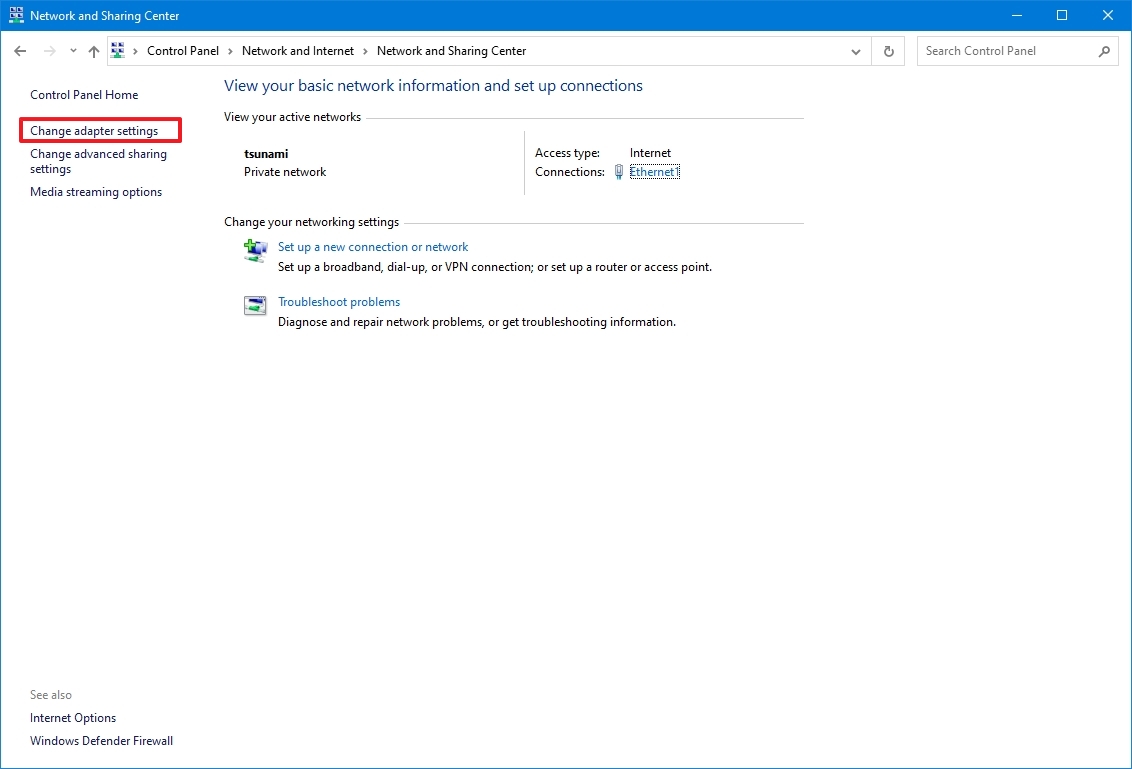
To determine the network adapter speed with the Control Panel settings, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Control Panel.
- Click on Network and Internet.
- Click on Network and Sharing Center.
- Click the "Change adapter settings" in the left pane.
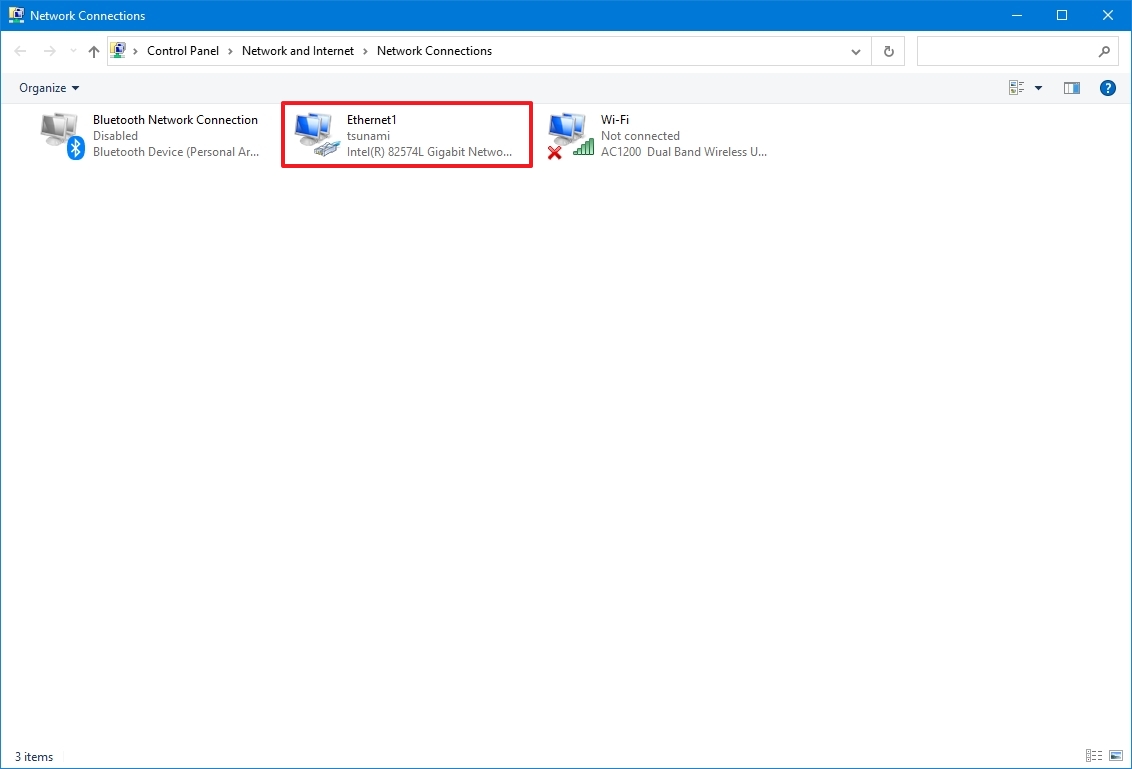
- Double-click the network adapter (Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
- Check the connection speed in the Speed field.
- Quick note: If you're looking at a Wi-Fi adapter, you can also confirm the signal quality.
After completing the steps, you'll better understand the connection speed for the Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapter connected to the network.
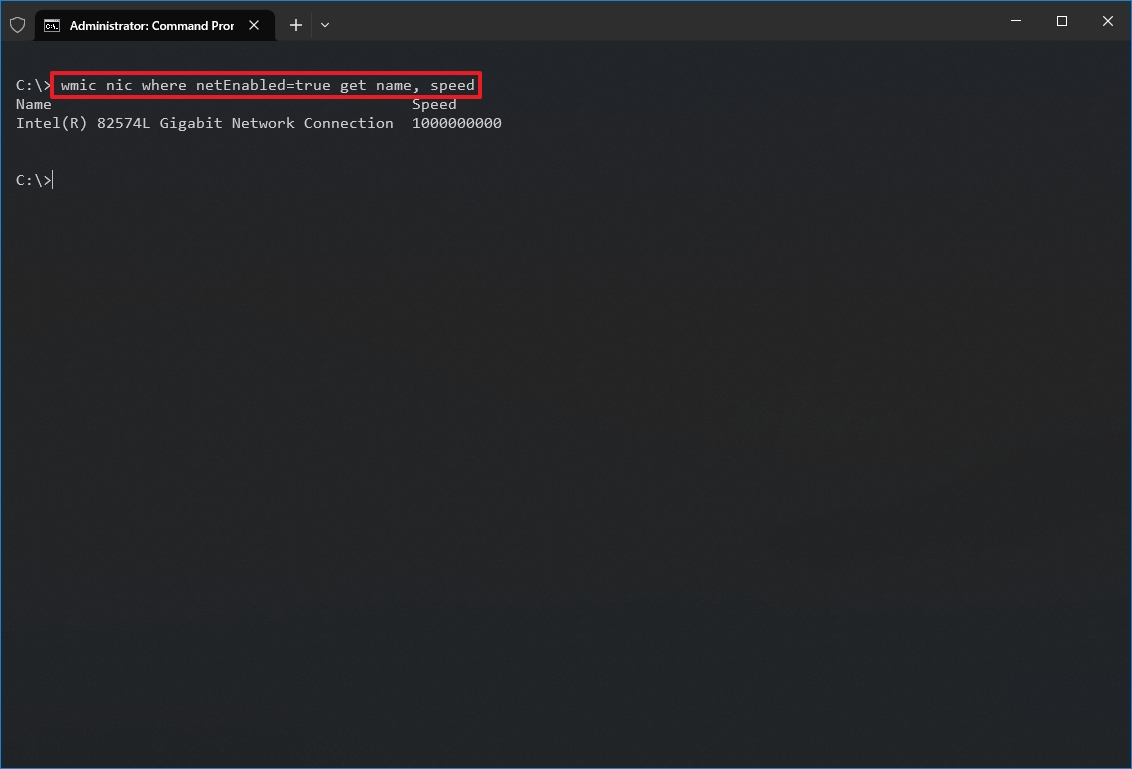
How to check network adapter speed from Command Prompt
To find out the speed for the wireless or wired adapter with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt and click the top result to open the console.
- Type the following command to determine the connection speed for all the Ethernet and Wi-Fi adapters and press Enter: wmic nic where netEnabled=true get name, speed
- Confirm the network adapter speed.
Once you complete the steps, you'll be able to determine the speed (in bits) the card uses to connect to the network.
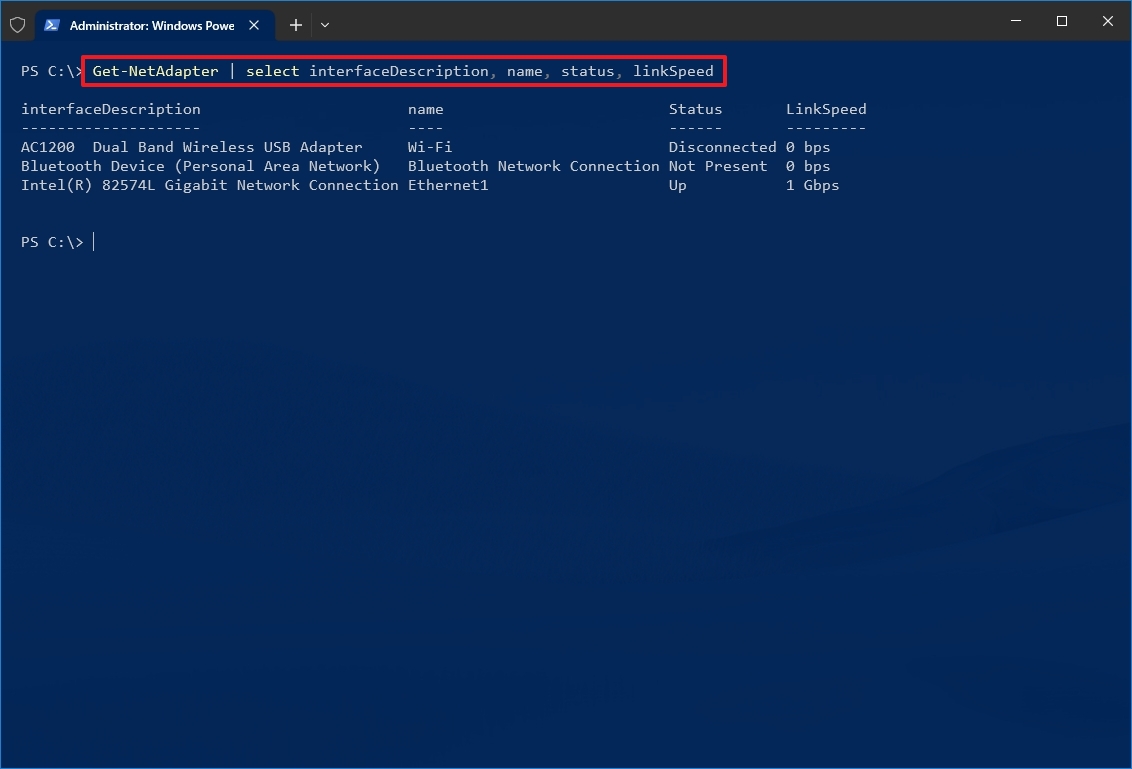
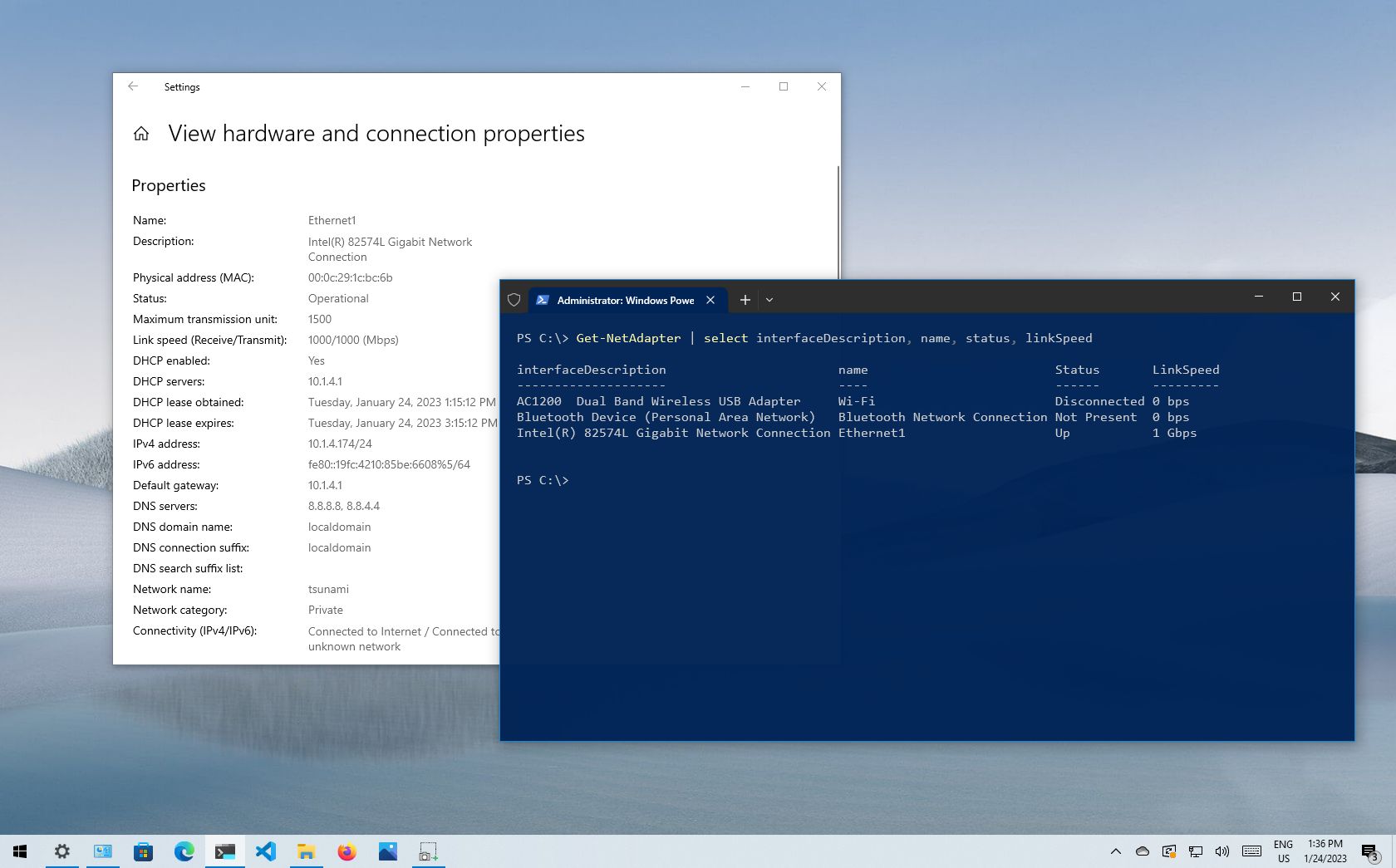
How to check network adapter speed from PowerShell
To check the Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection speed on Windows 10 with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell and click the top result to open the console.
- Type the following command to determine the connection speed for all the Ethernet and Wi-Fi adapters and press Enter: Get-NetAdapter | select interfaceDescription, name, status, linkSpeed
- Check the Wi-Fi or Ethernet network card connection speed.
After you complete the steps, the PowerShell output will display the connection speeds in a user-friendly format (for example, 780 Mbps and 1 Gbps).
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 or Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know

Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 22 years of combined experience in IT and technical writing. He holds various professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA and has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.