How to use DiskPart to clean and format drive not working on Windows 10
If a drive is causing problems on Windows 10, it could be a logical issue that can be fixed with a few commands.
TL;DR: How to format a drive on Windows 10
- Open Start, launch Command Prompt as administrator, and enter diskpart.
- Type list disk and hit Enter, then select disk DISK-NUMBER (replace with the number of your chosen disk), and finally clean.
If you’re dealing with a USB flash drive or external hard drive that’s not working correctly on Windows 10 (perhaps it's inaccessible, corrupted, or not formatting properly), you can use the DiskPart command-line tool to wipe and restore the storage to a working condition.
DiskPart is a powerful built-in utility that allows you to manage storage at a low level, including cleaning and reformatting drives, creating partitions, and converting partition styles. It often works better when tools like "Disk Management" or the "Format" option in File Explorer fall short, especially if a drive has logical errors or won’t initialize.
Windows 10 supports two partition styles: Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT).
- MBR is the traditional format, compatible with legacy BIOS systems.
- GPT is the modern standard, used in systems with UEFI firmware. It’s more robust and supports drives larger than 2TB, as well as more than four primary partitions.
While GPT is generally preferred, especially for newer devices and internal drives, MBR remains useful for external drives and compatibility with legacy systems. This guide covers how to use DiskPart to clean and format a drive using either of the two partition styles.
In this how-to guide, I'll outline the steps to use DiskPart to clean and format a hard drive, fixing data corruption and other issues on Windows 10.
Warning: These steps will erase everything on the selected drive, and you cannot undo the changes. If the drive is still accessible, it's recommended to back up the data before proceeding. If multiple drives are connected to your device, disconnect them to avoid selecting the wrong one.
These instructions has been updated to ensure accuracy and reflect changes to the process in the operating system.
How to fix drive (MBR) problems with DiskPart on Windows 10
To fix hard drive issues on Windows 10 with DiskPart, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
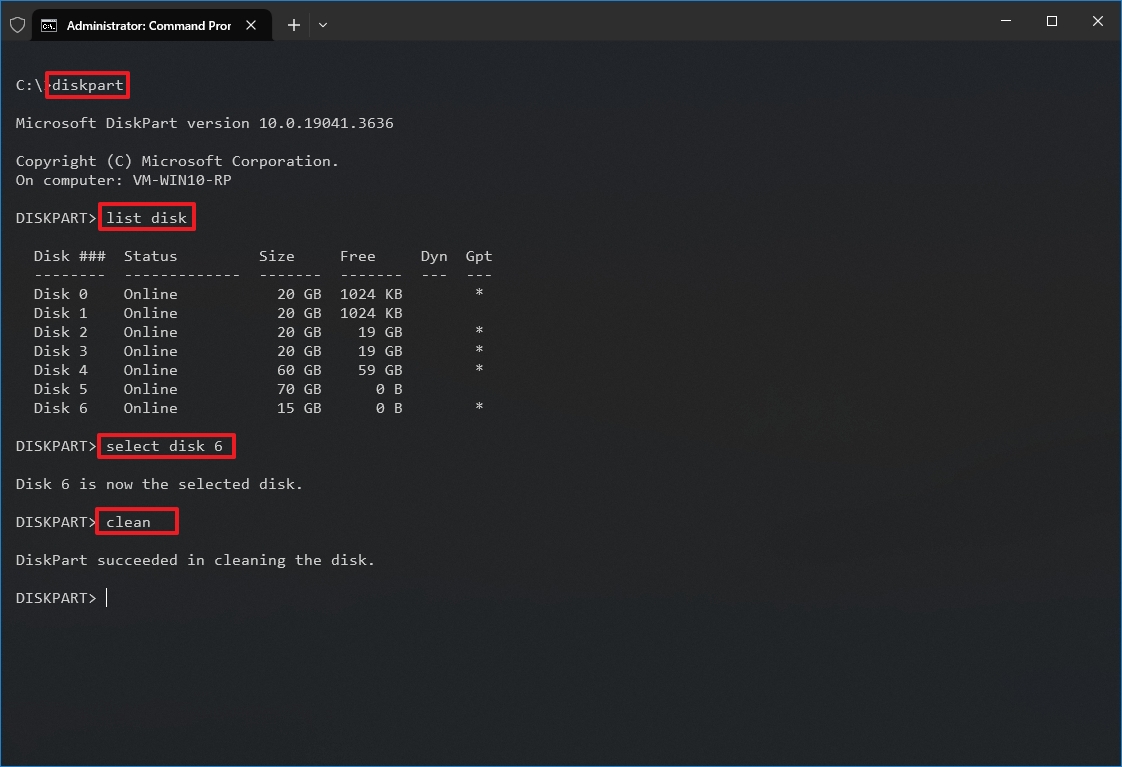
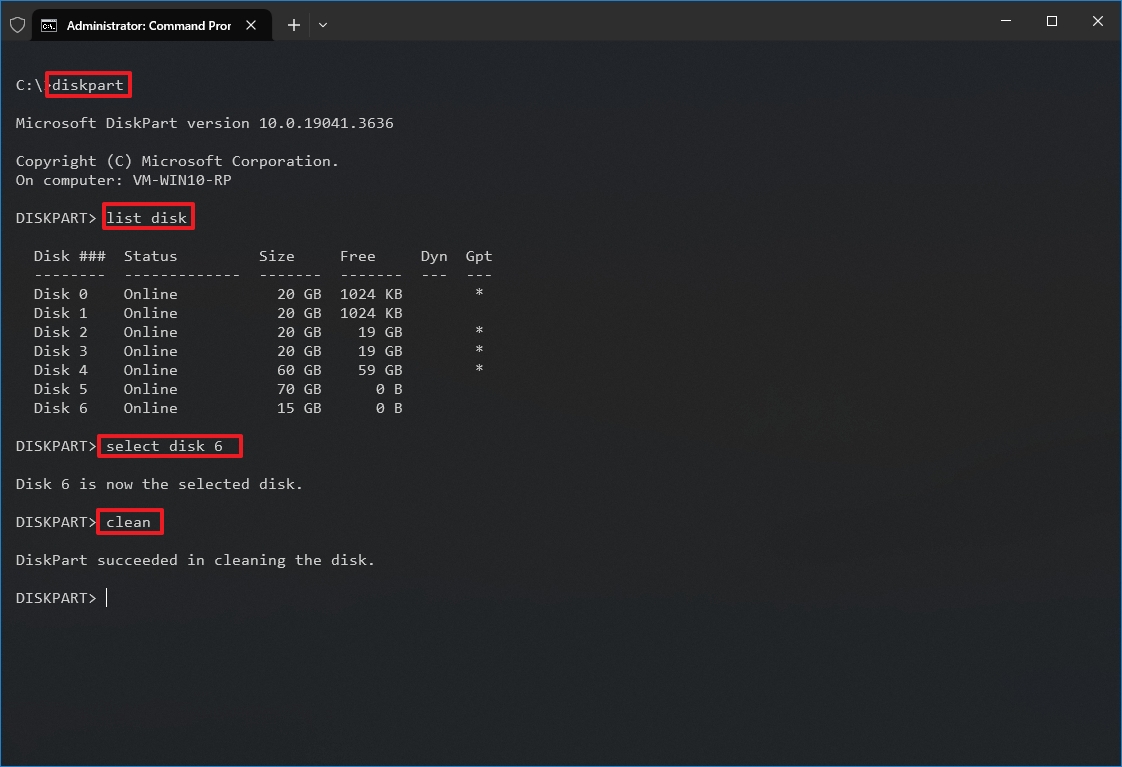
- Type the following command to launch DiskPart and press Enter: diskpart
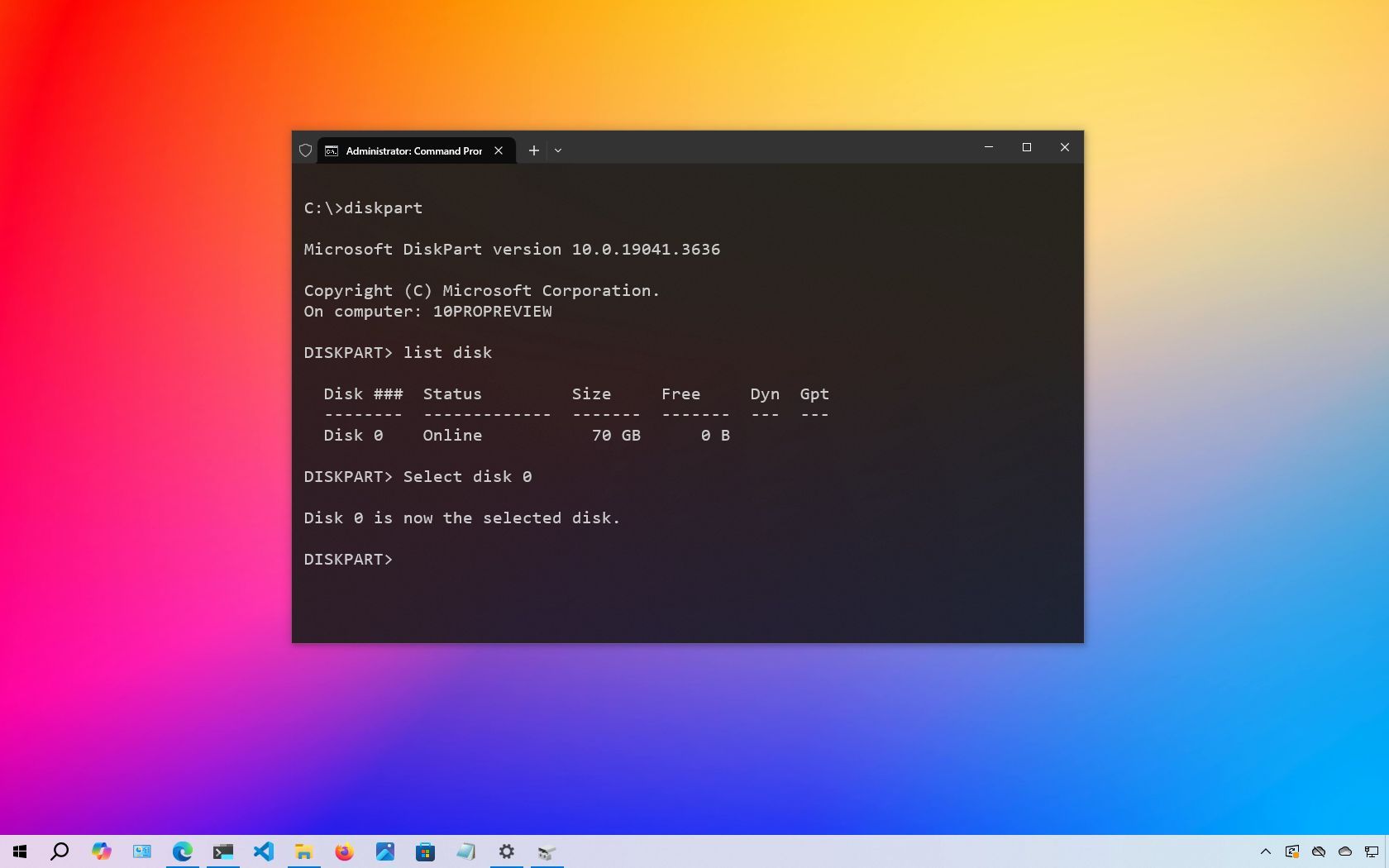
- Type the following command to list all the active drives and press Enter: list disk
- Type the following command to select the drive to clean and press Enter: select disk DISK-NUMBER
In the command, replace "DISK-NUMBER" with the drive number you want to repair as it appears in the "Disk" column. You could erase the wrong drive if you do not perform this step correctly. Proceed with caution.
- Type the following command to wipe out the drive and press Enter: clean
- Type the following command to confirm the drive is still selected, and press Enter: list disk
- Quick note: The output should include an asterisk (*) next to the selected drive. If the correct storage is not specified, perform step 5 again.
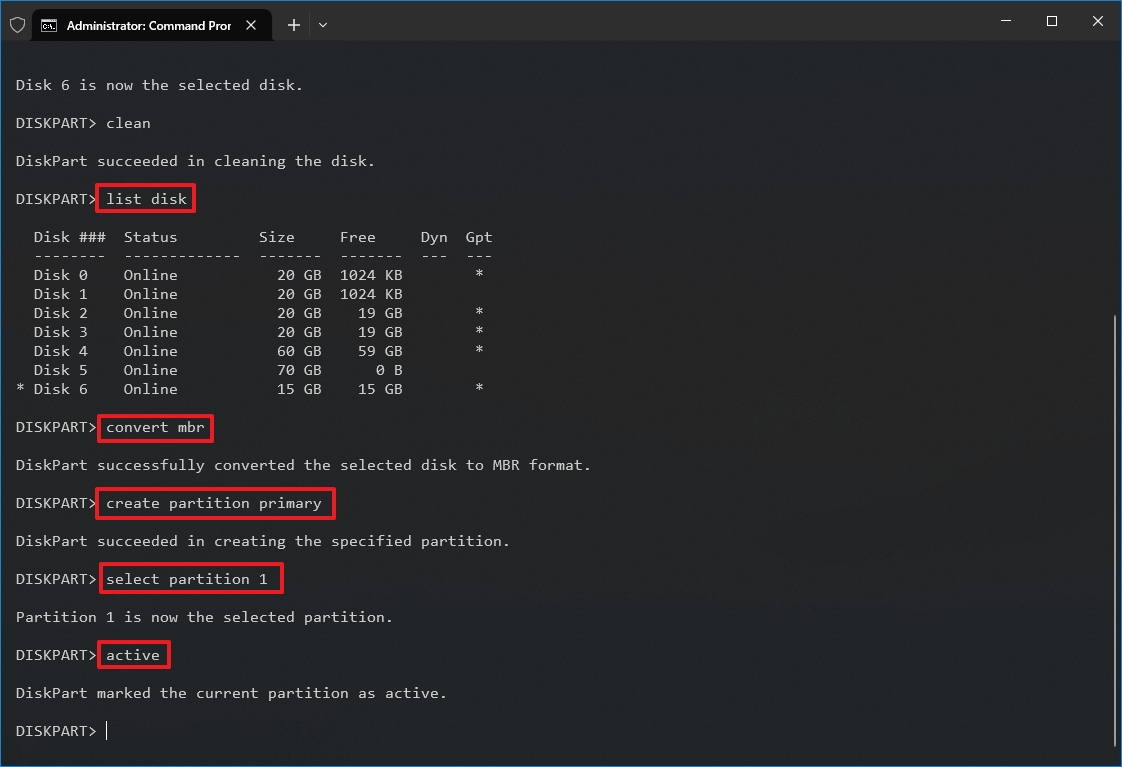
- (Optional) Type the following command to convert the drive to an MBR partition style and press Enter: convert mbr
- Quick note: This step is only required if the storage is configured as GPT, and you must use MBR partition style. If the partition is already MBR, you don't have to run the command, but running it won't affect the process. You should be able to determine the partition type with the "list disk" command. If the drive doesn't have a GPT mark (*), it's an MBR partition.
- Type the following command to create a new partition and press Enter: create partition primary
- Type the following command to select the new primary partition and press Enter: select partition 1
- Type the following command to make the partition active and press Enter: active
- Quick tip: You only have to set a partition as active when using MBR. You can determine if the drive uses an MBR or GPT partition style with the "list disk" command. If the partition has a mark in the GPT column, it's not an MBR partition. If you have to set up a GPT partition style, use the other steps (see below).
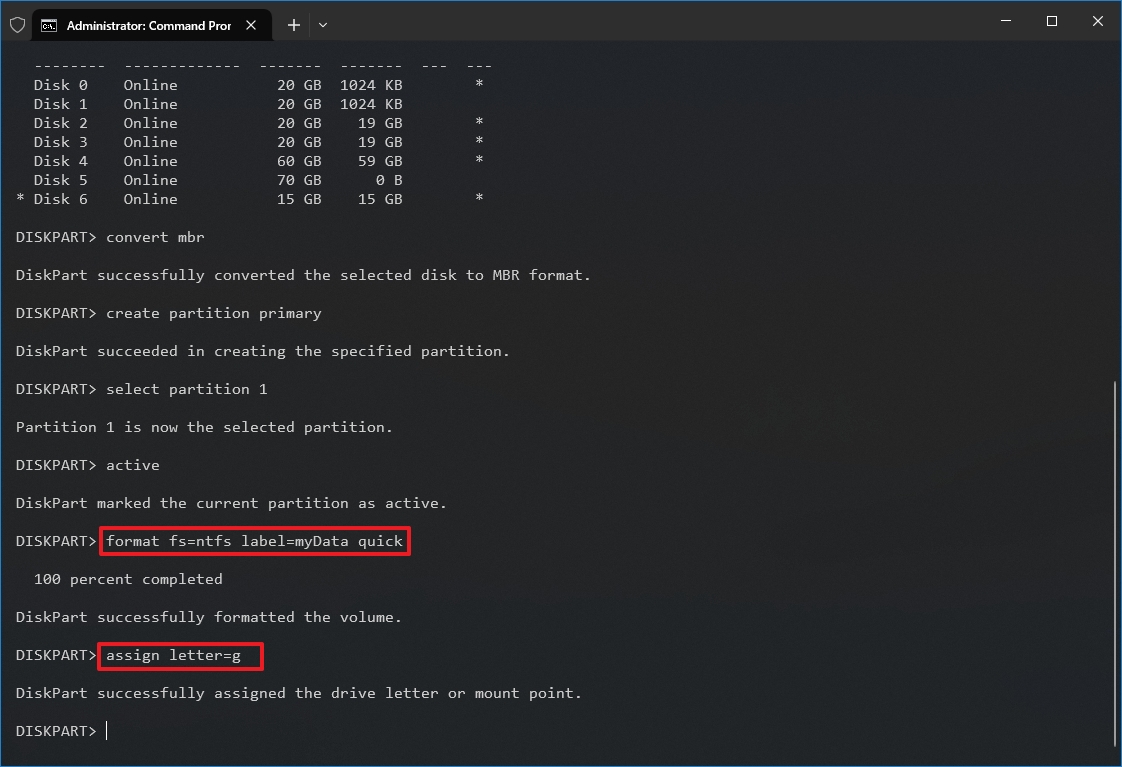
- Type the following command to format the partition using the NTFS file system, set a drive label, and press Enter: format fs=FILE-SYSTEM label=DRIVE-LABEL quick
In the command, replace "FILE-SYSTEM" with the name of the file system to use, such as "NTFS" or "FAT32," and replace "DRIVE-LABEL" with the name of the drive as you want it to appear on File Explorer. The "quick" option isn't required, but it will perform a format faster. However, it's best to skip the option if you are unsure about the drive's condition. The format could take a long time, depending on the size of the hard drive. This example formats the drive using the NTFS file system and names the partition "myData": format fs=ntfs label=myData quick
- Type the following command to assign a letter and make the drive available on File Explorer, and press Enter: assign letter=DRIVE-LETTER
In the command, change "DRIVE-LETTER" for the letter to use on the drive, which is not assigned to another device. This example assigns the "G" letter: assign letter=g
- Type the following command to terminate DiskPart and press Enter: exit
- Type the following command to close Command Prompt and press Enter: exit
Once you complete the steps, if the drive does not have physical issues, it should be accessible again through File Explorer.
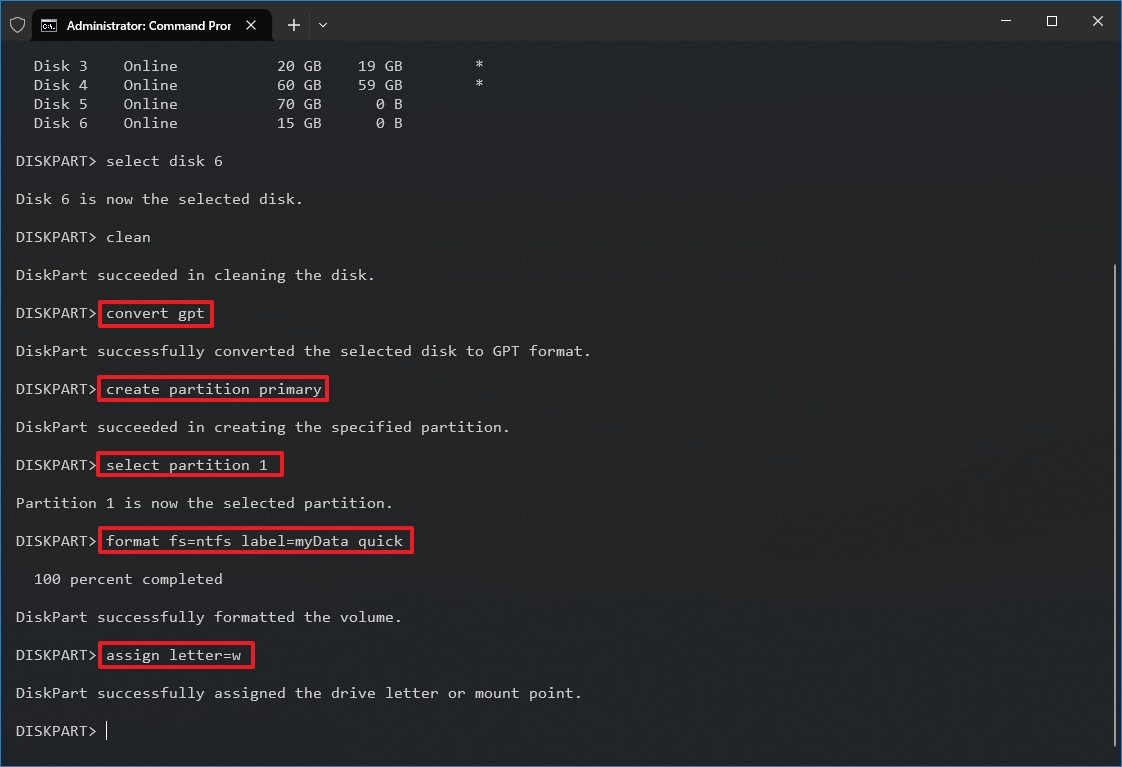
How to fix drive (GPT) problems with DiskPart on Windows 10
To use DiskPart to fix drive issues with GPT partition style, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to run DiskPart and press Enter: diskpart
- Type the following command to list all the active drives and press Enter: list disk
- Type the following command to select the drive you want to clean and press Enter: select disk DISK-NUMBER
In the command, replace "DISK-NUMBER" with the drive number to repair, as it appears in the "Disk" column.
- Type the following command to wipe out the drive and press Enter: clean
- Type the following command to confirm the drive is still selected and press Enter: list disk
- Quick note: The output should include an asterisk (*) next to the selected drive. If the correct storage is not specified, repeat step 5 one more time.
- Type the following command to convert the partition style to GPT and press Enter: convert gpt
- Type the following command to create a new partition and press Enter: create partition primary
- Type the following command to select the new primary partition and press Enter: select partition 1
- Type the following command to format the partition with the NTFS file system, set a drive label, and press Enter: format fs=FILE-SYSTEM label=DRIVE-LABEL quick
In the command, replace "FILE-SYSTEM" with the name of the file system you want to use, such as "NTFS" or "FAT32," and replace "DRIVE-LABEL" with the name of the drive as you want it to appear on File Explorer. The quick option is optional for faster formatting. However, if you're unsure about the drive's condition, it's best to skip this option. The format could take a long time, depending on the size of the hard drive. This example formats the drive using the NTFS file system and names the partition "myData": format fs=ntfs label=myData quick
- Type the following command to assign a letter and make the drive available on File Explorer, and press Enter: assign letter=DRIVE-LETTER
In the command, change "DRIVE-LETTER" for the letter to use on the drive, which is not assigned to another device. This example sets the "W" letter: assign letter=w
- Type the following command to terminate DiskPart and press Enter: exit
- Type the following command to close Command Prompt and press Enter: exit
After you complete the steps, the drive should be fixed with a GPT partition style and accessible from File Explorer.
Finally, it's worth noting that support for Windows 10 will end on October 14, 2025. After this date, Microsoft will no longer release security or maintenance updates and will also cease to provide any support.
You can use these instructions to prepare your device and upgrade from Windows 10 to 11.
FAQs
How do I launch DiskPart with administrator rights?
Open the Start menu, search for "Command Prompt" and right-click the result, select Run as administrator. Type diskpart and press Enter.
How can I list and select the correct drive in DiskPart?
In DiskPart, run list disk to view all drives, note the disk number, then enter select disk DISK-NUMBER (replace DISK-NUMBER with your intended disk).
What does the clean command do in DiskPart?
Typing clean erases all partitions and data on the selected disk, returning it to an unallocated state. This will erase everything, and you cannot undo the changes.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:

Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 22 years of combined experience in IT and technical writing. He holds various professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA and has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.