Join the AI revolution with NVIDIA
NVIDIA GeForce RTX GPUs power the AI tools that are changing our lives - don’t get left behind!
AI hit the mainstream in a big way last year. All of a sudden we had ChatGPT, AI-generated art, and incredible tools for everything from photo and video editing to coding and gaming. It’s no exaggeration to say that every part of computing is being revolutionized by this technology.
What most people don’t know is that many of these extraordinary technologies are powered by the NVIDIA GeForce RTX platform of hardware and software. RTX graphics cards carry specialized hardware that’s tailor-made for AI computations, and it executes them many, many times faster than a CPU ever could. AI technology used to require sprawling computer networks and was only accessible to a select group of people. Now, with a GeForce RTX GPU, it’s running on your PC or laptop and enhancing almost everything you do.
And remember, even though these astonishing tools seem very advanced, this is just the beginning. Over the next few years we will see even more big leaps forward, likely in ways we can’t even imagine today.
Tools like ChatGPT and AI-generated art have received huge amounts of attention, but there are so many other AI features that are just as incredible that most people have never heard of. Let’s do a run down of some of the most exciting applications of AI - and NVIDIA’s role in it all - so you can see how it can massively improve things you probably haven’t even thought about. Whether you’re gaming, coding, streaming video or using creative applications, AI often fixes things you’ve accepted as clunky, annoying, or just impossible to do.
Next time you’re considering a hardware upgrade, it makes sense to think about getting an RTX GPU so you can start enjoying all the benefits now - and set yourself up to run all the increasingly AI-based software of the future.
AI for gamers
Let’s start with gaming, because these AI tools and features are extraordinary - and fun to know about even if you don’t play games. The big one is DLSS, a technology developed by NVIDIA which can multiply your performance on the fly using AI techniques. DLSS can render frames at a lower resolution then jump in and reconstruct the scene at a higher resolution. It can also generate entirely new frames, giving you a higher frame rate at high resolution. You’ll see frame rates that are up to four times faster than before.
The newest version, DLSS 3.5, has a new AI model called Ray Reconstruction that creates even higher quality ray traced images. It is shown off to great effect by Cyberpunk 2077: Phantom Liberty, generating phenomenal, photorealistic visuals.
Take a look here:
DLSS also makes it possible to get high resolution renders in real-time when working in 3D applications, transforming a clunky, frustrating process into a smooth and elegant workflow.
Another big AI tool for gaming is NVIDIA’s RTX Remix, a modding platform that enables you to create modernized versions of classic games. It captures all the game assets and uses AI to upscale them and add high quality textures and materials.
And let’s not forget NVIDIA ACE for Games, coming to future game titles, which uses AI-powered natural language processing to give intelligence and evolving personalities to non-playable characters in video games. It makes it possible to have unscripted conversations with characters, giving you a whole new level of interactivity with the game.
AI for creativity
The impact of AI, led by NVIDIA, on professional applications for 3D modeling, visual effects, and photo and video editing is so profound that it constitutes a creative revolution. It’s completely transforming the working lives of creative professionals, and it’s also doing amazing things for anyone who does any kind of photo or video editing.
So many age-old frustrating problems have been overcome by AI. For example, Topaz Labs’ Gigapixel AI image resizer lets you enlarge images by up to 600 percent and improve image quality - something that most of us thought impossible until it happened.
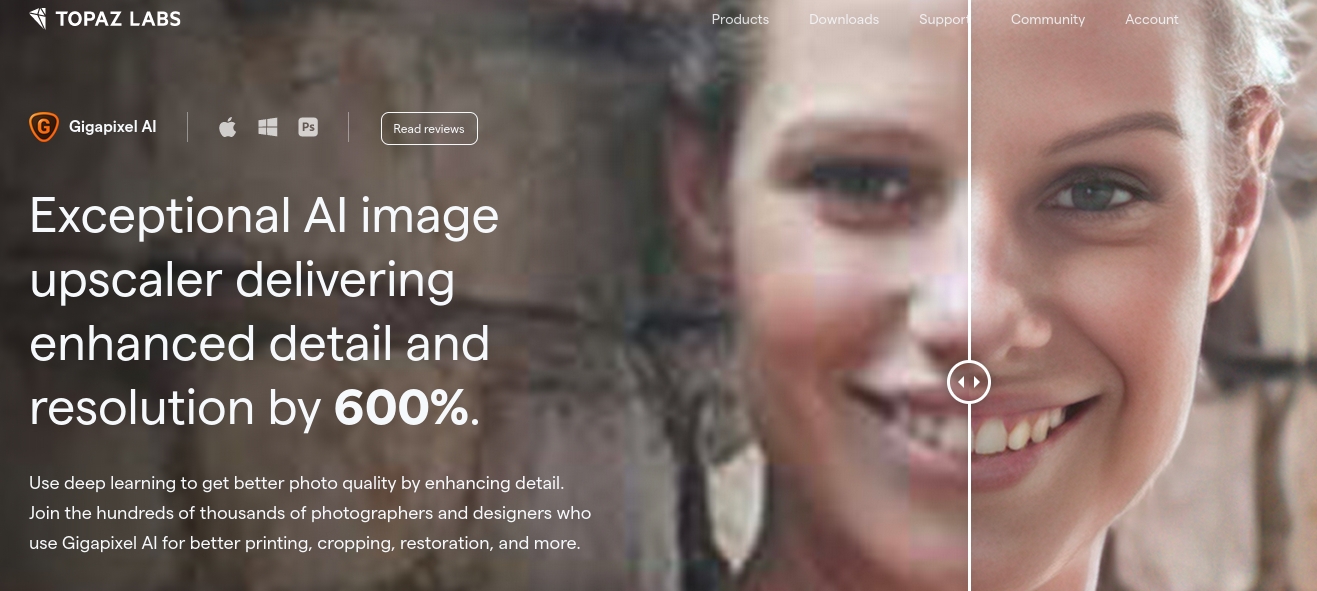
Or, similarly, if you want to change the aspect ratio of an image, you can use an AI uncropping tool that will extend your image by generating extra material that fits seamlessly and looks like a part of the original.
For creative professionals working in VFX or video games, many laborious, time-consuming tasks are made easy with AI. For example, it’s now possible to mask and track objects across multiple frames of a video with AI-powered magic masks, instead of spending hours painstakingly drawing around them in every single frame.
And speed, of course, is the biggest gamechanger. Blender runs 5.4 times faster with an RTX card, and image generation tools such as Stable Diffusion are 4.5 times quicker. In general, you can expect a 2x speed boost in DaVinci Resolve, and 3x for Photoshop. There are certain workflows that are ten times faster with NVIDIA’s RTX AI technology.
NVIDIA has worked with software manufacturers to optimize their creative apps for RTX, so they can take full advantage of the hardware.
On top of this, there is NVIDIA Studio, a suite of powerful applications for creatives built by NVIDIA. It includes NVIDIA Omniverse, which vastly improves 3D workflows by making 3D apps interoperable; NVIDIA Broadcast, which uses AI to isolate your voice, remove background noise and improve the quality of your video streams; and NVIDIA Canvas, which enables you to draw photorealistic landscapes.
AI for everyone
Gaming and creativity are the two big ones that are associated with GeForce RTX graphics cards, but there are so many other things that are enhanced by AI.
Take video streaming, for example. An exciting new feature that came out this year is RTX Video Super Resolution, which upscales streamed video - from Netflix, YouTube or other services - to 4K. It works in Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge browsers, and is done on the fly, so you can just press play and enjoy clear, sharp video.
Anyone who uses video calling, whether for work, education, or just staying in touch, will find the experience massively improved by the aforementioned NVIDIA Broadcast. It’s so powerful it can make your messy bedroom with construction noise in the background seem like a home studio. It can hide your surroundings by putting a different background behind you, cut out any unwanted noise, and enhance the quality of your voice. You can create a professional-quality broadcast from almost anywhere.

And the emerging breed of generative AI apps is something that can benefit almost everyone. These apps quickly generate new content that you can use as a starting point for many different kinds of projects - it could be text, images, 3D models, animations, sounds, slides for a presentation, or any other type of creative work.
Most of these apps are powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) - ChatGPT is an LLM. Many LLMs now run on the desktop and are used for tasks such as drafting copy, summarizing documents, extracting insights from data, and many other general day-to-day to do-list items. They are resource-intensive, and require powerful hardware such as an RTX GPU to work efficiently.
NVIDIA GPUs and the cloud
Many AI apps run in the cloud - so where is all that processing power coming from? Again, it’s NVIDIA.
The AI research lab OpenAI received its first NVIDIA DGX AI supercomputer in 2016, and that machine now powers the ChatGPT LLM. Today, half of all Fortune 100 companies have NVIDIA DGX supercomputers running full-time on AI operations and other resource-intensive work.
NVIDIA GPUs have transformed cloud services. All kinds of AI-based systems are now run on NVIDIA GPUs via the cloud - everything from voice recognition to autonomous factory operations.
So, you may wonder, if AI-based apps can run in the cloud, do you really need an RTX GPU in your computer?
While you can certainly enjoy the use of many AI tools without a local GPU, a lot of the features we’ve talked about here do require an RTX GPU in your machine for best results.
For some applications, speed is imperative. For example, gamers want things to happen instantly. Speed is also an issue for those working with large data sets, as it can be inefficient to upload them to the cloud to be worked on when they could be processed locally.
Availability is a factor for many people, especially those working in locations with patchy internet access - a local GPU ensures your AI-based apps are available even when the internet is not.
And privacy is the final consideration. Many people don’t want their data online, and some companies, especially those handling client data, have to deal with strict security requirements that makes handling everything locally the simplest option.
The future of AI
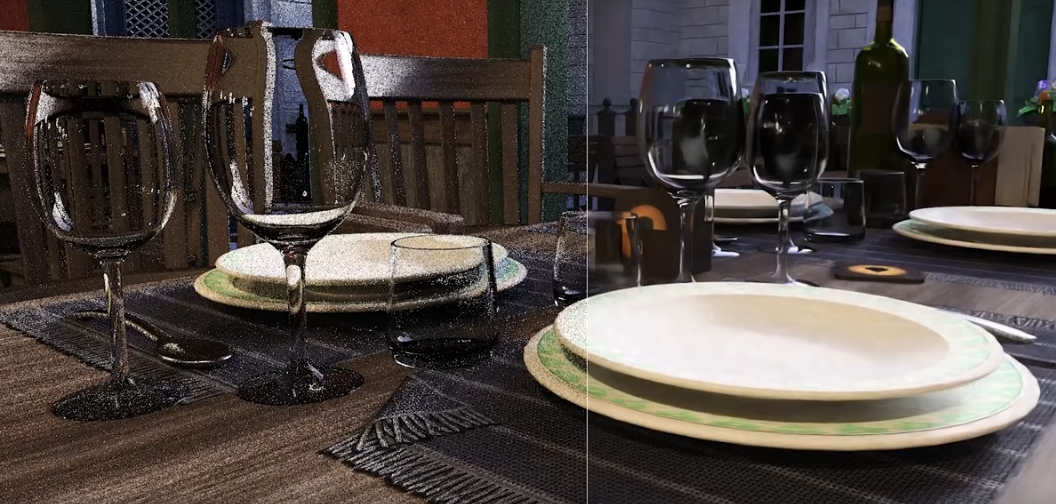

AI is going to continue to transform the way we do things over the next few years and beyond. Incredible new features are coming out all the time, and our expectations with respect to computing tasks are going to be very different in the near future.
NVIDIA is leading the charge, providing developers with tools to come up with ever-more powerful features, and delivering the phenomenal hardware that drives it all.
If you’re looking to buy a new PC, getting one with an RTX GPU will stand you in good stead for what is to come.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
Home to the most invested and passionate Microsoft fans, Windows Central is the next generation destination for news, reviews, advice and buying recommendations on the Windows, PC and Xbox ecosystems, following all products, apps, software, AI advancements, and accessories. We've been around for more than decade, and we take our jobs seriously. Windows Central writers and editors value accuracy and editorial independence in everything we do, never receiving compensation for coverage and never pulling punches.