Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Copilot+ AI features or proven Intel Core Ultra performance?
The XPS 13 (9345) is the right choice if you want a Copilot+ PC with advanced AI features.
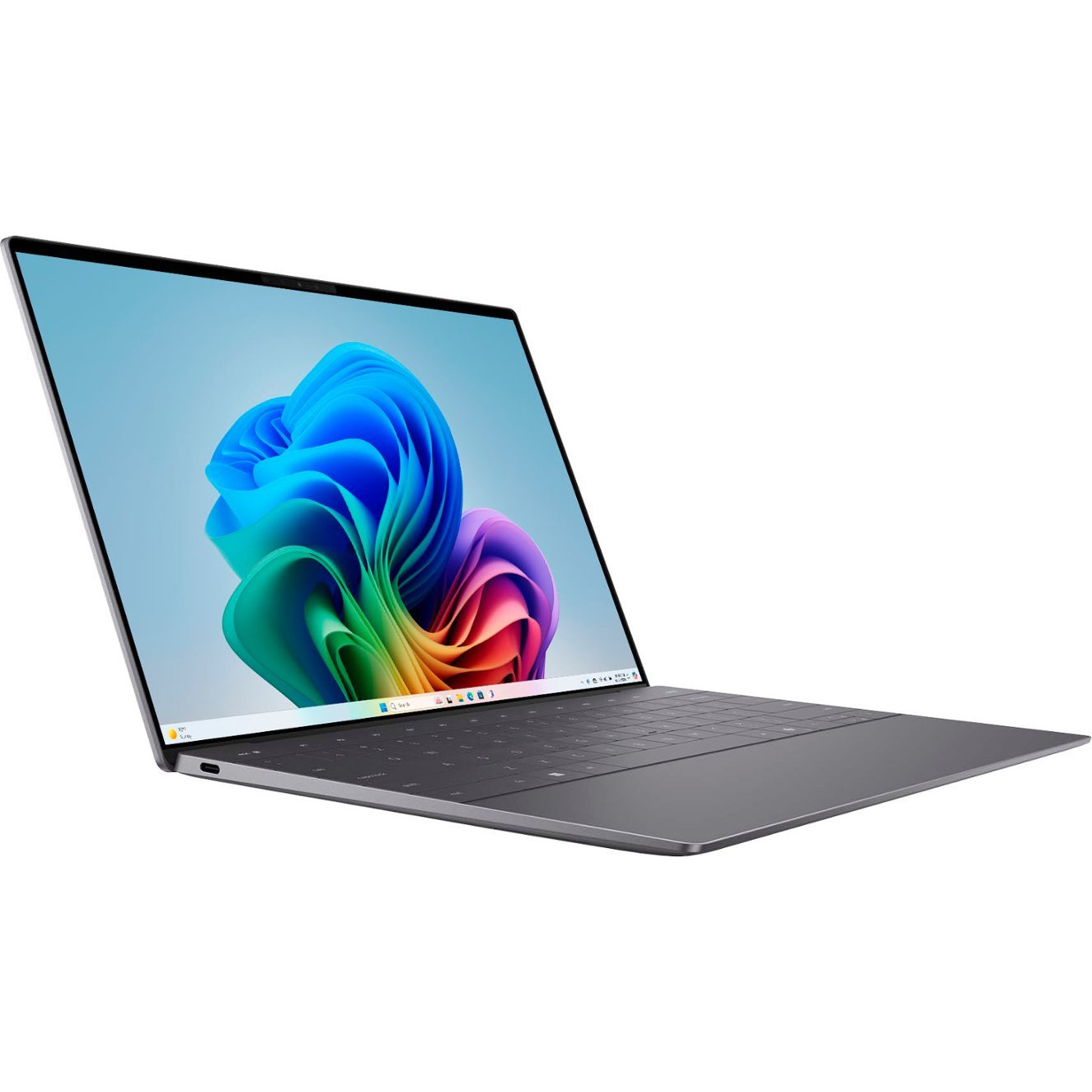

Dell's XPS 13 (9345) is powered by Qualcomm's efficient and powerful Snapdragon X Elite and X Plus chips, complete with NPU capable of handling Copilot+ AI features. It's otherwise identical to its Intel-based sibling, making this the go-to choice if you're interested in advanced Windows AI features like Windows Recall and Live Caption.
For
- Access to Copilot+ features
- Strong Snapdragon X performance and efficiency
- Three high-end display options
- Compact and premium build
Against
- Limited ports, no Thunderbolt
- Not everyone loves the design
- ARM still has some limitations
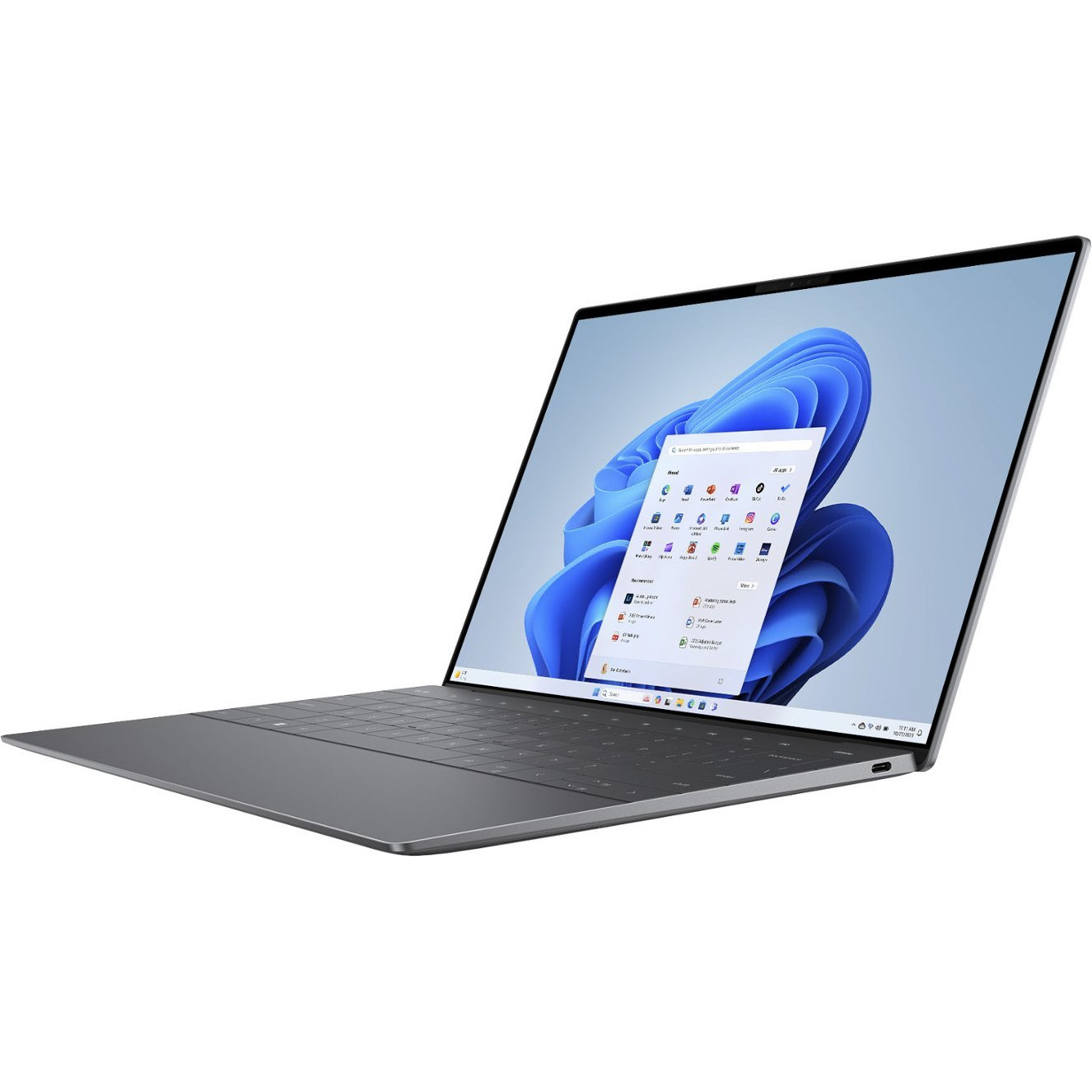

The XPS 13 (9340) likely won't be as powerful or efficient as the 9345 with Snapdragon X chips, but it remains a great option if you'd rather not get into the new Copilot+ features in Windows 11. You're really not missing out on any physical features, and you can expect the same futuristic and premium design.
For
- Intel Core Ultra performance
- Three high-end display options
- Premium and compact build
- No emulation needed for apps
Against
- Limited ports
- Design isn't for everyone
- No Copilot+ access
Dell's XPS 13 (9345) is a Copilot+ PC announced in May 2024. It's powered by Qualcomm's Snapdragon X chips with a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) powerful enough to handle new localized AI features coming to Windows 11, and it should prove to be a powerful and efficient AI PC.
The Windows on ARM laptop goes up against its sibling XPS 13 (9340), another premium laptop powered by Intel's Core Ultra processors (CPU). The laptops are physically identical, with most changes coming inside or to connectivity options. With a similar starting price, it might be tough to figure out which laptop is better for your needs. Let's break down the similarities and differences to help you make the right decision.
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Specs
Before we get into the deeper comparison of these two premium Windows laptops, it's worth taking a look at the raw specifications available to configure.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Dell XPS 13 (9345) | Dell XPS 13 (9340) |
|---|---|---|
CPU | Snapdragon X Elite (X1E-80-100), Snapdragon X Plus (X1P-64-100) | Intel Core Ultra 5 125H, Core Ultra 7 155H, Core Ultra 7 165H |
RAM | 16GB, 32GB, 64GB LPDDR5x-8400MHz, soldered | 8GB, 16GB, 32GB, 64GB LPDDR5x-7467MHz, soldered |
GPU | Qualcomm Adreno (integrated) | Intel Arc (integrated) |
NPU | Qualcomm Hexagon (45 TOPS) | Intel AI Boost (~10 TOPS) |
Storage | Up to 2TB M.2 PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSD (4TB post-launch) | Up to 4TB M.2 PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSD |
Camera | FHD RGB + IR, Windows Hello, HPD | FHD RGB + IR, Windows Hello, HPD |
Speakers | Four 2W speakers, Dolby Atmos | Four 2W speakers, Dolby Atmos |
Display | 13.4 inches, 1920x1200 (FHD+), non-touch, 500 nits, 120Hz, Dolby Vision, anti-glare | 13.4 inches, 1920x1200 (FHD+), non-touch, 500 nits, 120Hz, Dolby Vision. anti-glare |
| Row 8 - Cell 0 | 13.4 inches, 2560x1600 (QHD+), touch, 500 nits, 120Hz, Dolby Vision, anti-reflective | 13.4 inches, 2560x1600 (QHD+), touch, 500 nits, 120Hz, Dolby Vision, anti-reflective |
| Row 9 - Cell 0 | 13.4 inches, 2880x1800 (3K), OLED, touch, 400 nits, 60Hz, Dolby Vision, anti-reflective | 13.4 inches, 2880x1800 (3K), OLED, touch, 400 nits, 60Hz, Dolby Vision, anti-reflective |
Ports | Two USB4 (PD, DisplayPort, 40Gbps) | Two Thunderbolt 4 |
Wireless | Qualcomm Wi-Fi 7, Bluetooth 5.4 | Intel Killer Wi-Fi 7, Bluetooth 5.4 |
Battery | 55Wh | 55Wh |
Dimensions | 11.63 x 7.84 x 0.58 inches (295.4mm x 199.1mm x 14.8mm) | 11.62 x 7.84 x 0.58 inches (295.3mm x 199.1mm x 14.8mm) |
Weight | From 2.59 pounds (1.19kg) | From 2.6 pounds (1.17kg) |
Price | From $1,299 | From $1,299 |
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Price and availability
The XPS 13 (9345) is available to preorder at Dell's website and third-party retailer Best Buy. At Dell, there's so far just one model available; it starts at $1,299 and includes a Snapdragon X Elite System-on-Chip (SoC), 16GB of LPDDR5x RAM, 512GB M.2 PCIe 4.0 NVMe solid-state drive (SSD), and 13.4-inch FHD+ non-touch display.
Best Buy has a far better preorder deal on numerous Copilot+ PCs, but only for a limited time and only for Best Buy Plus and Total members. Best Buy is throwing in a free 50-inch Insignia F30 Series 4K TV with any Copilot+ laptops (Samsung preorders come with a similar Samsung TV).
Preorder prices start at $1,500 at Best Buy for a model with a Snapdragon X Elite chip, 16GB of RAM, 512GB SSD, and a 13.4-inch OLED touch display. So if you want that OLED upgrade for better color and contrast, Best Buy is currently the place to shop. Dell XPS 13 (9345) models are expected to ship on June 28, 2024.
The Intel-based XPS 13 (9340) is readily available at Dell's website and third-party retailers. Looking at Dell's website, models with an Intel Core Ultra 7 CPU, 8GB of RAM, 512GB SSD, and FHD+ non-touch display start at $1,299. Similar models with 16GB of RAM start at $1,400 at Best Buy.
Scaling the XPS 13 (9340) to include 64GB of RAM, 2TB SSD, and 3K OLED display raises the price to about $2,599 at Dell.
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Design and features

Dell didn't make any significant physical changes to the Windows on ARM XPS 13 (9345) compared to the Intel-based 9340 model. If you're concerned about things like portability, pointing, or typing, both XPS 13 models deliver the same experience. They're both built to a high standard with a machined aluminum frame, and they share compact dimensions and reasonable weight.
The laptop design extends back to the XPS 13 Plus (9320) we reviewed in 2022, which was very much ahead of its time. It's still unlike most other Ultrabooks on the market, and the design has now extended to the XPS 14 and XPS 16.
The XPS 13 9345 and 9340 have a lattice-free keyboard with large keycaps and 1mm of key travel. The zero-lattice design means there's minimal spacing between keys, but it's easy to get used to. Editor-in-Chief Daniel Rubino said in his XPS 13 Plus review, "As a touch-typist, I had zero problems adjusting to the layout and feel. Indeed, I was typing away with confidence within a minute, requiring no learning curve for adjustment."
What might take more time to get used to are the capacitive touch buttons used in the top Function row. If you often need the Escape or F keys, you'll probably find this choice annoying at best. Dell also blended a haptic touchpad into one wide piece of Gorilla Glass that covers the palm rests. You can't see the edges of the pointer, but it's large enough that you shouldn't ever miss it. The haptic sensors and actuators beneath the surface simulate physical movements and clicks, and it's all customizable through Windows 11.

The laptops have a quad-speaker setup with 8W total output and Dolby Atmos support. The speakers are installed on the side edges of the laptop's bottom panel, and the sound quality is outstanding. You might get some muffling with the PC in your lap, but there really wasn't any space in the keyboard surround for Dell to employ a top-firing design.
Above the display is a 1080p webcam with an IR sensor for Windows Hello. Both laptops can employ Windows Studio Effects to improve their video, and both laptops offer human presence detection for added security.
Connectivity is where the XPS 13 9345 and 9340 show some differences. Port selection is extremely limited across devices with just two USB-C ports. On the Intel-based XPS 13 9340, those USB-C ports support Thunderbolt 4, while the ARM-based 9345 model uses the USB4 standard due to Intel Thunderbolt licensing. Dell does specify that its USB4 ports offer 40Gbps bandwidth, Power Delivery, and DisplayPort, so there shouldn't be a huge difference. Our guide on using USB4 with Thunderbolt docks has more information.
Wireless connectivity is also slightly different. The ARM-based XPS 13 9345 uses a Qualcomm chip for Wi-Fi 7 and Bluetooth 5.4, while the Intel-based 9340 uses an Intel Killer chip for the same connectivity standards.
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Display

Dell didn't make any changes to the XPS 13's displays for the Copilot+ version. Both laptops are listed as having three different 13.4-inch display options with a 16:10 aspect ratio, though the options available will vary by region and retailer.
The most affordable screen has an FHD+ resolution, non-touch panel, 500 nits brightness, 120Hz refresh rate, anti-glare finish, and Dolby Vision. Next is a QHD+ resolution with a similar 500 nits brightness, 120Hz refresh rate, and Dolby Vision support. It has an anti-reflective finish and touch functionality.
The most expensive display has what Dell calls a 3K resolution (2880x1800). It's touch-enabled with an OLED panel for deep color and contrast, it hits 400 nits brightness and a 60Hz refresh rate, and it supports Dolby Vision. Its anti-reflective panel helps reduce glare.
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Performance and battery
The biggest change to the XPS 13 (9345) is one you can't see from the outside. It's powered by Qualcomm's Snapdragon X Elite and Snapdragon X Plus SoCs, each with an NPU capable of up to 45 TOPS of local AI performance. That number is significant, as Microsoft has stated that its Copilot+ features coming to Windows 11 require at least 40 TOPS.
That leaves the Intel-based XPS 13 (9340) with NPU capable of about 10 TOPS behind. The Core Ultra 5 and Core Ultra 7 H-series chips are impressive in their own right, but Qualcomm's hardware should offer better performance and efficiency if we can believe claims ahead of testing ourselves.
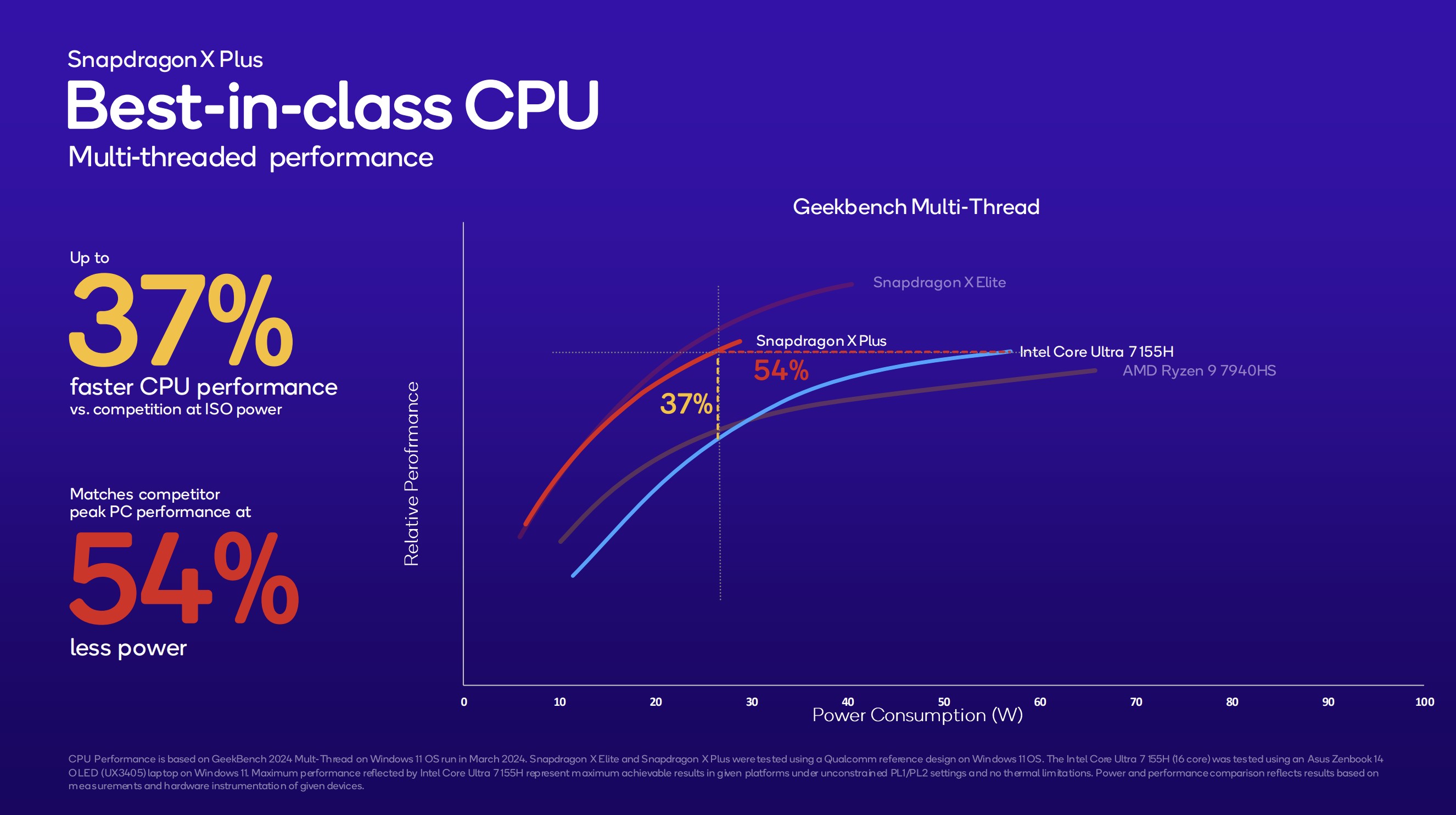
As you can see in the chart above, Qualcomm claims that its X Plus chip runs at 54% better efficiency and 37% better performance than a Core Ultra 7 155H CPU. Qualcomm also includes an X Elite chip in the chart, which is likely the most powerful X1E-84-100 variant. Even with the XPS 13 (9345) using the mid-range X1E-80-100 version, you should still see efficiency and performance improvements compared to Intel Core Ultra.
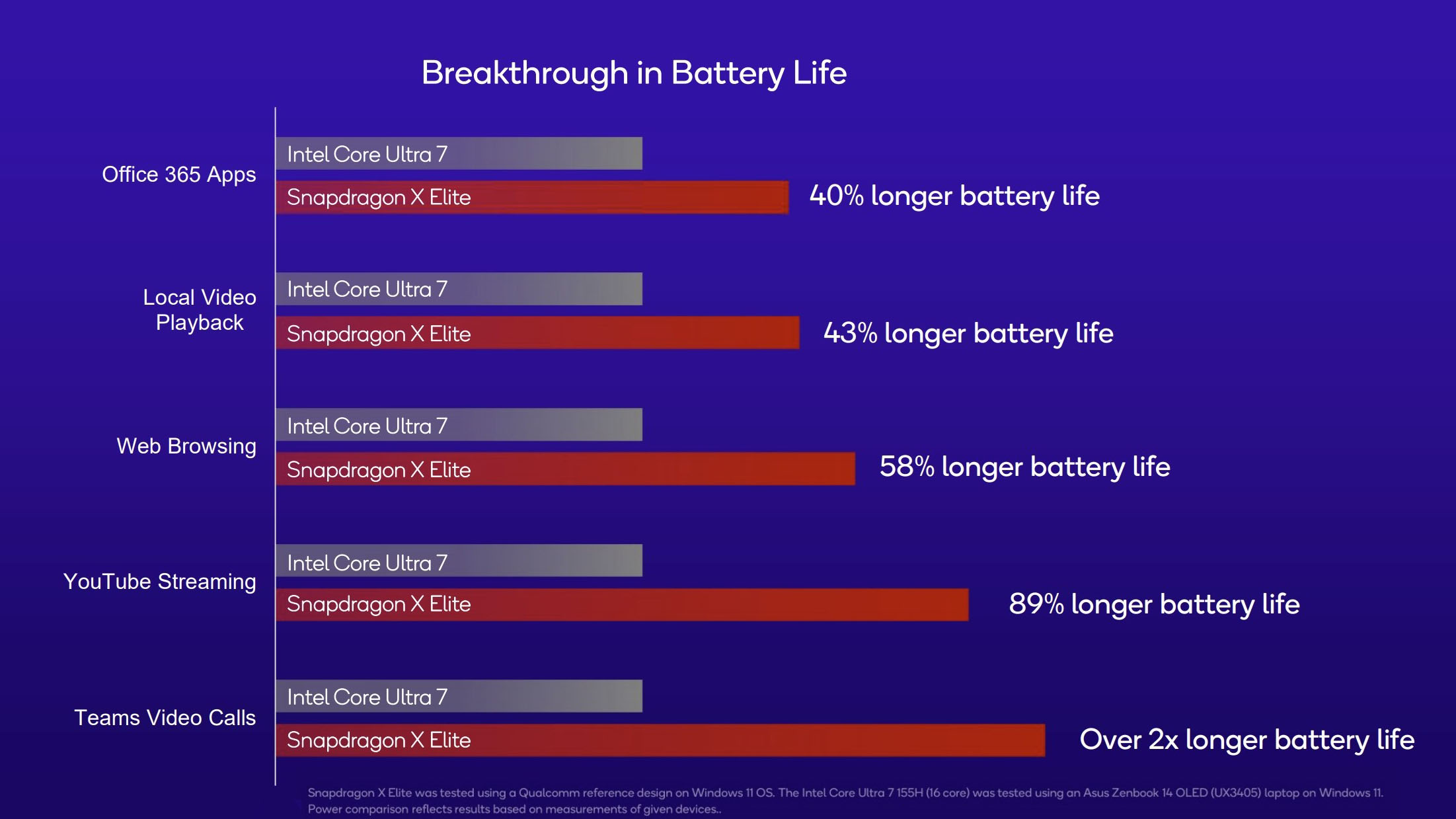
Qualcomm also showed off battery life with its X Elite chip compared to a Core Ultra 7 155H. Again, we'll have to test these claims ourselves, but it's looking like you should be able to get much better runtimes in most applications with the Snapdragon chips. Both XPS 13 models come with a 55Wh battery.
Being an ARM64 PC, the XPS 13 (9345) will require emulation to run some apps not compiled natively for the ARM architecture. While the list of apps compiled for ARM64 continues to grow and emulation is set to get even better with Microsoft's new Prism technology, you might run into some issues with drivers.
Nevertheless, as Windows Central Ben Wilson discovered in his testing, you shouldn't worry much about app compatibility on ARM.
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Copilot+ and AI

As mentioned, the XPS 13 (9345) with Snapdragon X hardware is the only option if you'd like to get in on Copilot+ features in Windows 11. Because these features are intended to run locally without reaching out to Microsoft's cloud, you need an NPU with at least 40 TOPS of power. The Hexagon NPU in the Snapdragon X SoC hits 45 TOPS, while the Core Ultra AI Boost NPU hovers around 10 TOPS.
So what features are coming with Copilot+? Windows Recall is proving to be the most controversial addition, as it allows users to leverage AI to search through a continuous series of screenshots taken of everything you see and do on your PC.
Auto Super Resolution boosts performance for gamers as a Super Resolution technique built right into Windows, while Live Captions provides real-time translations to English in live and pre-recorded audio and video. Windows Studio Effects is also seeing some improvements, and you'll now be able to create images and text using local AI.
Dell XPS 13 (9345) vs. XPS 13 (9340): Which should you buy?
Choosing the best Dell laptop for you will ultimately come down to the performance hardware inside. Qualcomm made some big promises when it comes to power and efficiency, and we're expecting significant improvements compared to Intel's Core Ultra 7 H-series chips.
There's also the matter of the Snapdragon X NPU, which is powerful enough to make the cut for Copilot+ AI features in Windows 11. If you'd like to try these out, you'll have to stick with the 9345 model.
One area where the XPS 13 (9340) might pull ahead is pricing. I've spotted models at a discount, and landing something for hundreds off the regular price might be too good to pass up if you're shopping with a tighter budget.
Be sure to check out more great AI laptops if these aren't quite what you need.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.

Cale Hunt brings to Windows Central more than eight years of experience writing about laptops, PCs, accessories, games, and beyond. If it runs Windows or in some way complements the hardware, there’s a good chance he knows about it, has written about it, or is already busy testing it.
