Early Intel Xe Super Sampling (XeSS) demo shows promise for PC gamers
Intel has shown off its fancy new upscaling technology.

What you should know
- Digital Foundry published an exclusive in-depth video review of Intel's new Xe Super Sampling technology.
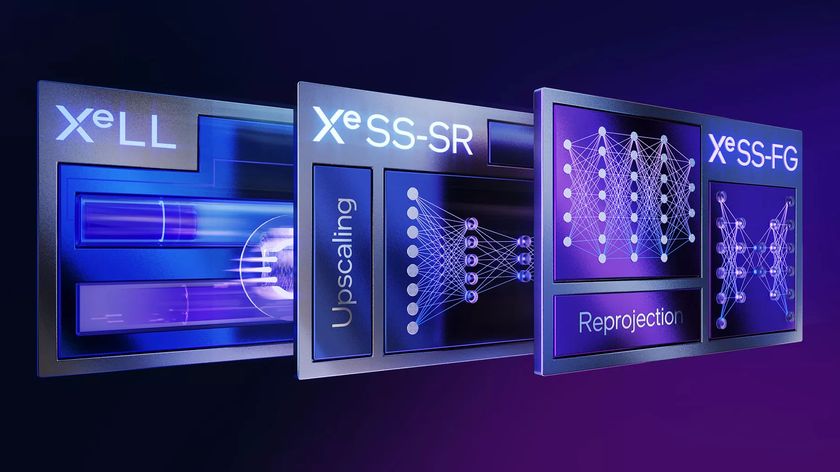
- Intel XeSS is the company's own take on AI-based image reconstruction upscaling.
- The technology will improve the visuals of a game while also boosting framerates on Intel Arc GPUs.
Digital Foundry has published an exclusive in-depth video review of Intel's Xe Super Sampling. The technology, which is the company's own AI-based image reconstruction upscaler, is showcased in the video to perform admirably compared to NVIDIA DLSS when it was originally released. One can expect to see similar results as NVIDIA DLSS and AMD FSR in games that are supported. The question is: how good will it be at launch?
Looking at AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution vs. NVIDIA DLSS, Intel's XeSS functions similarly to DLSS, utilizing an AI algorithm to intelligently add detail to the upscaled image. Where XeSS differs from DLSS is the support of all types of graphics cards, including those from AMD and NVIDIA, as well as Intel's integrated graphics processing on CPUs.
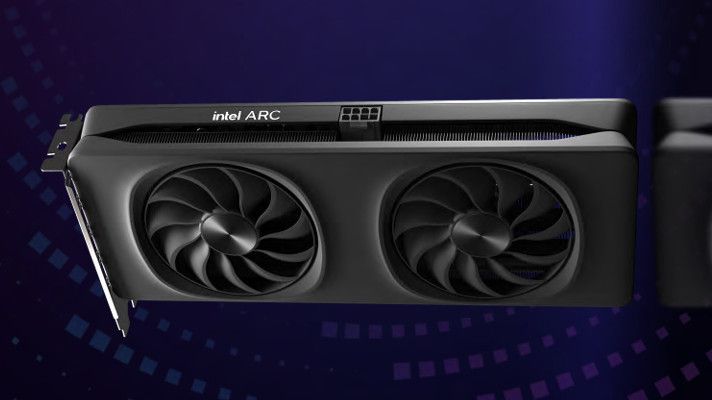
As noted by our friends over at Tom's Hardware, Digital Foundry used an Arc Alchemist A770 graphics card running a special build of Shadow of the Tomb Raider that supports Intel XeSS. The team tested the game at FHD (1080p), QHD (1440p), and 4K UHD (2160p) resolutions. As shown in the video review, performance was solid with up to an 88% improvement in the frame rate at 4K.
This was with XeSS set to "performance" mode. Balanced, quality, and ultra-quality modes saw notable improvements of 66%, 47%, and 23%, respectively. Other resolutions didn't have as much of an impact with XeSS enabled. 1440p saw a 52% gain with XeSS, which is still a considerable improvement in performance.
Comparing XeSS to an older version of NVIDIA DLSS saw the company's upscaler perform admirably by providing clear visuals. Comparing the image quality of both systems running in the game, it was difficult to tell them apart. Interestingly, XeSS outperformed the temporal anti-aliasing (TAA) implementation in Shadow of Tomb Raider, which was running at native resolution.
It wasn't a perfect demonstration, however. Intel needs to refine certain aspects of XeSS to improve how the technology handles vegetation, water, and clothing. It remains to be seen just how good Intel's best graphics card will be at launch, but things are looking good for the company so far.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.

Rich Edmonds was formerly a Senior Editor of PC hardware at Windows Central, covering everything related to PC components and NAS. He's been involved in technology for more than a decade and knows a thing or two about the magic inside a PC chassis. You can follow him on Twitter at @RichEdmonds.