

Latest and greatest from Intel
The Intel Core i9-12900K brings Team Blue back into focus for anyone who wants top-end performance for intensive gaming and specialized work. It brings PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 RAM support, though it does require a new motherboard for the fresh LGA 1700 socket.
For
- Exceptional performance
- 125W TDP at stock
- PCIe 5.0 support
- DDR5 RAM support
- Competitive price
Against
- No bundled cooler
- Requires new motherboard
- Runs hot when loaded/overclocked

AMD's powerhouse
The Ryzen 9 5950X can still keep up (and in some cases surpass) the Core i9-12900K, though it does generally cost more. You don't need a new motherboard since it's still using the AM4 socket, but you don't get DDR5 RAM support and PCIe tops out at 4.0. If you need a high-performance CPU for heavy workloads or gaming, this is still a top choice.
For
- 105W TDP at stock
- PCIe 4.0 support
- Still amazing performance
- 16 cores, 32 threads
Against
- Generally costs more
- No bundled cooler
- No DDR5 RAM support
- Tops out at PCIe 4.0
These two flagship chips are among the best processors available today, and either one is ultimately going to deliver a ton of power for anyone with lofty gaming, design, or development goals. The Core i9-12900K is fresh on the market with an "Intel 7" (10nm) manufacturing process, new "big.LITTLE" hybrid core design, DDR5 RAM support, and PCIe 5.0.
The Ryzen 9 5950X has been out for about a year, but it's still a top option for high-performance builds. It's built with a 7nm manufacturing process, it has 16 total cores and 32 threads, and it offers PCIe 4.0 support. It's still using the AM4 socket, meaning your older motherboard should work with the chip.
Let's take a further look at these two CPUs by breaking down the features and performance.
Core i9-12900K vs. Ryzen 9 5950X: Features and performance
Intel's new big.LITTLE hybrid design that comes with the Alder Lake generation is one we've seen in CPUs from ARM and Apple. It essentially mixes power-efficient single-threaded cores (E cores) with high-performance multi-threaded cores (P cores) in the same package.
The E cores take care of low-priority tasks, while the P cores are free to take on the heavy lifting. This is why in the chart below you might notice the thread count being a bit off; there are eight multi-threaded P cores (which means 16 threads) and eight single-threaded E cores. That's a total of 24 threads, down from the Ryzen 9's 32 threads.
| Header Cell - Column 0 | Intel Core i9-12900K | AMD Ryzen 9 5950X |
|---|---|---|
| Cores | 16(8P, 8E) | 16 |
| Threads | 24 | 32 |
| TDP | 125W | 105W |
| Base clock | P: 3.2GHzE: 2.4GHz | 3.4GHz |
| Boost | P: 5.1GHzE: 3.9GHz | 4.9GHz |
| Turbo Boost Max 3.0 | 5.2GHz | None |
| Overclockable | Yes | Yes |
| L3 cache | 30MB | 32MB |
| Manufacturing node | 10nm | 7nm |
| Memory | DDR4-3200DDR5-4800Up to 128GB | DDR4-3200Up to 128GB |
| Integrated graphics | Intel UHD 770 | None |
| Socket | LGA 1700 | AM4 |
The Core i9-12900K also brings support for DDR5 RAM and PCIe 5.0. While these two technologies aren't quite mature enough to make a huge difference right now — the best DDR5 RAM for 12th Gen Intel CPUs is sold out everywhere — they do set you up nicely for future upgrades. These new chips are quite future-proof, but you will need to invest in a new motherboard due to 12th Gen Intel CPUs using a new LGA 1700 socket.
Upgrading to the Ryzen 9 5950X doesn't require quite as much of an upgrade, as it's still compatible with the same AM4 socket that AMD has been using for years. However, a modern motherboard is always recommended to get the most out of your CPU. Our collection of the best motherboards has a ton of options if you're wondering where to start. The Ryzen 9 5950X does not include integrated graphics, though this isn't as much of an issue as these chips are usually paired up with one of the best graphics cards available.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.

In terms of performance, these two CPUs are quite closely matched. The Ryzen 9 5950X has 16 standard multi-threaded cores with a base clock of 3.4GHz and a boost up to 4.9GHz. It is overclockable, and it has a baseline 105W TDP. That's quite a bit lower than the Core i9-12900K's 125W base TDP.
Intel's P cores have a base clock of 3.2GHz and a boost clock of 5.1GHz. Its E cores have a base clock of 2.4GHz and a boost clock of 3.9GHz. There's also Intel's Turbo Boost Max 3.0, which pushes the clock up to 5.2GHz on certain cores for single-threaded tasks.
Clock speeds and other statistics look great on paper, but how do these CPUs perform in benchmarks? We tested both to see how they compare.
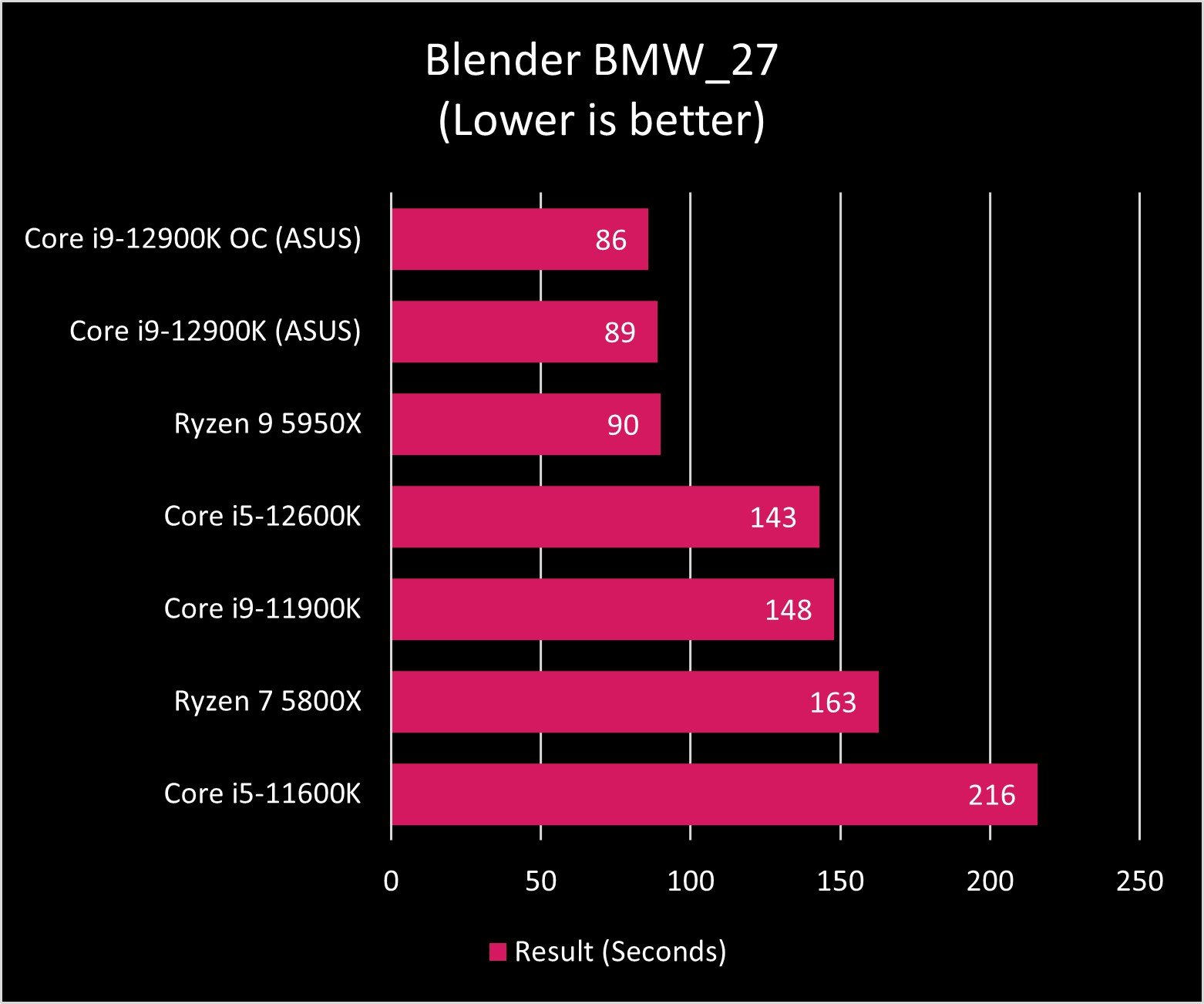
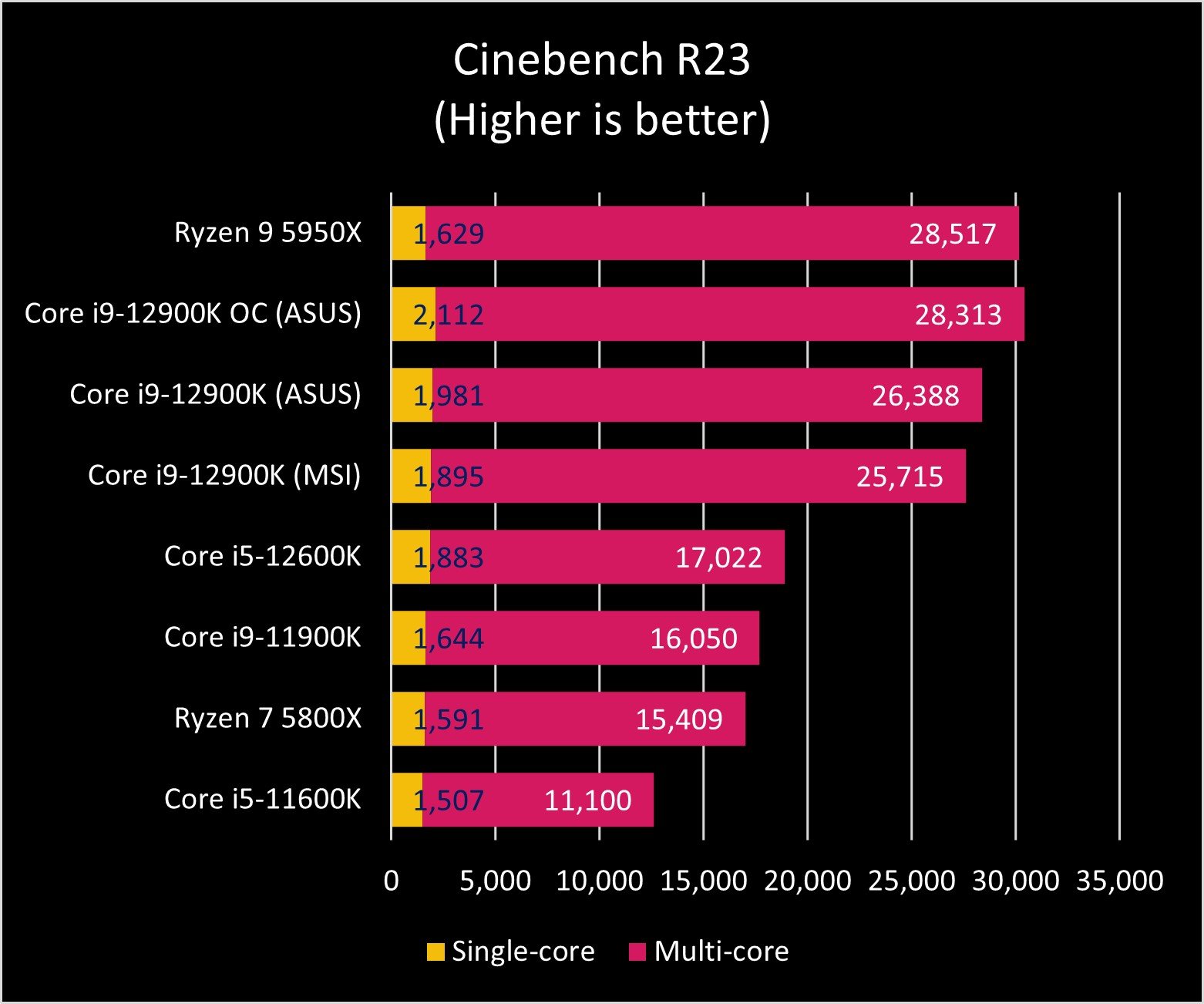
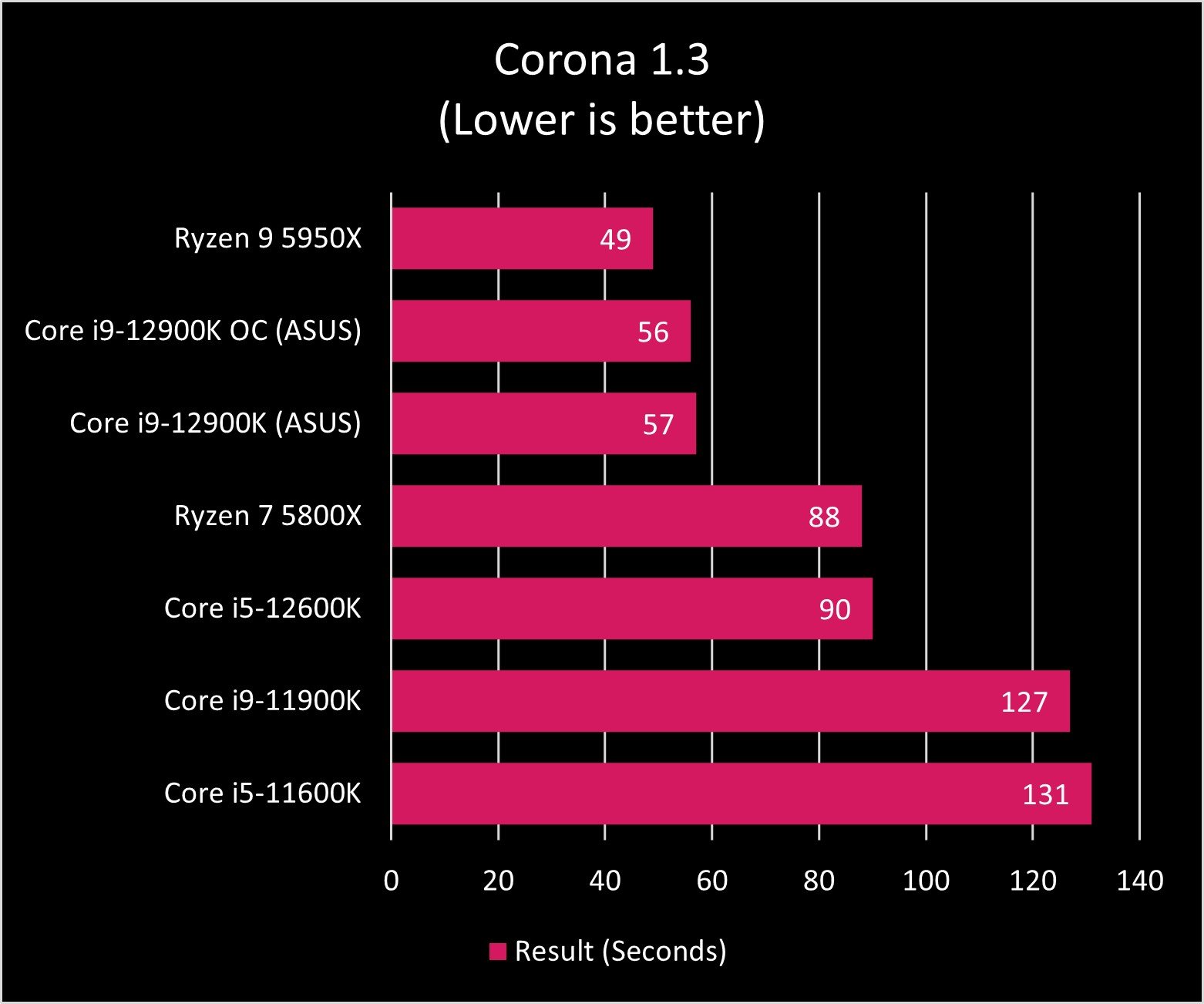
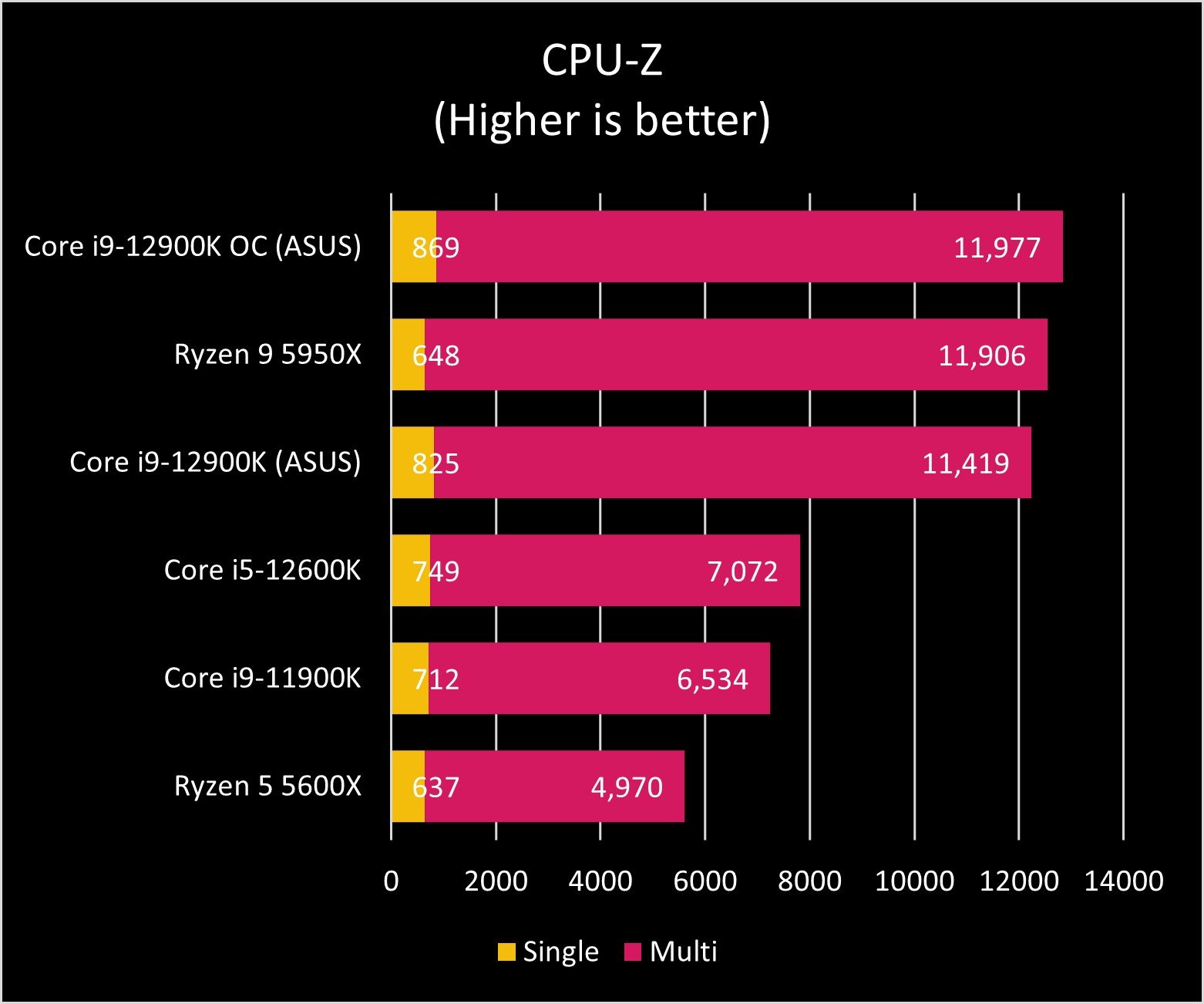
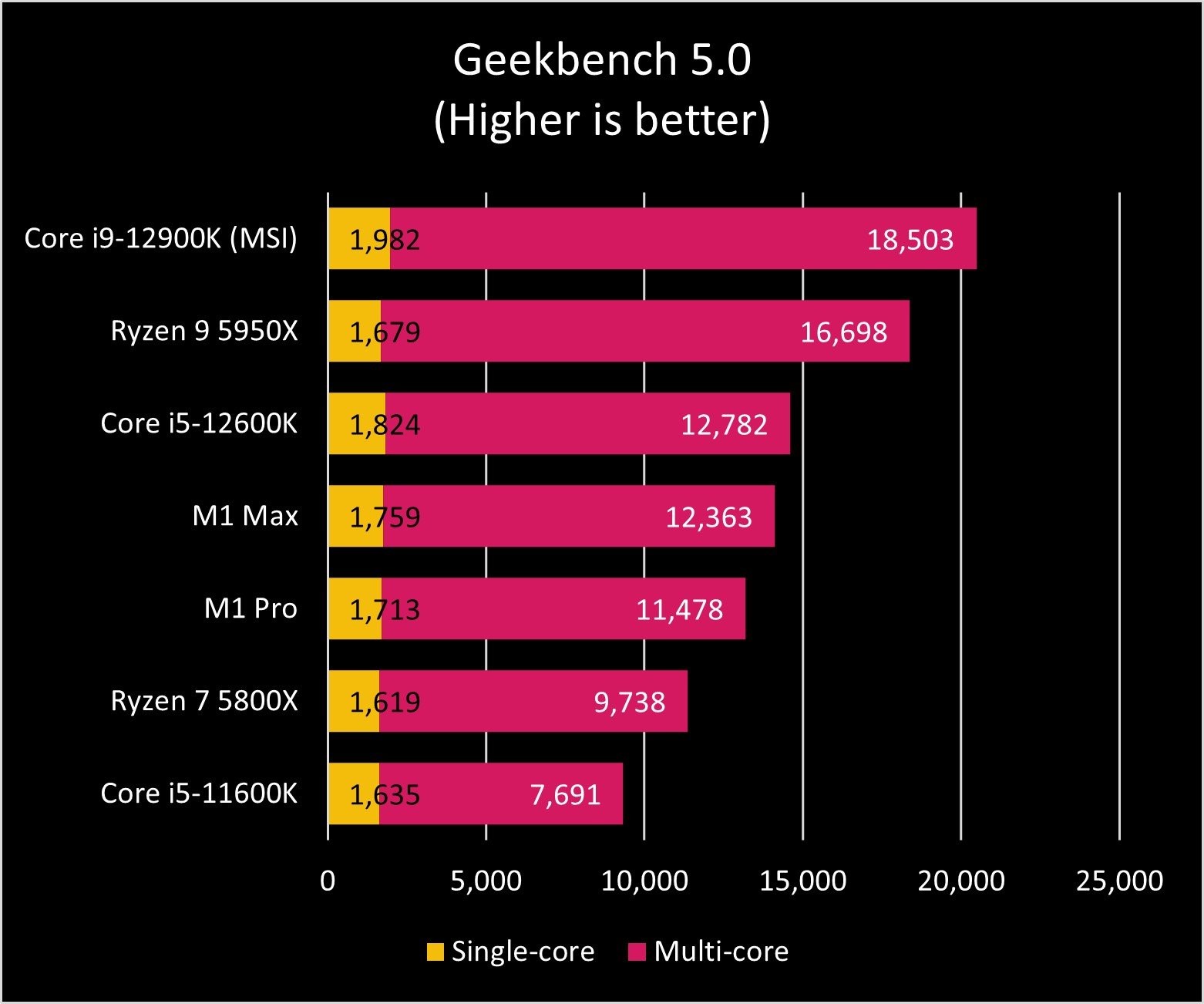
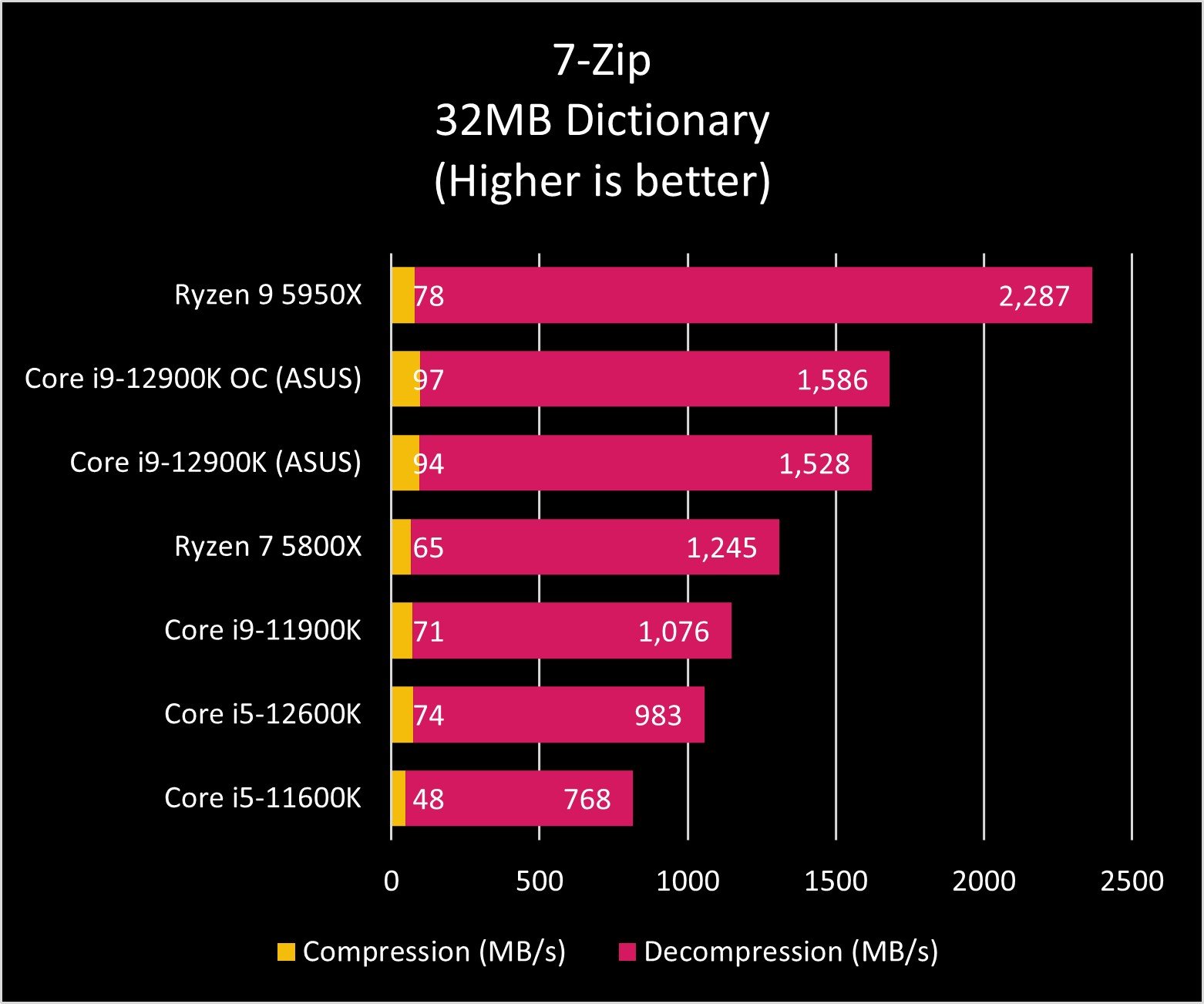
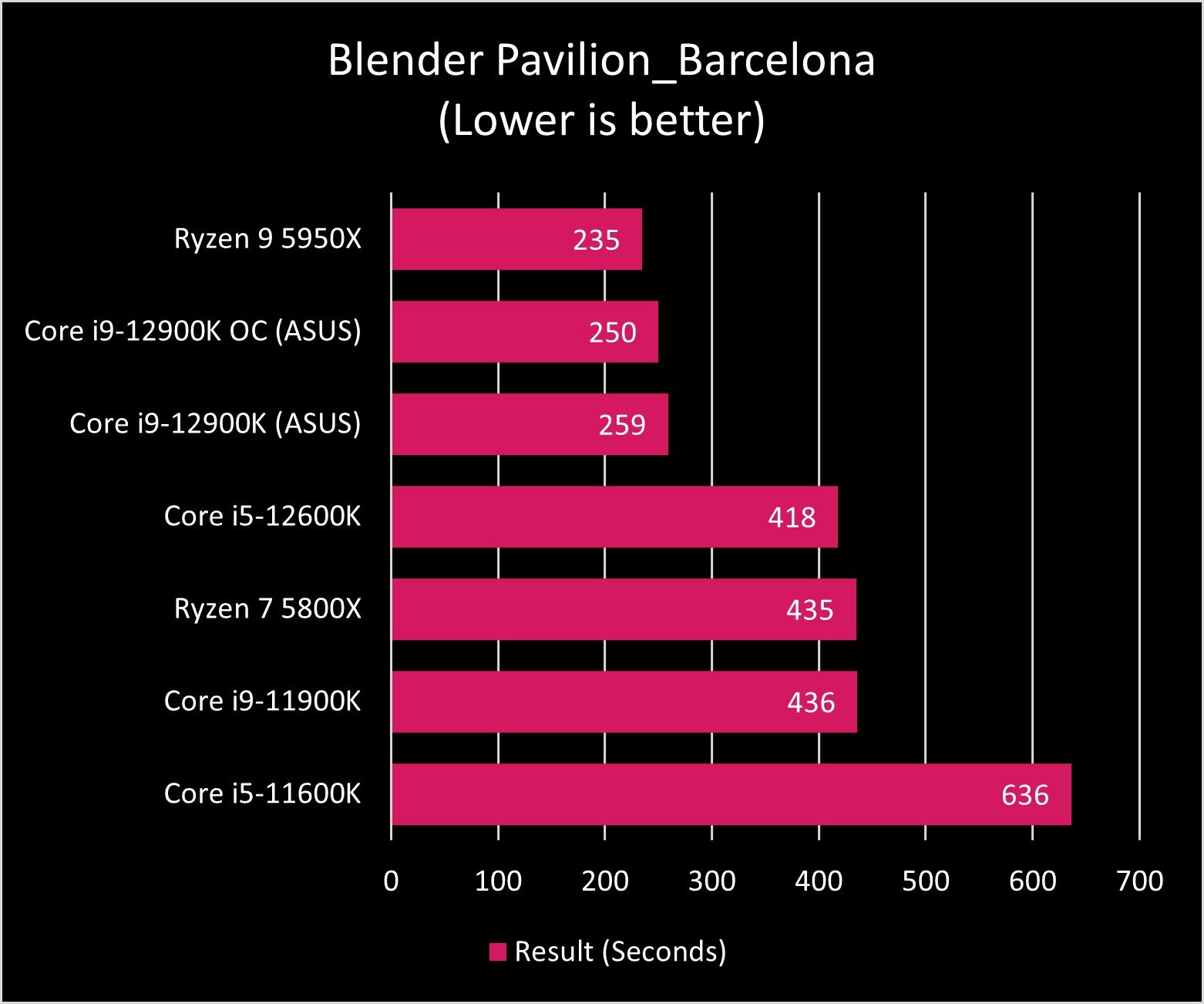
As you can see in the graphs above, the Core i9-12900K and Ryzen 9 5950X exchange blows across benchmark tests. AMD's processor still seems to be the master of heavy multi-core tasks, though Intel is no slouch in that department either. And when it comes to single-core performance, Intel reigns.
The bottom line here is that both CPUs deliver an incredible amount of power. Their specific features differ in a few ways, but both are modern powerhouses ready to take on a heavy life of gaming or specialized work. The Core i9-12900K costs less than the Ryzen 9 5950X, but you do have to consider the price of adding a new motherboard for the new socket, as well as new RAM if you decide to opt for a DDR5 board. If you instead go with AMD's Ryzen 9 5950X and already have an AMD build, chances are you'll be able to save money overall by reusing the motherboard and other components.
Setting up for the future
Intel's Core i9-12900K brings exceptional performance, as well as future-proof support for DDR5 RAM and PCIe 5.0. If you're looking at a completely new build, this is certainly a compelling option that should have AMD a bit worried.

Intel is now back in the game with the launch of Alder Lake processors. The Core i9-12900K is the flagship chip with plenty of cores and threads, as well as ample performance for intensive tasks and gaming.
Undeniable multi-core performance
AMD's Ryzen 9 5950X is a beast of a processor, capable of besting the Core i9-12900K in a bunch of multi-core benchmarks. It might not be as future-proof due to its DDR4 and PCIe 4.0 support, but it's much easier to use in an upgrade for current AMD systems.

Cale Hunt brings to Windows Central more than eight years of experience writing about laptops, PCs, accessories, games, and beyond. If it runs Windows or in some way complements the hardware, there’s a good chance he knows about it, has written about it, or is already busy testing it.
